| title | tags | categories | keywords | description | cover | abbrlink | date | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Spring源码系列-第8章-SpringMVC子容器和Spring父容器的启动原理 |
|
|
Spring,框架,spring源码 |
SpringMVC子容器和Spring父容器的启动原理 |
c8dd1418 |
2022-06-20 05:01:02 -0700 |
根据官方文档写咱们的测试类
package cn.imlql.web;
import cn.imlql.web.config.AppConfig;
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration;
/**
* 只要写了这个,相当于配置了SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet
* 1、Tomcat一启动就加载他
* 1)、创建了容器、制定了配置类(所有ioc、aop等spring的功能就ok)
* 2)、注册一个Servlet; DispatcherServlet;
* 3)、以后所有的请求都交给了 DispatcherServlet;
* 效果,访问Tomcat部署的这个Web应用下的所有请求都会被 DispatcherServlet 处理
* DispatcherServlet就会进入强大的基于注解的mvc处理流程(@GetMapping)
* 必须Servlet3.0以上才可以;Tomcat6.0以上才支持Servlet3.0规范
*
* Servlet3.0是javaEE的Web的规范标准,Tomcat是Servlet3.0规范的一个实现;
*/
public class AppStarter implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { //Spring会给我们传入servletContext
//创建ioc容器
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(AppConfig.class); //传入一个配置类
//以上截止,ioc容器都没有启动
//自己newDispatcherServlet,并传入容器
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(context);
//利用Servlet规范
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/"); //映射路径,写/就是所有的请求都交给DispatcherServlet
}
}@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(){
return "Hello, SpringMVC!";
}
}@ComponentScan("cn.imlql.web")
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
}根路径是在这里配的,tomcat的配置自己百度下,很简单
下面会用到SPI,这里先讲一下
spi-demo
├── api-db-impl-mysql/
| ├── api-db-impl-mysql.iml
| ├── pom.xml
| ├── src/
| | ├── main/
| | | ├── java/
| | | | └── com/
| | | | └── imlql/
| | | | └── mysql/
| | | | └── MySQLSaveService.java
| | | └── resources/
| | | └── META-INF/
| | | └── services/
| | | └── cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService
| | └── test/
| | └── java/
| └── target/
| ├── classes/
| | ├── com/
| | | └── imlql/
| | | └── mysql/
| | | └── MySQLSaveService.class
| | └── META-INF/
| | └── services/
| | └── cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService
| └── generated-sources/
| └── annotations/
├── api-db-impl-redis/
| ├── api-db-impl-redis.iml
| ├── pom.xml
| ├── src/
| | ├── main/
| | | ├── java/
| | | | └── com/
| | | | └── imlql/
| | | | └── redis/
| | | | └── RedisSaveService.java
| | | └── resources/
| | | └── META-INF/
| | | └── services/
| | | └── cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService
| | └── test/
| | └── java/
| └── target/
| ├── classes/
| | ├── com/
| | | └── imlql/
| | | └── redis/
| | | └── RedisSaveService.class
| | └── META-INF/
| | └── services/
| | └── cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService
| └── generated-sources/
| └── annotations/
├── api-db-interface/
| ├── api-db-interface.iml
| ├── pom.xml
| ├── src/
| | ├── main/
| | | ├── java/
| | | | └── com/
| | | | └── imlql/
| | | | └── data/
| | | | └── DataSaveService.java
| | | └── resources/
| | └── test/
| | └── java/
| └── target/
| ├── classes/
| | └── com/
| | └── imlql/
| | └── data/
| | └── DataSaveService.class
| └── generated-sources/
| └── annotations/
├── app/
| ├── app.iml
| ├── pom.xml
| ├── src/
| | ├── main/
| | | ├── java/
| | | | └── com/
| | | | └── imlql/
| | | | └── redis/
| | | | └── MainTest.java
| | | └── resources/
| | └── test/
| | └── java/
| └── target/
| ├── classes/
| | └── com/
| | └── imlql/
| | └── redis/
| | └── MainTest.class
| └── generated-sources/
| └── annotations/
├── pom.xml
└── spi-demo.imlimport cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
/**
* 1、 ServiceLoader:load()指定一个接口,
* 他就会加载当前系统里面所有的这个接口的【指定实现】
* 2、SPI(Service Provider Interface)
* 接口工程---提供接口
* ---- 实现工程1 : 实现接口 【META-INF/services 创建文件 接口名作为文件名 实现类全路径作为文件内容】
* ---- 实现工程2 : 实现接口
*
*
* 客户端----引用 工程1、或者 工程2
*
*
*
*/
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、加载 可用的接口实现
ServiceLoader<DataSaveService> load = ServiceLoader.load(DataSaveService.class);
//拿到实现进行调用
for (DataSaveService service : load) {
service.saveData("你好....");
}
}
}输出:
MySQL保存了数据.......你好....
Redis保存了数据.......你好....Java的SPI机制会默认加载类路径下META-INF/services的东西
public interface DataSaveService {
void saveData(String data);
}
public class MySQLSaveService implements DataSaveService {
@Override
public void saveData(String data) {
System.out.println("MySQL保存了数据......." + data);
}
}public class RedisSaveService implements DataSaveService {
@Override
public void saveData(String data) {
System.out.println("Redis保存了数据......."+data);
}
}api-db-impl-redis\src\main\resources\META-INF\services\cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService
cn.imlql.redis.RedisSaveServiceapi-db-impl-mysql\src\main\resources\META-INF\services\cn.imlql.data.DataSaveService
cn.imlql.mysql.MySQLSaveService你没看错就是这么简单
我只需要规定接口就可以开放给任何人实现
META-INF\services下的文件,本文统称为SPI文件
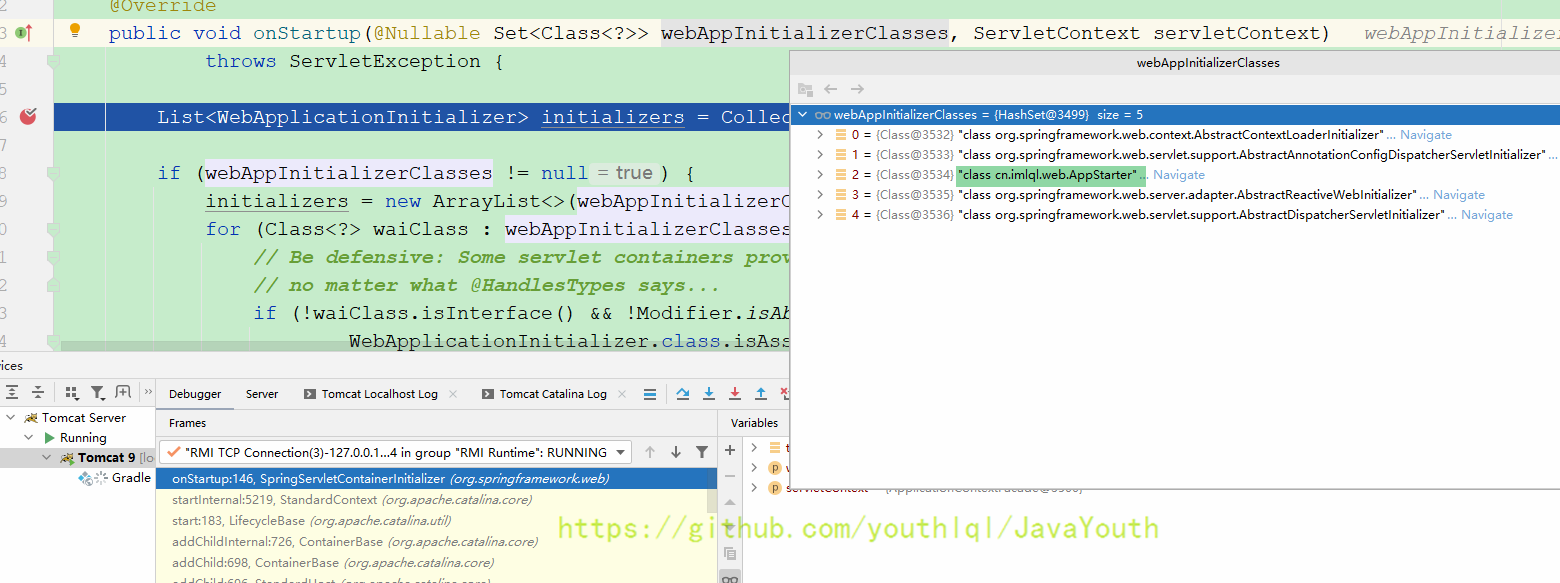
首先我们看到AppStarter实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口,官方文档是这样写的,那么WebApplicationInitializer肯定是能启动Web的核心
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {...}public interface ServletContainerInitializer {
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx)
throws ServletException;
}相当于tomcat一启动会加载SpringServletContainerInitializer
/**
* Servlet 3.0 {@link ServletContainerInitializer} designed to support code-based
* configuration of the servlet container using Spring's {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* SPI as opposed to (or possibly in combination with) the traditional
* {@code web.xml}-based approach.
*
* <h2>See Also</h2>
* See {@link WebApplicationInitializer} Javadoc for examples and detailed usage
* recommendations.<p>
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 3.1
* @see #onStartup(Set, ServletContext)
* @see WebApplicationInitializer
*/
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
/**
* Delegate the {@code ServletContext} to any {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* implementations present on the application classpath.
* <p>Because this class declares @{@code HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)},
* Servlet 3.0+ containers will automatically scan the classpath for implementations
* of Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer} interface and provide the set of all
* such types to the {@code webAppInitializerClasses} parameter of this method.
* <p>If no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations are found on the classpath,
* this method is effectively a no-op. An INFO-level log message will be issued notifying
* the user that the {@code ServletContainerInitializer} has indeed been invoked but that
* no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations were found.
* <p>Assuming that one or more {@code WebApplicationInitializer} types are detected,
* they will be instantiated (and <em>sorted</em> if the @{@link
* org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is present or
* the {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} interface has been
* implemented). Then the {@link WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)}
* method will be invoked on each instance, delegating the {@code ServletContext} such
* that each instance may register and configure servlets such as Spring's
* {@code DispatcherServlet}, listeners such as Spring's {@code ContextLoaderListener},
* or any other Servlet API componentry such as filters.
