SnapDump is a software for pharo to create and manage runtime snapshots. When developing software in pharo and an exception occurs we get a debugger window openend. This is not possible if the application is deployed in a server environment. Usually activity of a server is written in logfiles but logfiles are a very poor way of getting error feedback from your application. In pharo we can snapshot the state of the application when an exception occurs. This snapshot can be serialized using the fuel graph serializer and uploaded to a server. By uploading the snapshot to a server we can use SnapDump in a distributed scenario where multiple servers give feedback.
- SnapDump server: a SnapDump image that receive and store snapshots. It provides the API to manage snapshot.
- SnapDump handler: a SnapDump image that reports snapshots to a SnapDump server. It uses the API
- SnapDump client: a SnapDump image used to explore reported snapshots. It uses the API
SnapDump is available as docker application for easy deployment. Let's pull a stable version of the SnapDump server (check DockerHub to be up to date):
$ docker pull zweidenker/snap-dump:0.7.3
To keep the snapshots on server restart we need to create a volume where snapshots can be stored. You do this by invoking:
$ docker volume create SnapDump
SnapDump uses internally the port 5555 for the server. This can be mapped to a local port on the host by specifying on the docker commandline. To start the server with that port and the former created volume invoke:
$ docker run -p 8888:5555 -v SnapDump:/snapshots zweidenker/snap-dump:0.7.3
Now our SnapDump server is up and running, we would like to first: report exceptions from a SnapDump handler image , and second: retrieve our reported exceptions on a SnapDump client image.
As a use case, the SnapDump handler image can be the server side image of your application while the SnapDump client image would be your developer image.
To download a pharo image from command line you can use:
$ curl get.pharo.org/64/70+vm | bash
$ ./pharo-ui Pharo.image
To install SnapDump open a playground and execute:
Metacello new
repository: 'github://zweidenker/SnapDump:0.7.3';
baseline: #SnapDump;
load
To configure Snapdump on the handler image execute:
SnapDump hackUIManager; beHandler.
SnapDump uri: 'http://localhost:8888/api'.
SnapDump current projectName: 'projectname1' versionString: '0.7.3'.
This could be executed systematically when the image is deployed and starts.
Then to report an exception to our SnapDump server, use #SnapDump>>handleException: in the likes of:
SnapDump handleException: SDSnapshot dummyContextHere we are using a tiny sample context object for the purpose of testing SnapDump. Usually, one would catch a concrete Error object and report it using #handleException:
On the client image you want to see the exceptions previously reported. To configure and open the UI client execute:
"configure the SnapDump client to access the docker container"
SnapDump beOfType: #client.
SnapDump uri: 'http://localhost:8888/api'.
"open the ui"
SnapDump ui
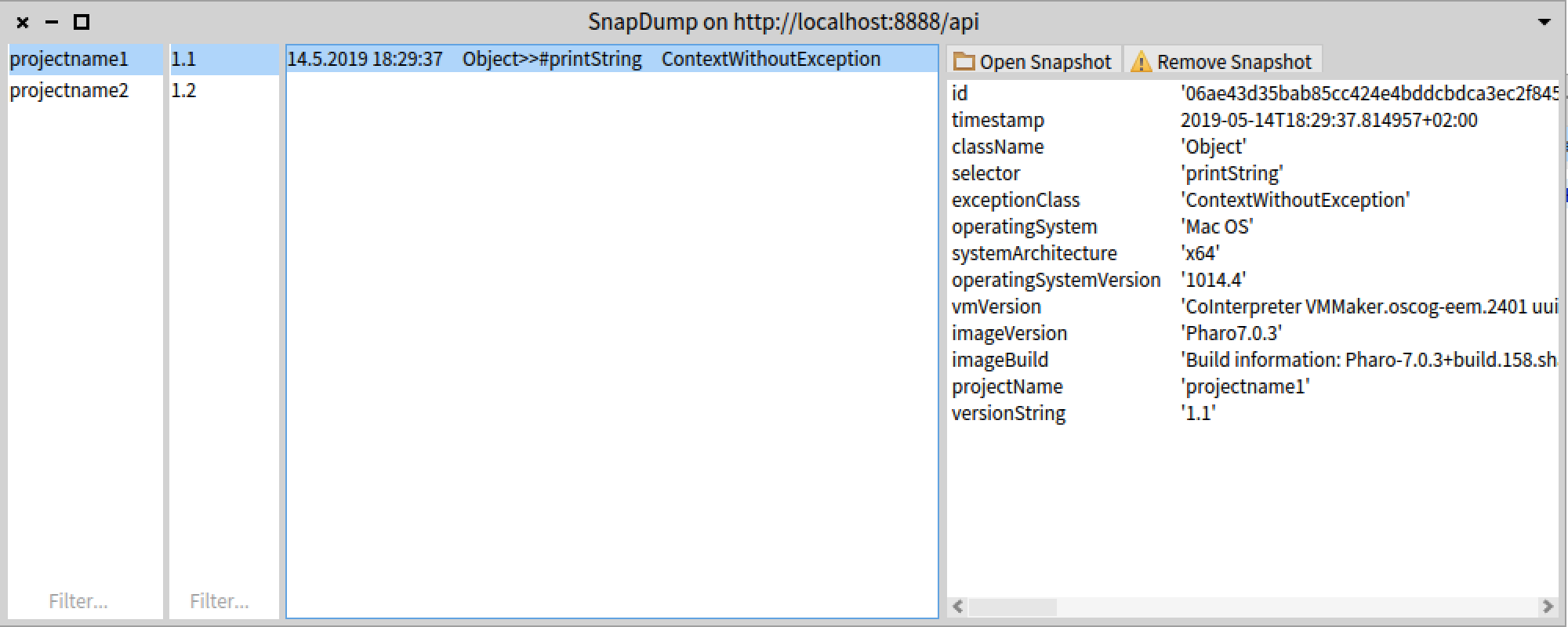
You should see this:
Selecting a snapshot gives detailled information about the snapshot. Pressing the "Open Snapshot" button will open a debugger with that snapshot.