The Automated Extended Aperture Photometry (autoEAP) is developed for high amplitude K2 variable stars. The details of autoEAP are published in Bódi et al.,2022,PASP,134,14503 and Plachy et al.,2019,ApJS,244,32. A short summary of automatization is published here.
To install the package, use:
pip install autoeapTo create your own photomery, you'll need a Target Pixel File, such as this one. Then, after starting Python, you can do:
yourtpf = '/path/to/your/tpf/ktwo212466080-c17_lpd-targ.fits'
import autoeap
time, flux, flux_err = autoeap.createlightcurve(yourtpf)Or if you want to let autoEAP download the TPF from MAST database, you can just provide a target name and optionally a campaign number:
import autoeap
targetID = 'EPIC 212466080'
campaign = 17
time, flux, flux_err = autoeap.createlightcurve(targetID,campaign=campaign)With this last line, you can create autoEAP photometry for any K2 variable star.
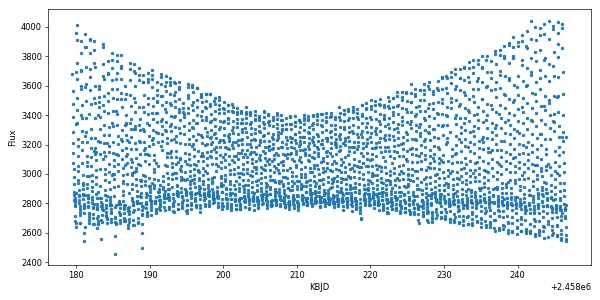
Plotting our results gives:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(time,flux,'.')
plt.xlabel('KBJD')
plt.ylabel('Flux')
plt.show()The details of the workflow is described in docs.
You can find Google Colab friendly tutorials in the examples.
If you want to apply K2SC correction for your freshly made raw-photometry, first you should install K2SC. AutoEAP is based on that package, so if you find K2SC useful, please cite Aigrain et al.,2016,MNRAS,459,2408.
Installation with george:
pip install george k2scAnd then without much hassle, you can apply the correction in python:
import autoeap
targetID = 'EPIC 212466080'
campaign = 17
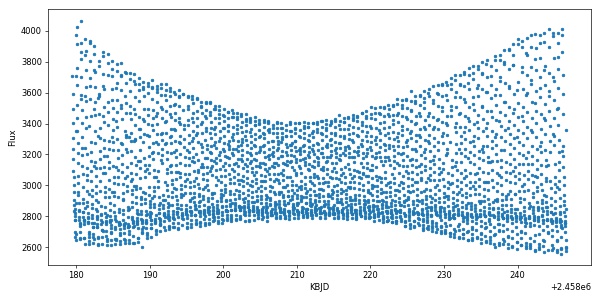
time, flux, flux_err = autoeap.createlightcurve(targetID,campaign=campaign,apply_K2SC=True)The result is quite delightful:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(time,flux,'.')
plt.xlabel('KBJD')
plt.ylabel('Flux')
plt.show()We have also built-in a method to remove trends using low-order splines. To correct the raw light curve, do:
import autoeap
time, flux, flux_err = autoeap.createlightcurve(yourtpf,detrend=True)Or do this to remove a spline from the K2SC light curve:
import autoeap
time, flux, flux_err = autoeap.createlightcurve(yourtpf,apply_K2SC=True,detrend=True)apply_K2SCIfTrue, after the raw photomery, K2SC will be applied to remove systematics from the extracted light curve.detrendIfTrue, after the raw photomery, a low-order spline will be fitted and removed from the extracted light curve. Ifapply_K2SCis alsoTrue, then this step will be done after the K2SC.save_lcIfTrue, the intermediate and the final light curves will be save as a file.save_apertureIfTruethe final aperture will be saved to a FITS file.campaignIf local TPF file is not found, it will be downloaded from MAST, butcampaignnumber should be defined as well, if the target has been observed in more than one campaign. Otherwise that campaign will be used in which the target were first observed.show_plotsIfTrue, all the plots that visualize each step of photometry will be displayed.save_plotsIfTrue, all the plots that visualize each step of photometry will be saved to a subdirectory.polyorderThe order of the detrending polynomial. Applies only ifdetrendisTrue. Default is'auto'.sigma_detrendThe number of standard deviations to use for sigma clipping limit before spline correction. Applies only ifdetrendisTrue. Default is10.max_missing_pos_corrMaximum number of missing position correction (POS_CORR) values. If too many POS_CORR is missing, then less reliable photometrically estimated centroids will be used for K2SC. Missing POS_CORR values reduce the number of light curve points! Default is10.THThreshold to segment each target in each TPF candence. Only used if targets cannot be separated normally. Default is8. Do not change this value unless you are aware of what you are doing!ROI_lowerThe aperture frequency grid range of interest threshold given in absolute number of selections above which pixels are considered to define the apertures. Do not change this value unless you are aware of what you are doing! Default is100.ROI_upperThe aperture frequency grid range of interest threshold given in relative number of selections w.r.t. the number of all cadences below which pixels are considered to define the apertures. Do not change this value unless you are aware of what you are doing! Default is0.85.**kwargsDictionary of arguments to be passed tok2sc.detrend. See options here.