* @param webAppInitializerClasses all implementations of
* {@link WebApplicationInitializer} found on the application classpath
* @param servletContext the servlet context to be initialized
* @see WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)
* @see AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
*/
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = Collections.emptyList();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
initializers = new ArrayList<>(webAppInitializerClasses.size());
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says... 所有的非接口非抽象的WebApplicationInitializer实现类
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) //集合负责保存满足上面条件的类
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
//下面会遍历所有满足要求的WebApplicationInitializer,调用他们的onStartup
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext); //所有的 WebApplicationInitializer 的 onStartup
}
}
}- 其中@HandlesTypes注解表示可以处理的类,在
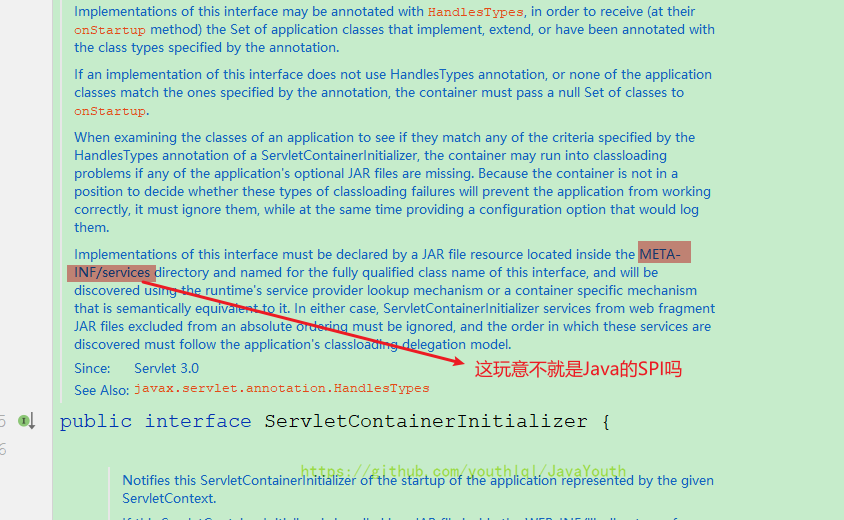
onStartup方法中,可以通过Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses获取得到。 - @HandlesTypes属于sun公司对Servlet定义的规范,包括tomcat,jetty等服务器都对它有不同的实现
- tomcat对于@HandlesTypes的具体实现咱们这里不深究,可以肯定的是一定用到了Java的SPI,如下。
ServiceLoader<DataSaveService> load = ServiceLoader.load(WebApplicationInitializer.class);- tomcat具体对于@HandlesTypes一定是和上面类似甚至是一样的代码来加载WebApplicationInitializer的实现
咱们给它的方法onStartup打上断点
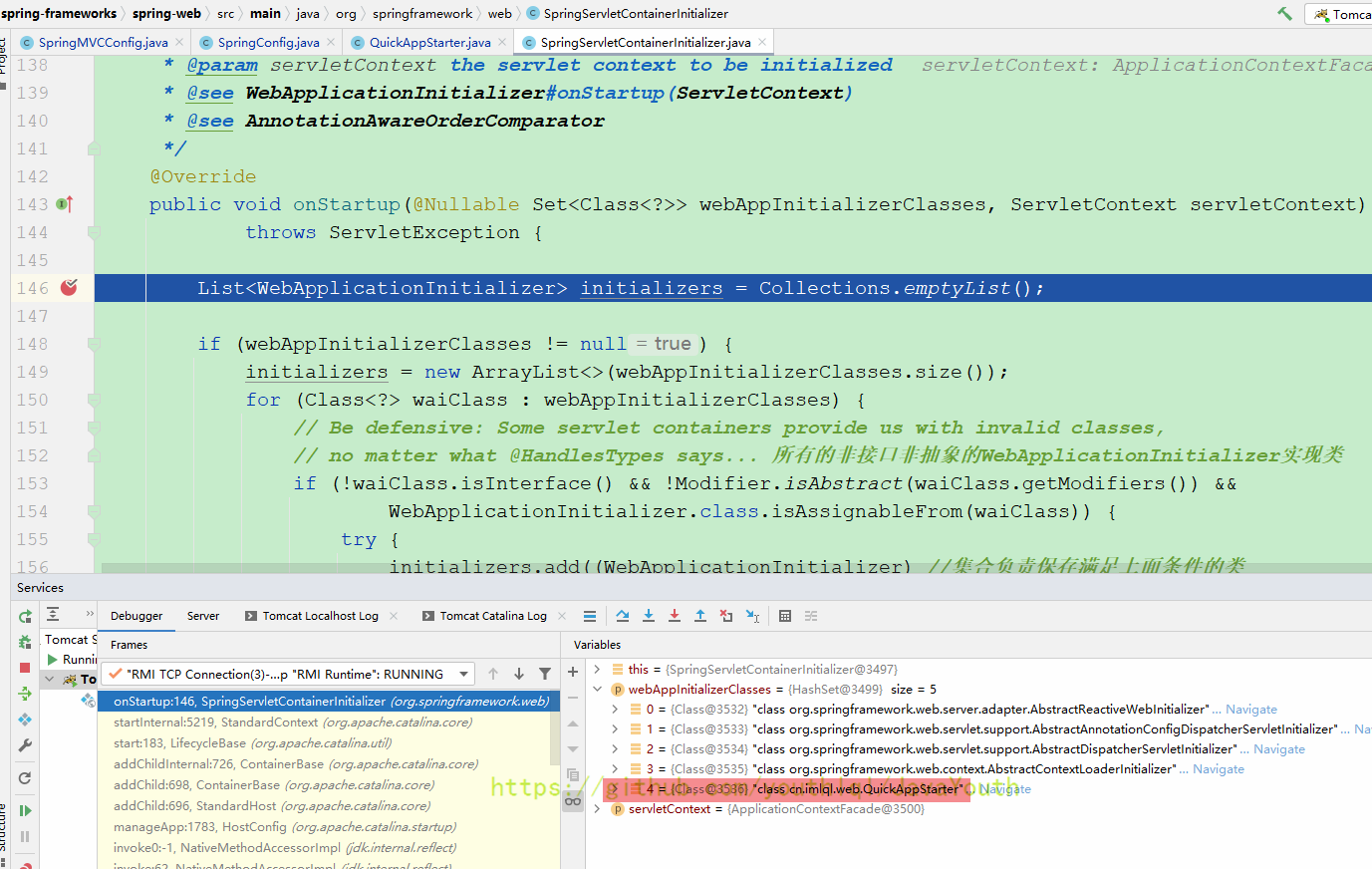
下面就是所有实现了WebApplicationInitializer的类
接着在最底下的for循环执行所有实现了WebApplicationInitializer的类的onStartup(),然后就走到了我们的AppStarter
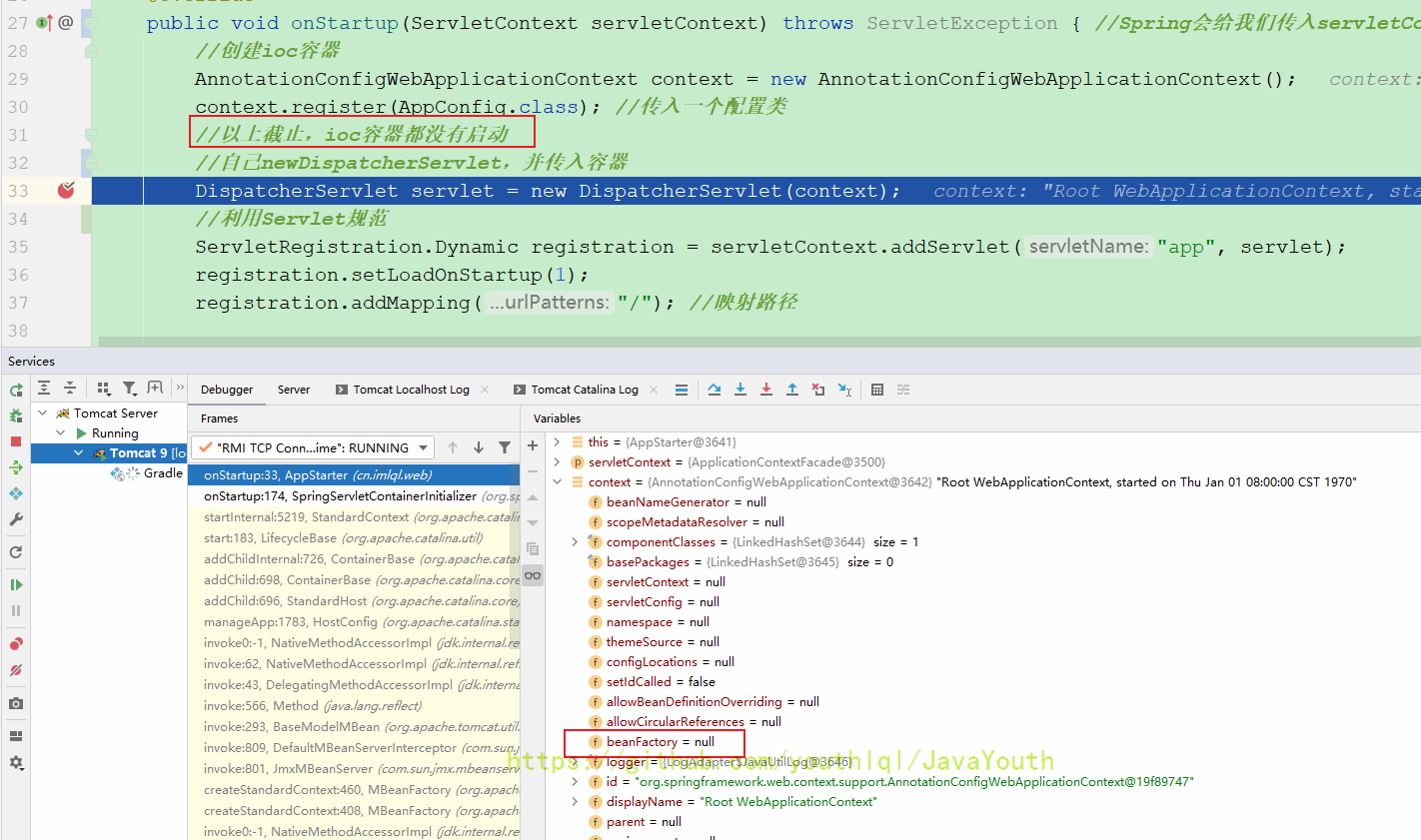
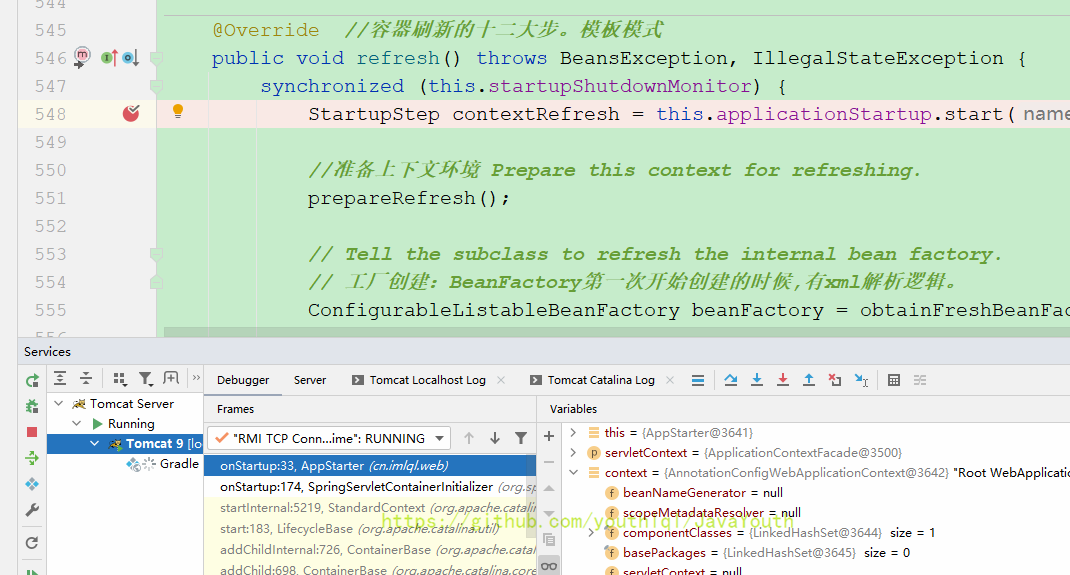
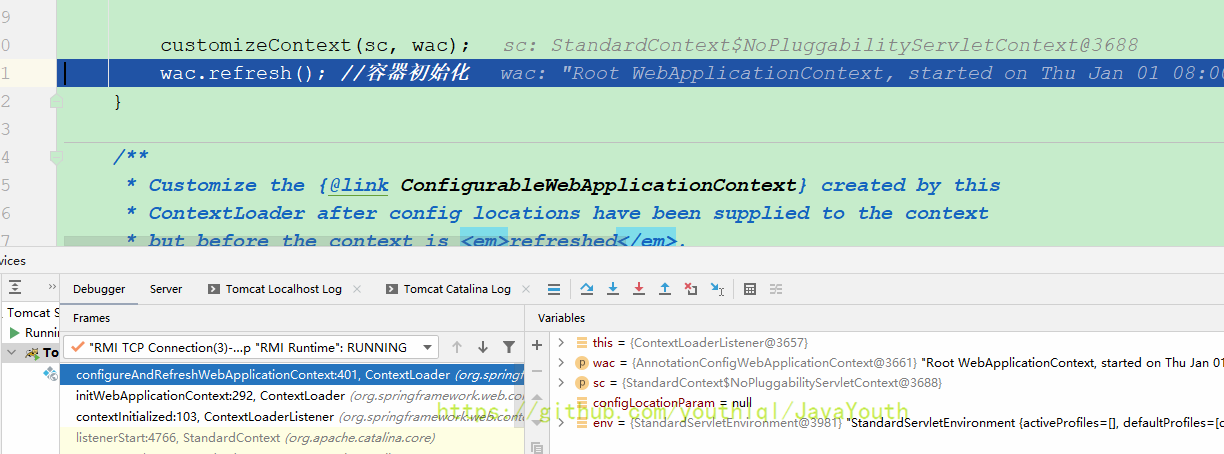
到这一步,ioc容器都没有创建,我们给refresh()打个断点,看什么时候启动的ioc
放行
我看的时候debug断点没有看到从AppStarter的哪一步跳到refresh()的。然后我一步一步走的时候发现不是在这个方法里调用的,注意看下面的图,DispatcherServlet已经new完了,但是debug依然没有跳到refresh(),说明不是在new DispatcherServlet()的时候创建的容器
不过我凭经验猜测Springmvc里最重要的是DispatcherServlet,会不会是DispatcherServlet的那一步启动了IOC,我们开始进行下面的尝试
-
tomcat会遵循sun公司的规范给每一个Servlet创建对象
-
所以DispatcherServlet肯定也会创建对象
-
Servlet的规范
- Servlet创建对象
- Servlet调用Init初始化
- 每次请求调用service处理
- tomcat停止的时候调用destroy进行销毁
- Serlvet是被谁调用开始初始化的属于tomcat的源码,我们这里不研究,我们这里只需要知道,每一个Servlet都会被初始化就可以了。
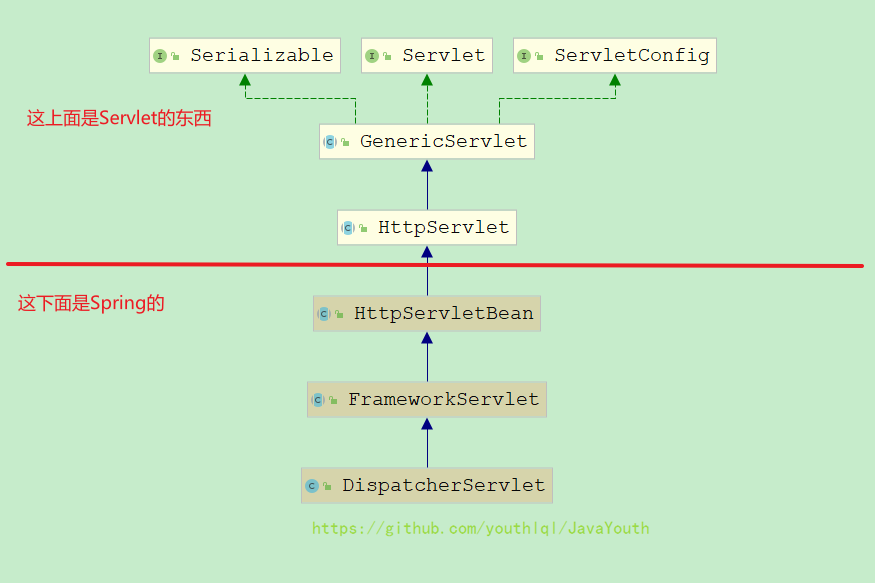
spring-web中有一个叫DispatcherServlet的类,很明显他是一个Servlet,所以tomcat启动的时候就会加载它,加载它的话当然是从父类一层一层加载的
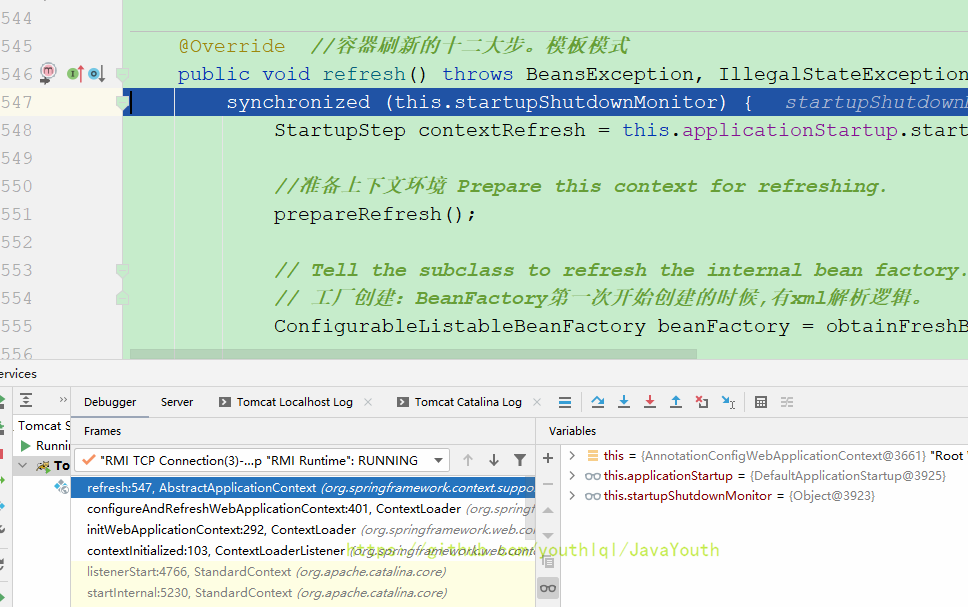
- 想要启动IOC容器,只可能是创建DispatcherServlet对象或者调用init()的时候来搞。上面我们也看到了,创建DispatcherServlet对象的时候debug调用栈并没有显示跳到了refresh方法,所以显然不是创建对象的时候
- 那就只有可能是调用init()的时候开始启动的IOC容器
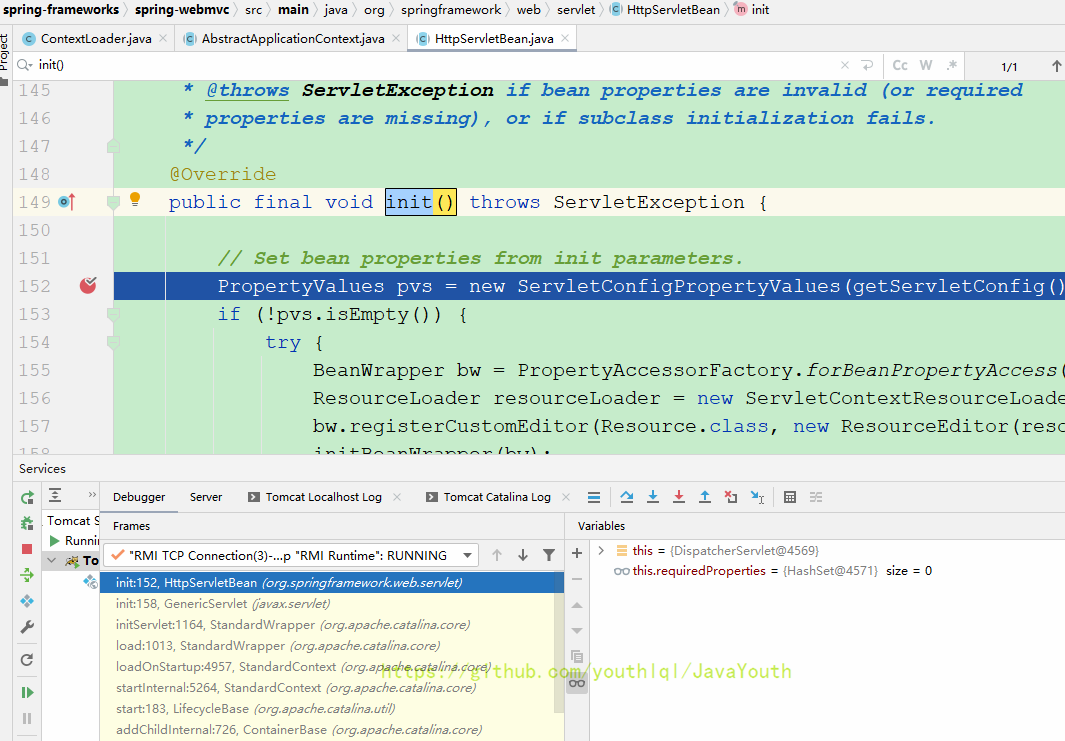
Servlet规范的init我看了下都是空的,从Spring的HttpServletBean才开始有东西,HttpServletBean的父类和接口对于init()都是空实现,下面我们就从HttpServletBean开始分析。
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
//模板方法模式。给子类留的喜欢干的事 Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
} /** 追踪看web应用启动做了什么。
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); //初始化WebIOC容器,那我们想一下大概率是在这里启动的IOC容器
initFrameworkServlet(); //这又是留给子类的
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}DispatcherServlet没有重写initFrameworkServlet()
最后得到结论
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); //初始化WebIOC容器,那我们想一下大概率是在这里启动的IOC容器下面开始具体分析
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/app-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value></param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>- 在web.xmI中配置C ontextl oaderListener,指定Spring配置文件的位置
- 在web.xml中配置 DispatcherServlet,指定SpringMVC配置文件位置
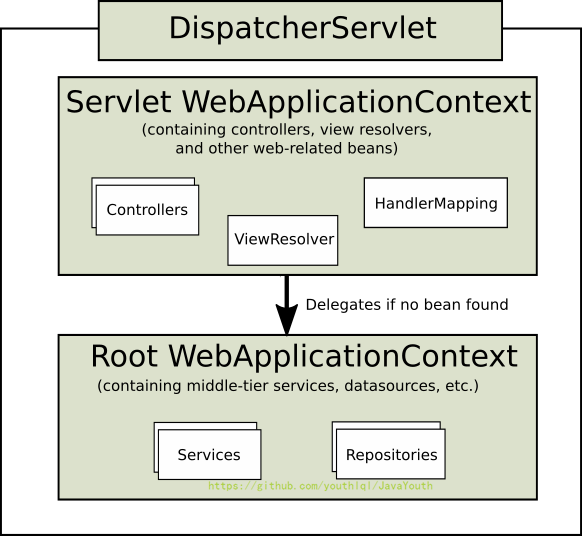
- 以上会产生父子容器
父容器(Spring配置文件进行包扫描并保存所有组件的容器)
子容器(SpringMVC配置文件进行包扫描并保存所有组件的容器)
webloc.setParent(springloc)。类似于双亲委派,容器隔离。先看当前容器有没有这个组件,当前容器没有再去父容器找有没有这个组件
后面的讲解都用这个测试类
/**
* 最快速的整合注解版SpringMVC和Spring的
*/
public class QuickAppStarter extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override //根容器的配置(Spring的配置文件===Spring的配置类)
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
@Override //web容器的配置(SpringMVC的配置文件===SpringMVC的配置类)
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{SpringMVCConfig.class};
}
@Override //Servlet的映射,DispatcherServlet的映射路径
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
@Override
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
// super.customizeRegistration(registration);
// registration.addMapping("");//
}
}/**
* SpringMVC只扫描controller组件,可以不指定父容器类,让MVC扫所有。@Component+@RequestMapping就生效了
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "cn.imlql.web", includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = Controller.class)
}, useDefaultFilters = false)
public class SpringMVCConfig {
//SpringMVC的子容器,能扫描的Spring容器中的组件
}/**
* Spring不扫描controller组件
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "cn.imlql.web",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = Controller.class)
})
public class SpringConfig {
//Spring的父容器
}父子容器隔离,因为有这句话webloc.setParent(springloc),springmvc这个子容器可以扫描到父容器Spring里面的组件,反之Spring父容器扫描不到springmvc这个子容器的组件。
//@Controller; 如果有父子容器 @Component,默认是在父容器中,还找不到
//@Component+@RequestMapping
@RestController
public class HelloController {
public HelloController(){
System.out.println("HelloController.....");
}
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello") // 所有的xxxMapping都是RequestMapping
public String sayHello(){
String mvc = helloService.say("MVC");
return mvc;
}
}@Service
public class HelloService {
public HelloService(){
System.out.println("HelloService.....");
}
public String say(String name){
return "Hello,"+name;
}
}public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Receives notification that the web application initialization
* process is starting.【翻译:在当前web应用启动以后(Tomcat把web应用加载了以后),调用contextInitialized方法】
*
* <p>All ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* initialization before any filters or servlets in the web
* application are initialized.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being initialized
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation takes no action.
*/
default public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {}
/**
* Receives notification that the ServletContext is about to be
* shut down.
*
* ......