After installation, autoEAP will be available from the command line:
autoEAP <EPIC number or TPF path> [options]
Listed below are the usage instructions:
$ autoeap --help
usage: autoeap [-h] [--campaign <campaign-number>] [--applyK2SC]
[--removespline] [--polyorder <detrending-polynomial-order>]
[--sigmadetrend <detrending-sigma-limit>] [--saveplots]
[--maxmissingposcorr <max-missing-pos-corr>]
[--TH <threshold-value>] [--ROIlower <lower-ROI-value>]
[--ROIupper <upper-ROI-value>]
<path-to-targettpf-or-EPIC-number>
Perform autoEAP photometry on K2 variable stars.
positional arguments:
<path-to-targettpf-or-EPIC-number>
The location of the local TPF file or an EPIC number to be downloaded from MAST. Valid inputs include: The name of the object as a string, e.g. 'ktwo251812081'. The EPIC identifier as an integer, e.g. 251812081.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--campaign <campaign-number>
If the target has been observed in more than one campaign, download this light curve. If not given, the first campaign will be downloaded.
--applyK2SC After the raw photomery, apply K2SC to remove systematics from the extracted light curve.
--detrend After the raw or K2SC photomery, remove a low-order spline from the extracted light curve.
--polyorder <detrending-polynomial-order>
The order of the detrending polynomial. Default is auto.
--sigmadetrend <detrending-sigma-limit>
The number of standard deviations to use for sigma clipping limit before spline correction. Default is 10.0
--saveplots Save all the plots that show each step into a subdirectory.
--maxmissingposcorr <max-missing-pos-corr>
Maximum number of missing position correction (POS_CORR) values. If too many POS_CORR is missing, then less reliable photometrically estimated centroids will be used for K2SC. Missing POS_CORR values reduce the number of light curve points!
--TH <threshold-value>
Threshold to segment each target in each TPF candence. Only used if targets cannot be separated normally. Default is 8.
--ROIlower <lower-ROI-value>
The aperture frequency grid range of interest threshold given in absolute number of selections above which pixels are considered to define the apertures. Default is 100.
--ROIupper <upper-ROI-value>
The aperture frequency grid range of interest threshold given in relative number of selections w.r.t. the number of all cadences below which pixels are considered to define the apertures. Default is 0.85.We provide photometry for targets for the following Guest Observation Programs: GO0055, GO1018, GO2040, GO3040, GO4069, GO5069, GO6082, GO7082, GO8037, GO10037, GO12111, GO13111, GO14058, GO15058, GO16058, GO17033, GO18033, GO19033.
Slightly less than 2000 RRLs. See: K2 approved targets & programs.
The data we have already created have been uploaded to our webpage.
The PDM-based polynomial fitting and detrending can be used as a standalone module to be applied to e.g. raw autoEAP light curves or any other data sets given a time series with times, fluxes and flux errors. The detrend_wrt_PDM method returns the corrected flux values.
from autoeap.detrender import detrend_wrt_PDM
corrflux = detrend_wrt_PDM(time, # Time values
flux, # Flux values
flux_err, # Flux errors
polyorder='auto', # Polynomial order or 'auto'
sigma=10, # Sigma value for sigma clipping before PDM calculation
show_plots=True, # Show the detrending process
save_plots=False, # Save the detrending process plot
filename=None) # to this file as PNG.Feel free to open PR / Issue, or contact us here or here.
If you use data provided by this pipeline please cite Bódi et al.,2022,PASP,134,14503 and Plachy et al.,2019,ApJS,244,32. Here are the BibTeX sources:
@ARTICLE{2022PASP..134a4503B,
author = {{B{\'o}di}, Attila and {Szab{\'o}}, P{\'a}l and {Plachy}, Emese and {Moln{\'a}r}, L{\'a}szl{\'o} and {Szab{\'o}}, R{\'o}bert},
title = "{Automated Extended Aperture Photometry of K2 Variable Stars}",
journal = {\pasp},
keywords = {1307, 1620, 1855, Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics, Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics},
year = 2022,
month = jan,
volume = {134},
number = {1031},
eid = {014503},
pages = {014503},
doi = {10.1088/1538-3873/ac4398},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {2112.07496},
primaryClass = {astro-ph.IM},
adsurl = {https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2022PASP..134a4503B},
adsnote = {Provided by the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System}
}
@ARTICLE{2019ApJS..244...32P,
author = {{Plachy}, Emese and {Moln{\'a}r}, L{\'a}szl{\'o} and {B{\'o}di}, Attila and {Skarka}, Marek and {Szab{\'o}}, P{\'a}l and {Szab{\'o}}, R{\'o}bert and {Klagyivik}, P{\'e}ter and {S{\'o}dor}, {\'A}d{\'a}m and {Pope}, Benjamin J.~S.},
title = "{Extended Aperture Photometry of K2 RR Lyrae stars}",
journal = {\apjs},
keywords = {RR Lyrae variable stars: 1410, Light curves (918, Space telescopes (1547, 1410, 918, 1547, Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics, Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics},
year = 2019,
month = oct,
volume = {244},
number = {2},
eid = {32},
pages = {32},
doi = {10.3847/1538-4365/ab4132},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {1909.00446},
primaryClass = {astro-ph.IM},
adsurl = {https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2019ApJS..244...32P},
adsnote = {Provided by the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System}
}
This project was made possible by the funding provided by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office of Hungary, funding granted under project 2018-2.1.7-UK_GYAK-2019-00009 and by the Lendület Program of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, project No LP2018-7.