*/
default public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {}
} public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = Collections.emptyList();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
initializers = new ArrayList<>(webAppInitializerClasses.size());
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says... 所有的非接口非抽象的WebApplicationInitializer实现类
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) //集合负责保存满足上面条件的类
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
//下面会遍历所有满足要求的WebApplicationInitializer,调用他们的onStartup
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext); //所有的 WebApplicationInitializer 的 onStartup
}
}
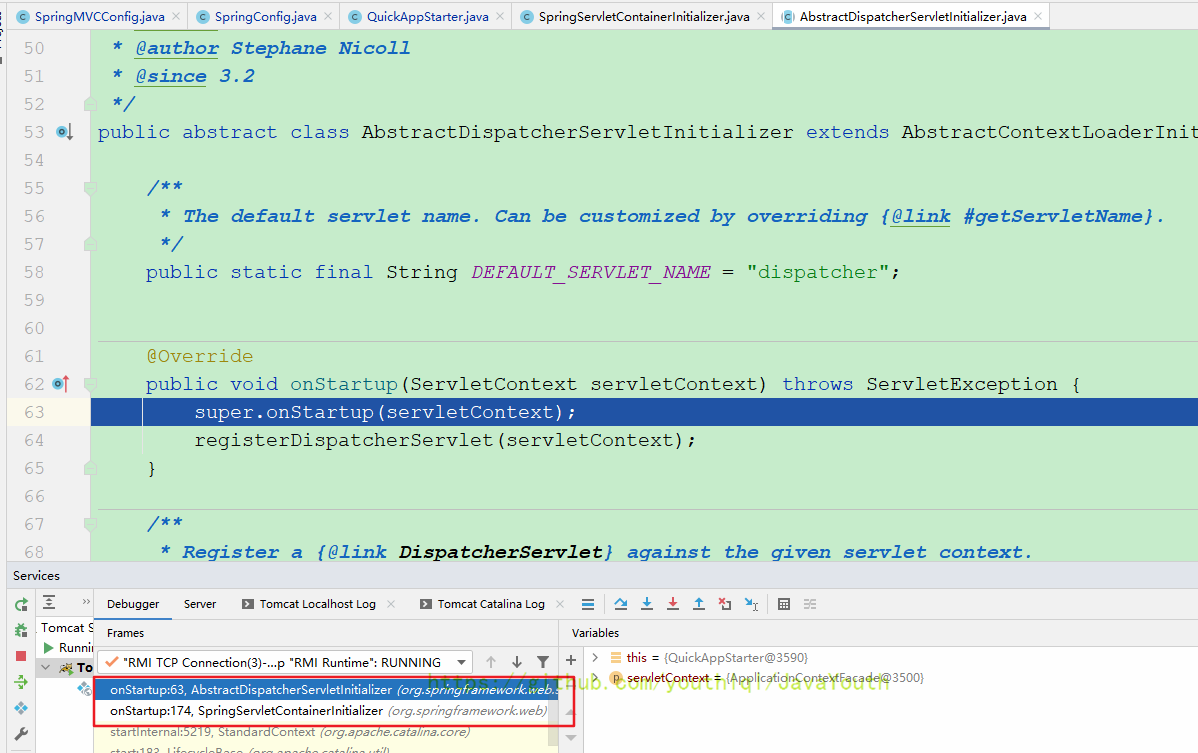
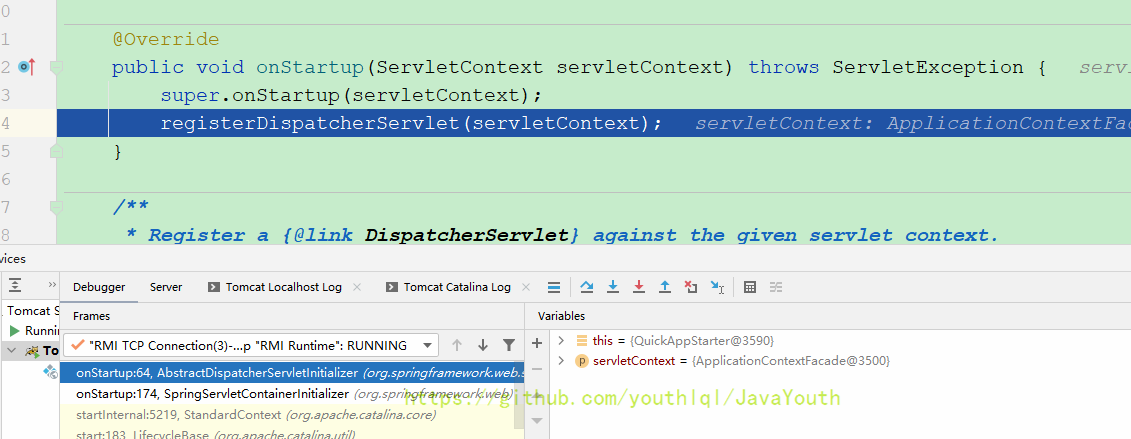
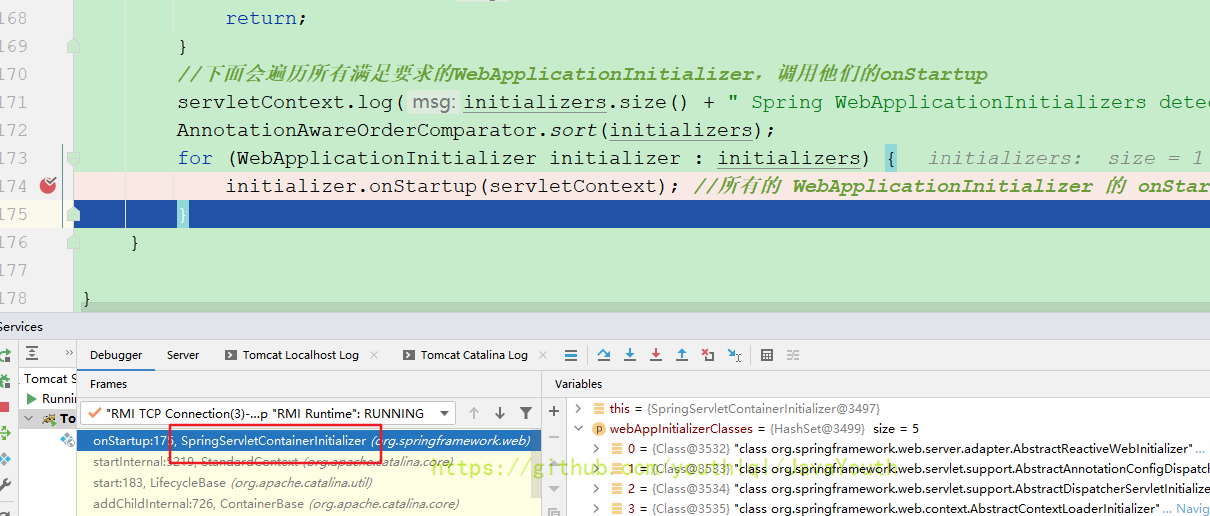
}当initializer是咱们的QuickAppStarter时,F7进入方法。
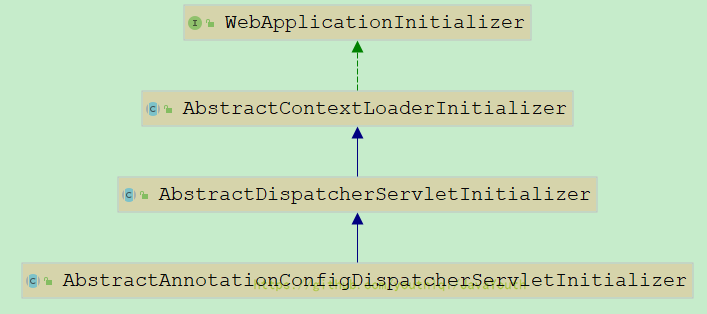
因为咱们的QuickAppStarter没有onStarup()所以就调用了父类AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer的,没想到AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer也是继续调用父类的
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
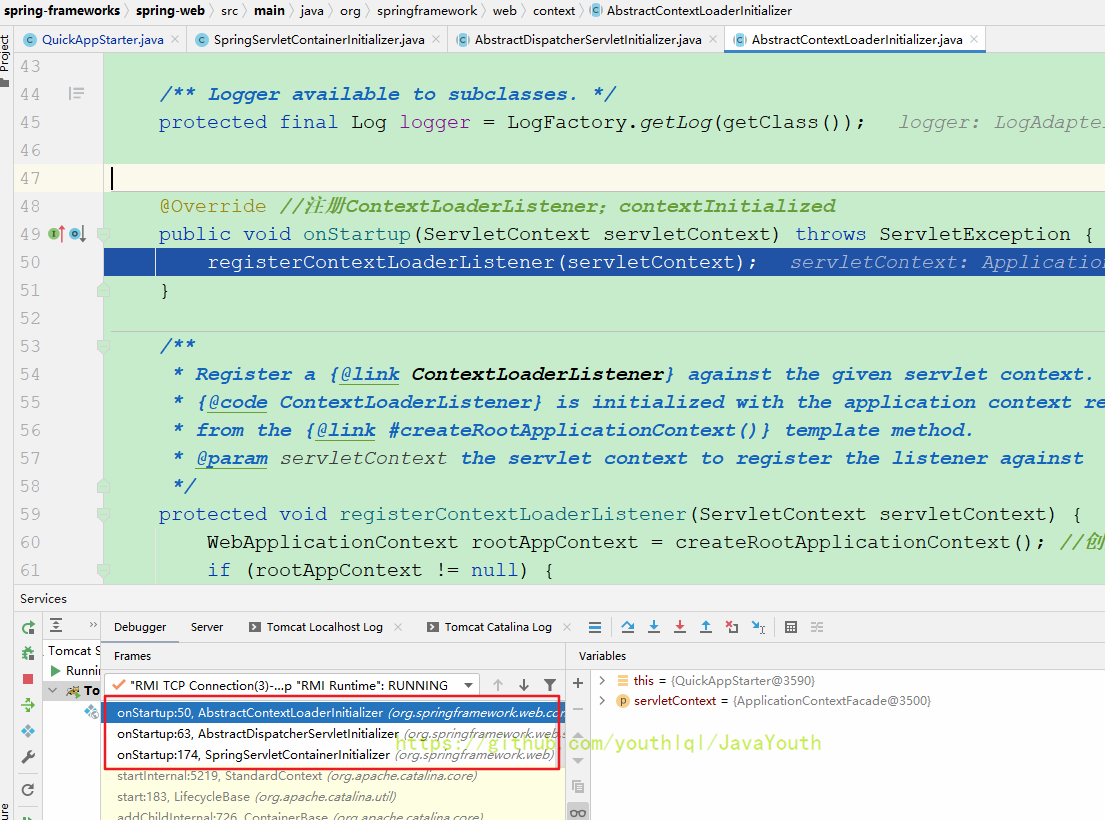
}public abstract class AbstractContextLoaderInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
/** Logger available to subclasses. */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Override //注册ContextLoaderListener;contextInitialized
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
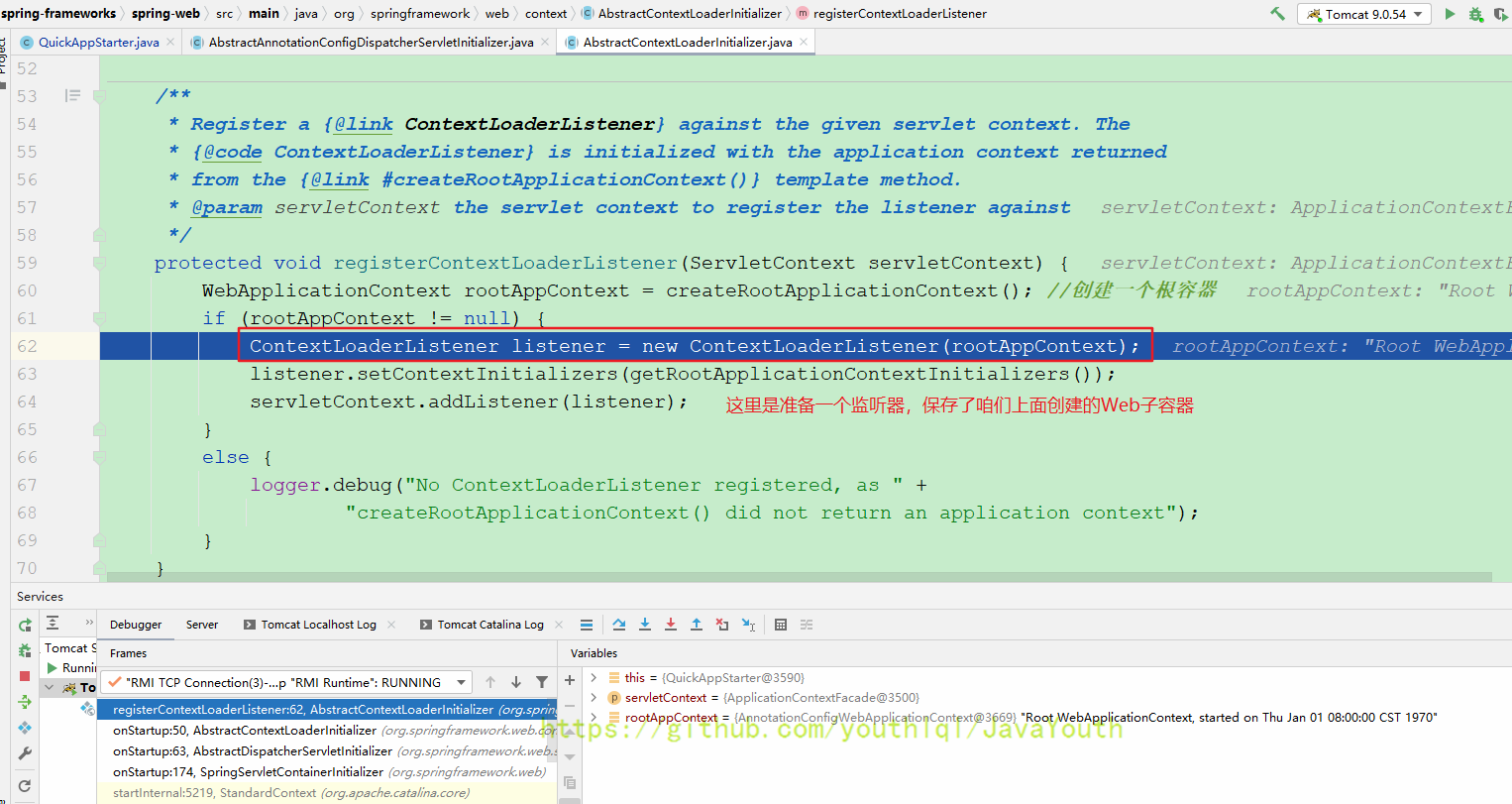
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext(); //创建一个根容器
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
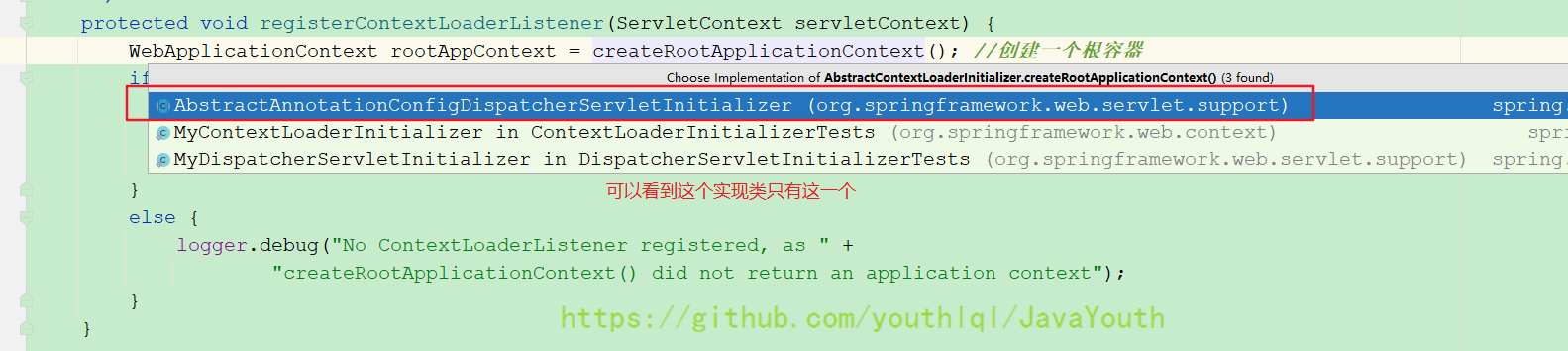
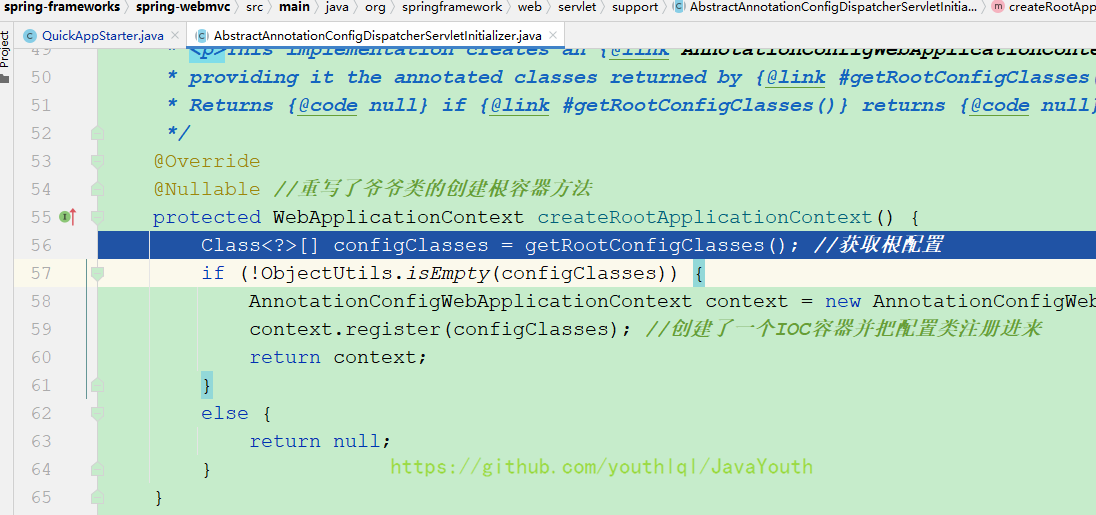
} @Nullable //重写了爷爷类的创建根容器方法
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses(); //获取根配置
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(configClasses); //创建了一个IOC容器并把配置类注册进来
return context;
}
else {
return null;
}
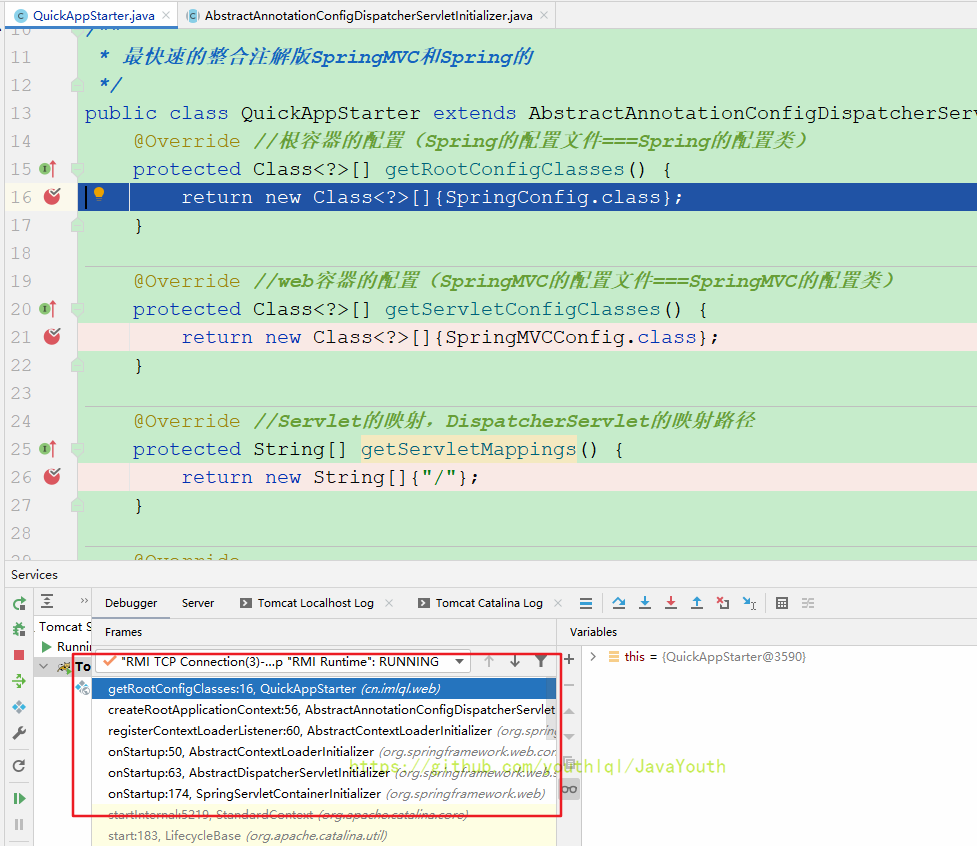
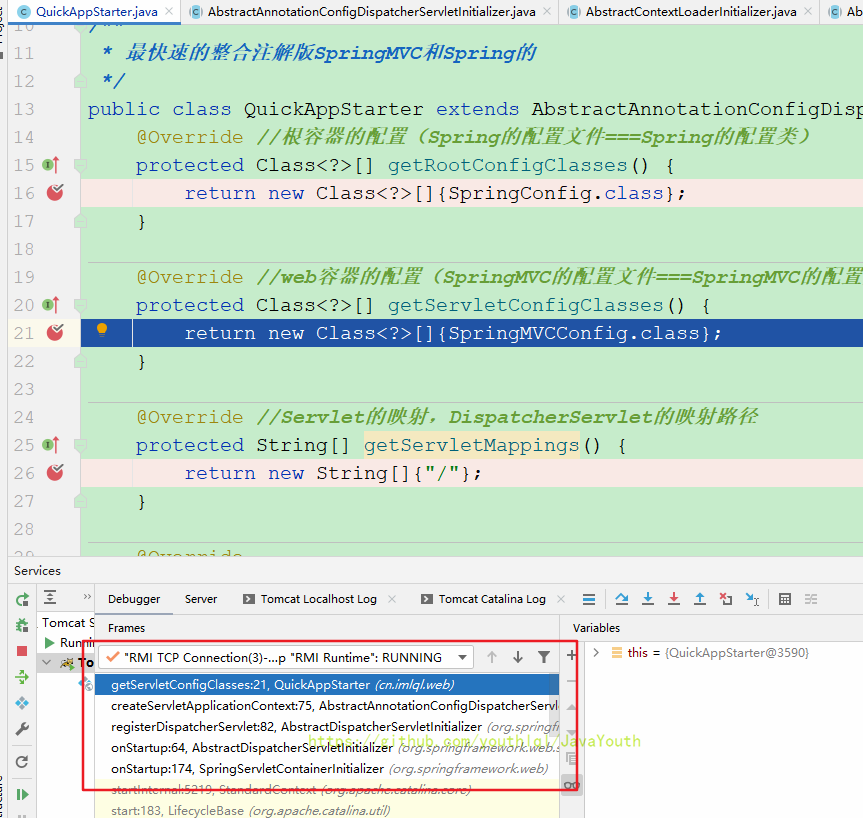
}getRootConfigClasses()正好是咱们QuickAppStarter这个子类重写的,debug F7进入
果不其然,调用了QuickAppStarter#getRootConfigClasses()
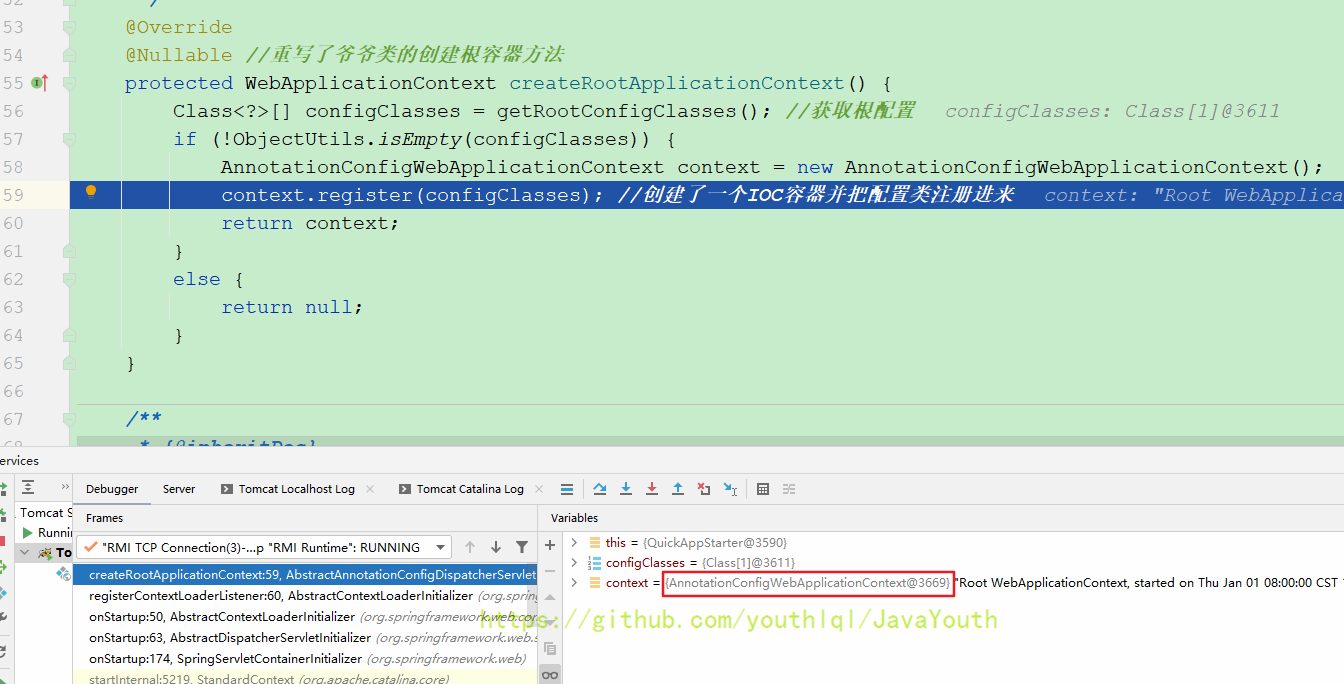
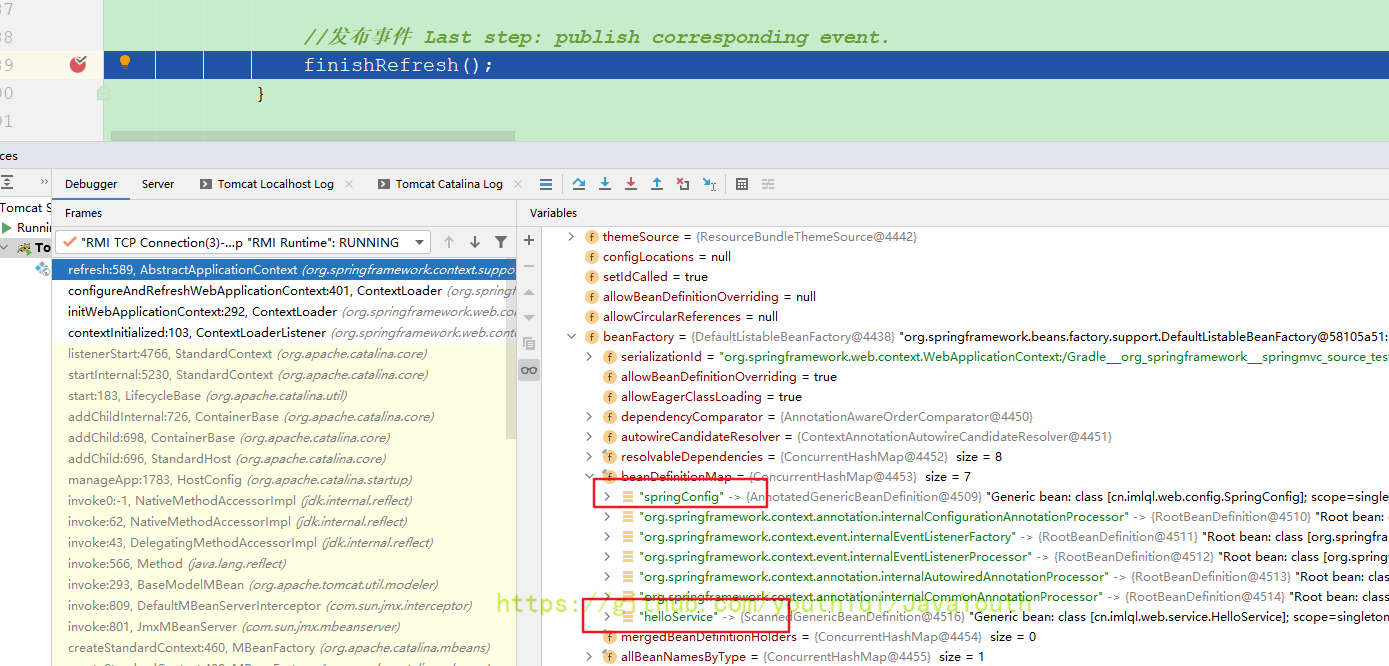
继续往下走创建Web容器,这是Spring父容器,因为你看它getRootConfigClasses()获取的是父容器配置
然后返回
图片上面写错了。应该改为:保存了上面创建的Spring-IOC父容器。Web子容器的创建在下面
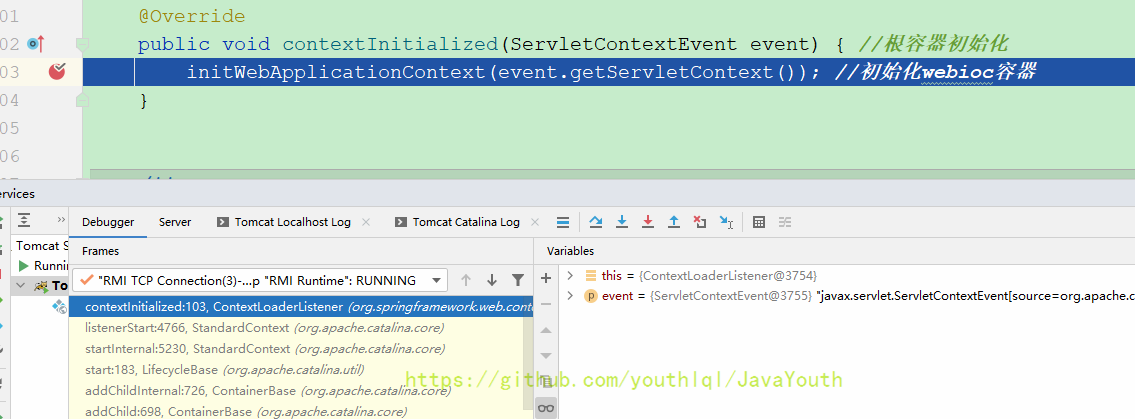
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
//在当前web应用启动以后(Tomcat把web应用加载了以后),调用contextInitialized方法
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { //根容器初始化
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); //初始化webioc容器
}
}上面是利用Servlet标准
接着就继续返回
下面才是创建Web子容器(也叫做Servlet容器)
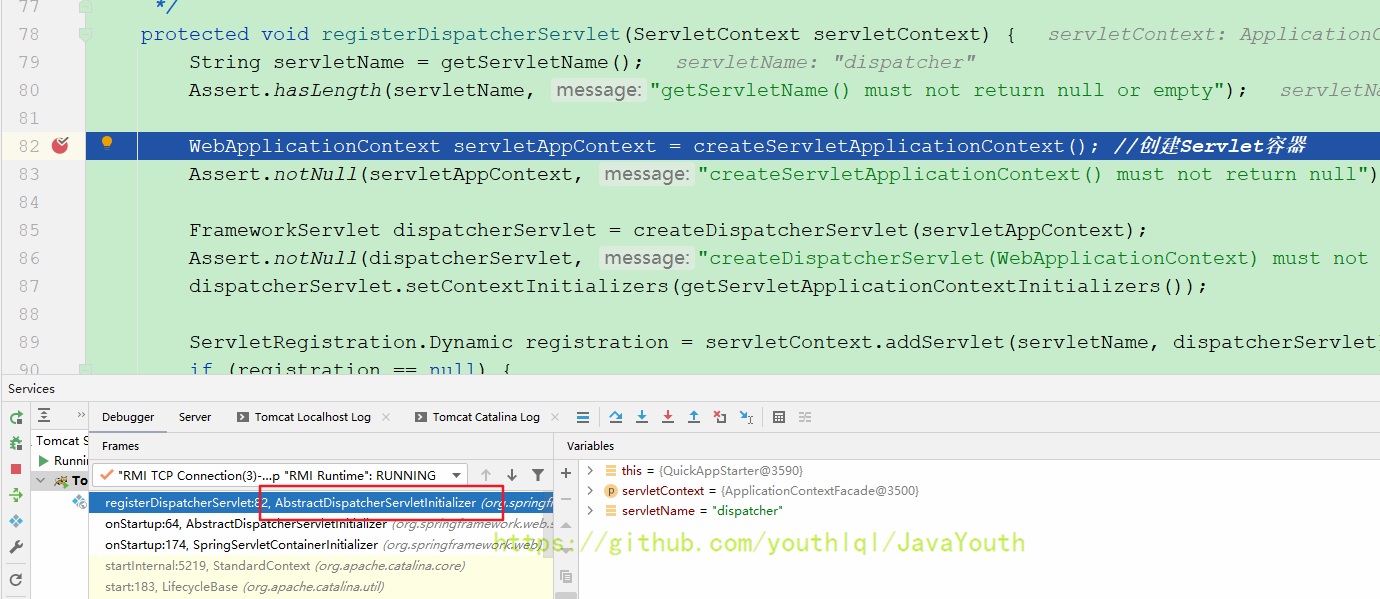
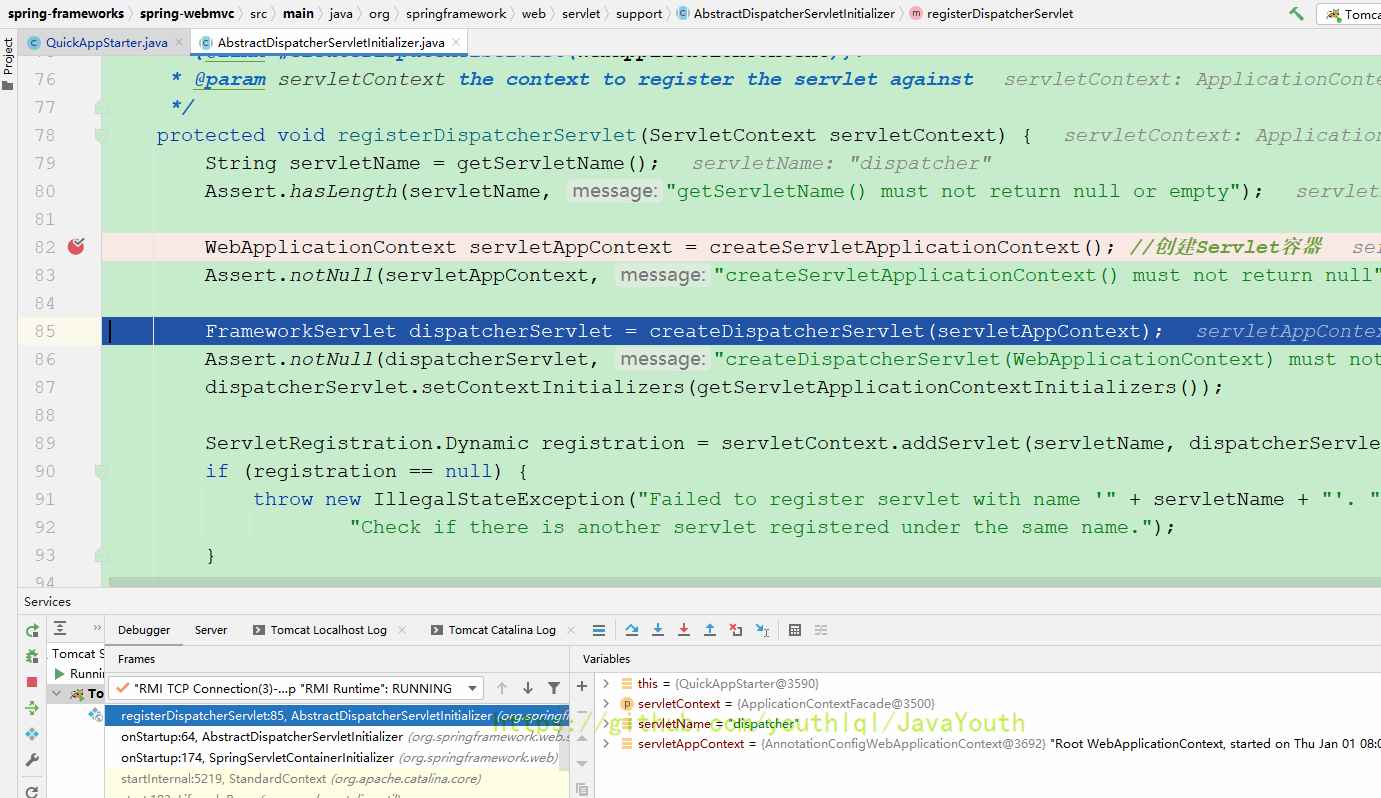
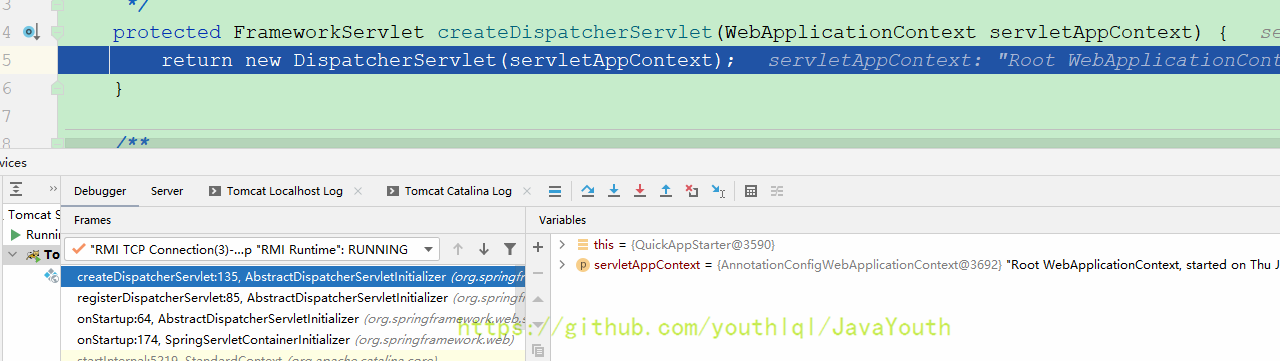
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext(); //创建Servlet容器
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings()); //根据我们指定的DispatcherServlet的路径进行注册
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
// 这个是留给我们自定义的方法,模板模式
customizeRegistration(registration);
}AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer#createServletApplicationContext()创建Web子容器(Servelt容器)
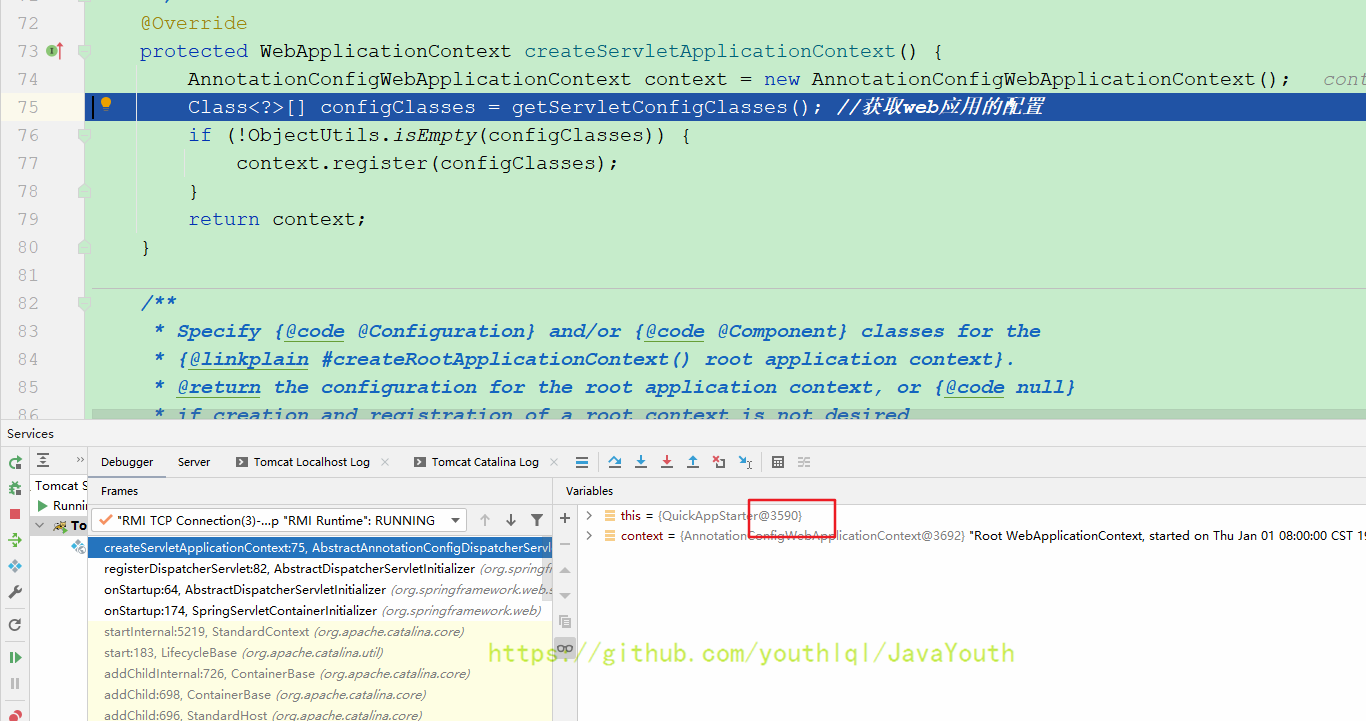
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
//
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses(); //获取web应用的配置
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}这里又new了一个容器,和上面那个容器一样都没有初始化。这里也是调用咱们QuickAppStarter重写的方法,因为这里调用的是getServletConfigClasses(),所以很明显这里的容器是Web子容器
然后就一路往回返,走到这里
继续F7进入
这里就是保存咱们上面刚创建的Web子容器,然后再返回
- 这里应用就加载完了,接下来干嘛呢?
- 你往前看看,咱们的Spring容器和Web子容器都是只是创建完了,都还没有初始化,甚至都没有webloc.setParent(springloc)这样产生父子容器的关系
- 回想下前面讲的,是不是有一个监听器,那你说把容器保存到监听器里,它能是干嘛的?猜想一下不就是应用加载完之后,发送一个什么事件,然后根据这个事件触发监听器初始化两大容器等等。
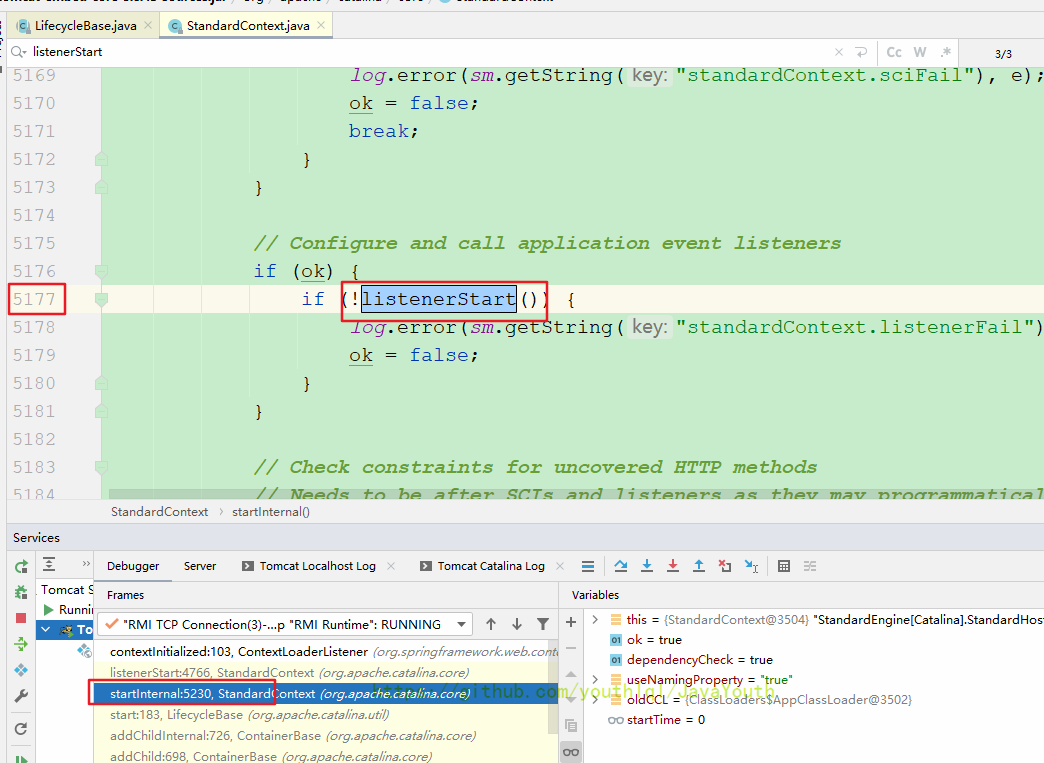
咱们就把那个监听器的初始化方法打个断点,然后F8放行试试呗
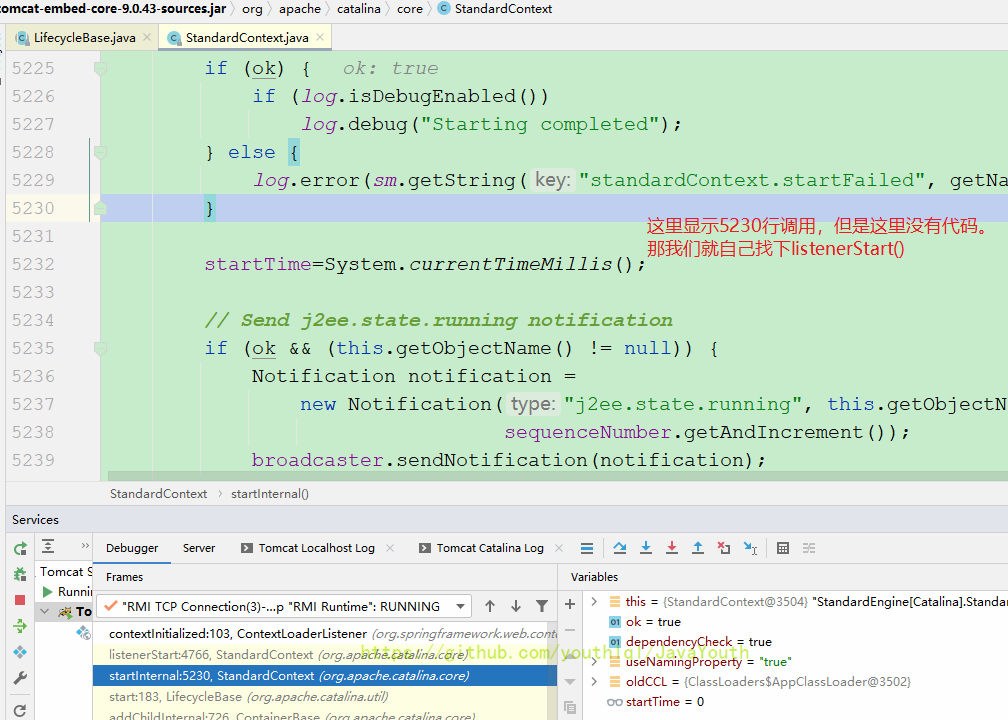
然后真的走到了这里。tomcat里的代码位置是乱的,乱的意思就是比如说上面写的是4766行的调用,但实际上那里是个}大括号。也不知道是什么问题,所以我们就大致看下tomcat的代码,不细究。
这里的调用还是对的
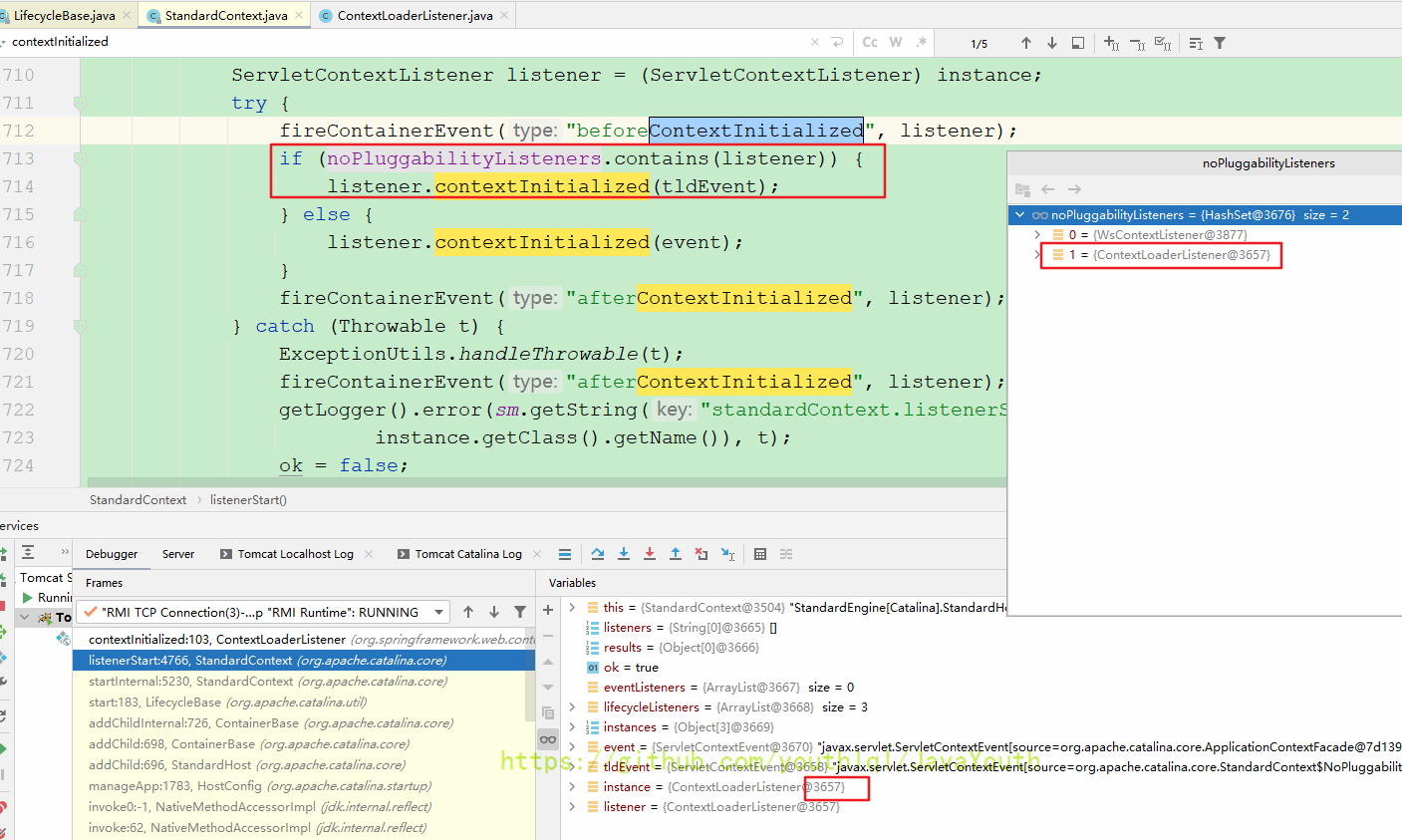
应该就是类似这样的调用
走的应该是第一个if
大致就是tomcat里的一个监听器基于事件回调的原理,咱们就不深究了。
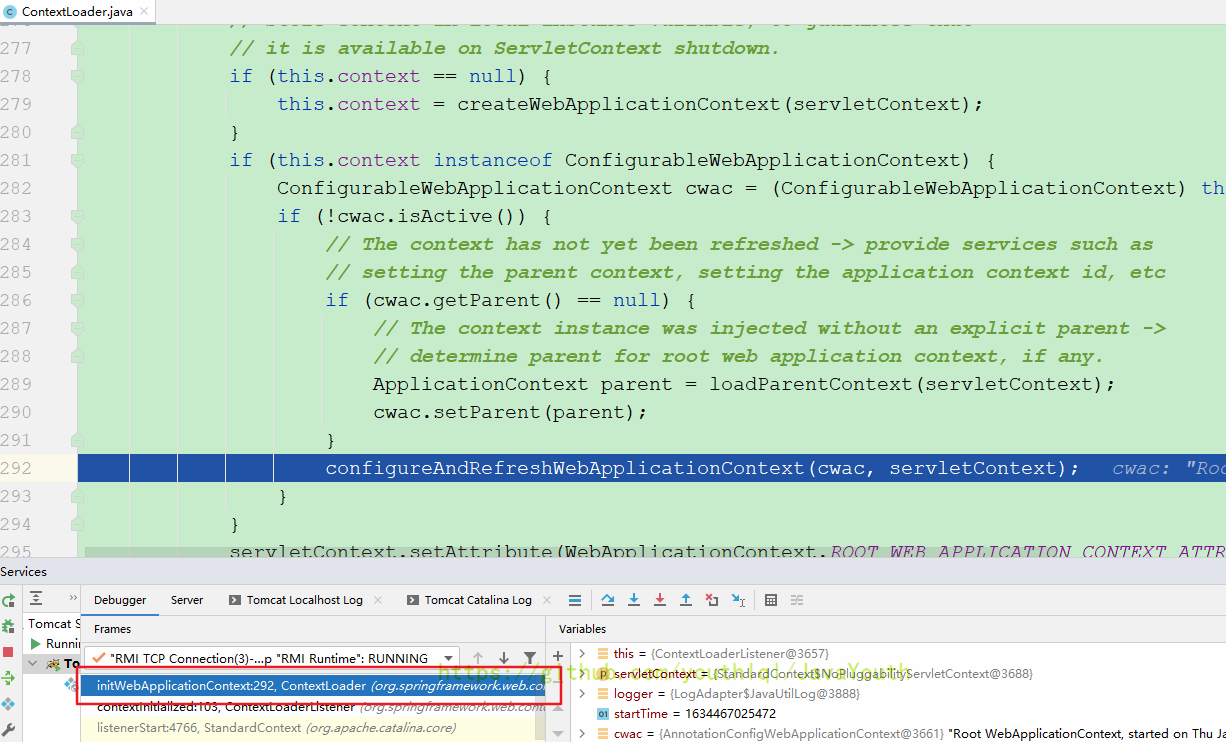
F7进入,这里因为我重新启动了一次,所以你看到根容器是@3661
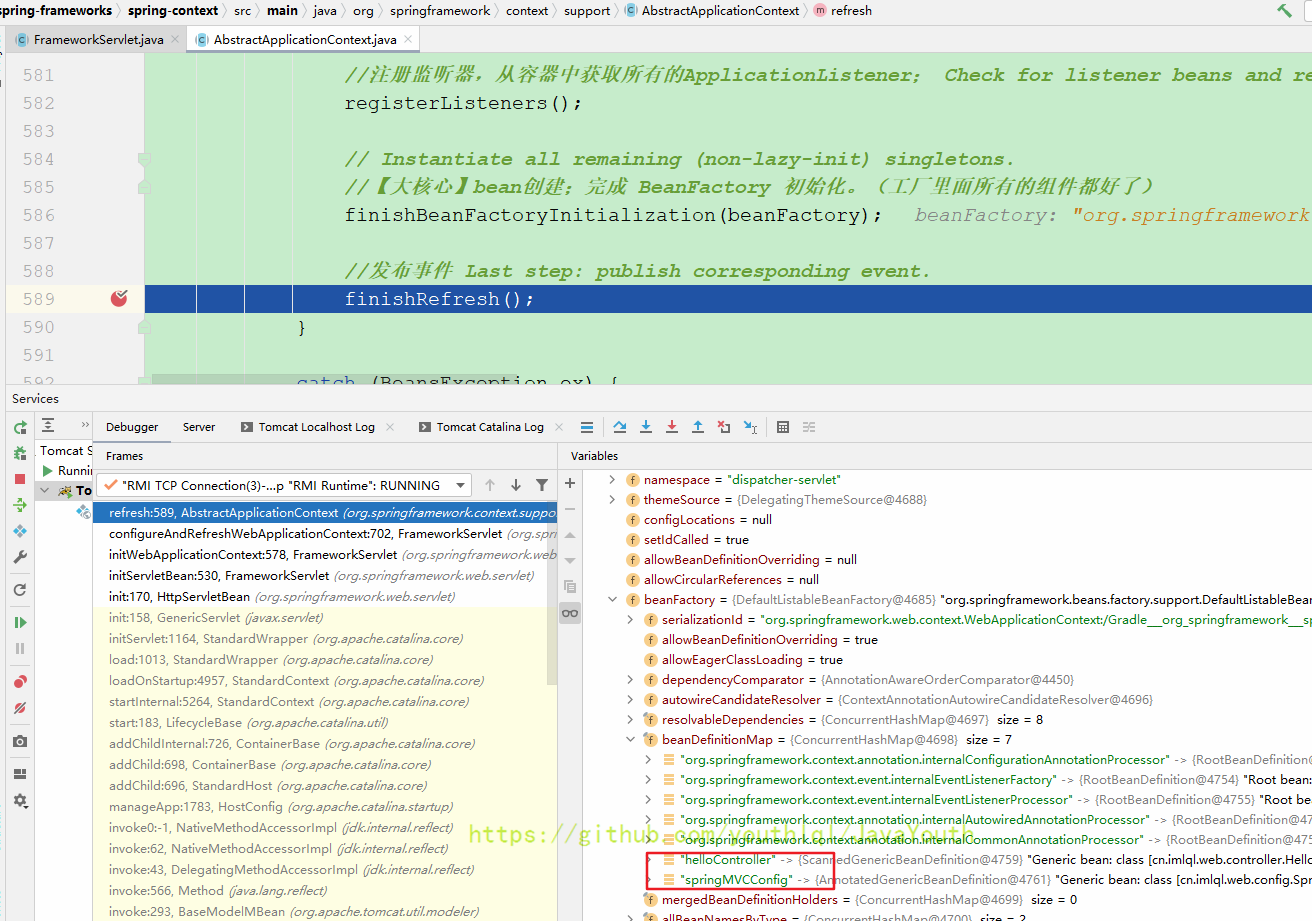
终于要调用refresh了
这里直接放行到容器refresh完毕看下父容器
父容器只扫描了,springconfig和helloService,我们继续放行看下Web子容器.
跳到了这里,为什么会跳到这里呢?记不记得之前我们用DispatcherServlet保存了Web子容器,这里就要调用DispatcherServlet的相关初始化方法
一路放行
上面父子容器关系形成了,并且父容器已经refresh完毕
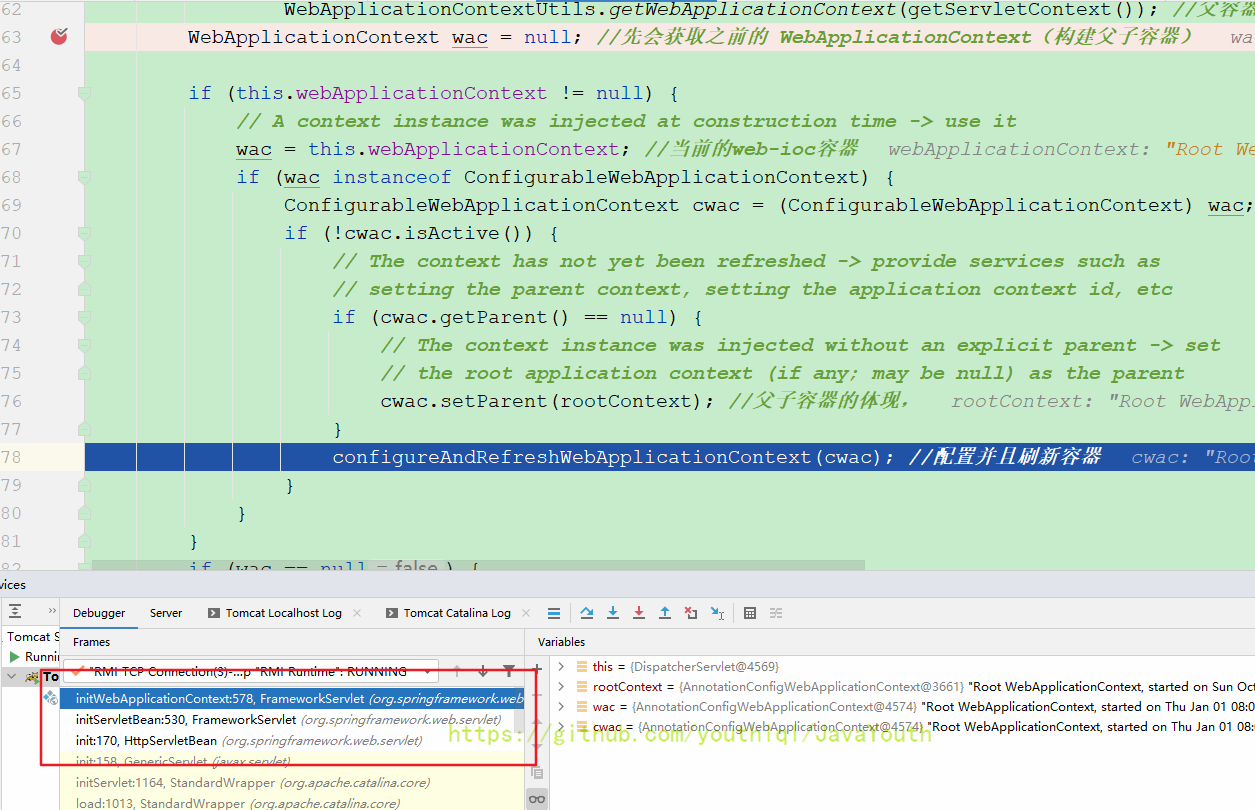
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); //父容器
WebApplicationContext wac = null; //先会获取之前的 WebApplicationContext(构建父子容器)
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext; //当前的web-ioc容器
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext); //父子容器的体现,
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); //配置并且刷新容器
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
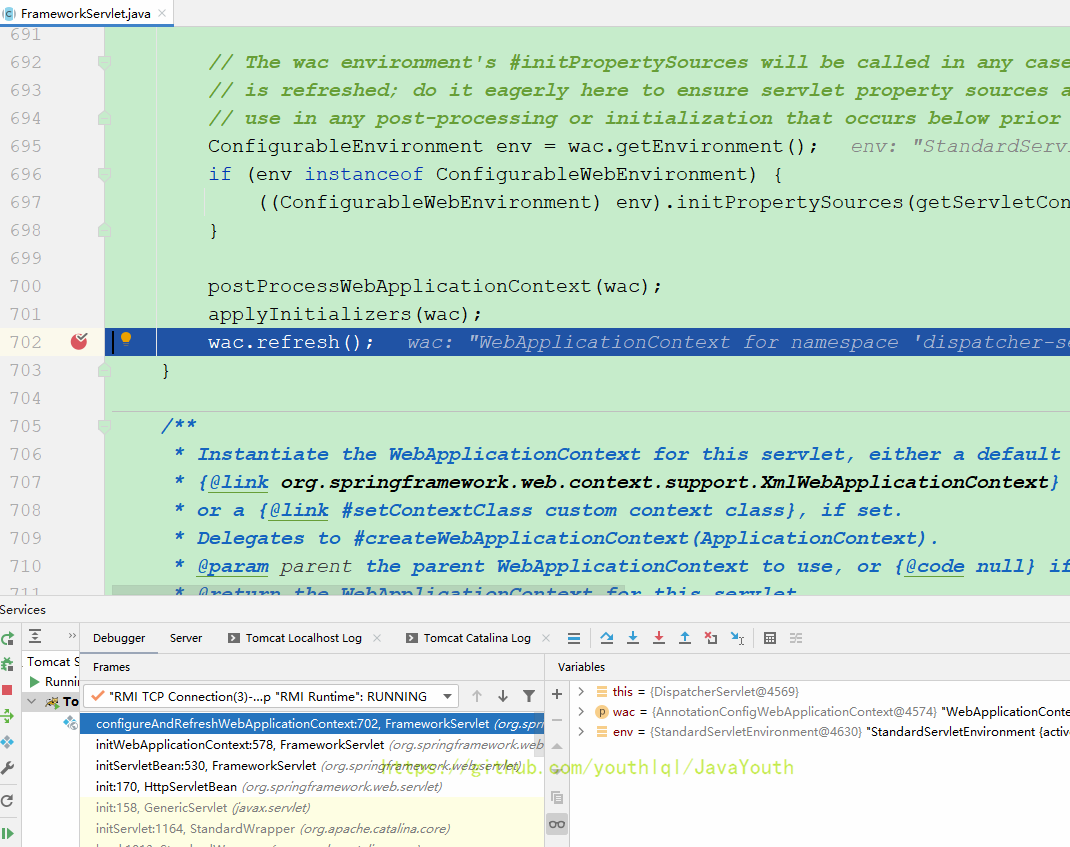
}再次来到Web子容器的刷新
- 然后我们看到子容器只有它自己的东西
- 虽然子容器只有controller,但是因为它保存了父容器。所以它是可以拿到HelloService的,也就是我们可以在HelloController里装配HelloService
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
}- 但是如果想在父容器里装配HelloController就会报错,父容器没有保存子容器。
public class HelloService {
@Autowired
HelloController helloController;
}- 这样就很好的实现容器隔离,避免Service乱引用Controller
- 实现父子容器隔离的前提就是前面写的SpringConfig不扫描controller,交给Web子容器
/**
* Spring不扫描controller组件
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "cn.imlql.web",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = Controller.class)
})
public class SpringConfig {
//Spring的父容器
}/**
* SpringMVC只扫描controller组件,可以不指定父容器类,让MVC扫所有。@Component+@RequestMapping就生效了
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "cn.imlql.web", includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = Controller.class)
}, useDefaultFilters = false)
public class SpringMVCConfig {
//SpringMVC的子容器,能扫描的Spring容器中的组件
}注意找组件的过程是先找自己的容器,自己没有再到父容器里找
- 总的来说Spring父容器和SpringMVC子容器启动过程是来自于tomcat的两个回调
- Serlvet应用启动,监听器回调刷新Spring父容器
- Servlet初始化,回调刷新SpringMVC子容器