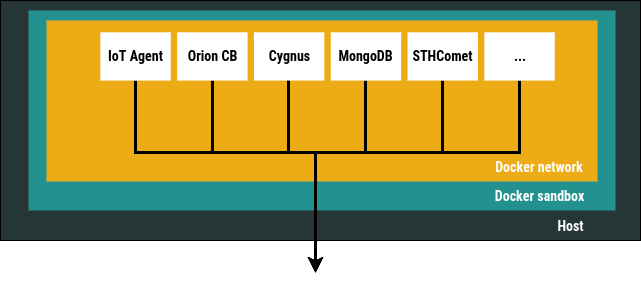
This repository contains a easy way to deploy the FIWARE IoT Stack through docker compose
All the services share the subnet and will be reachable through the dns namespaces provided by docker.
Postman collections covering the main functionalities of each of the services composing the architecture is provided. There are services not offering a API to interact with or providing a user interface, for this reasons the postman collection do not cover all the services deployed.
- docker
- docker-compose
All the services in the architecture are deployed using a docker-compose file therefore the configuration options are explicitly declared in this file. For services with complex configuration a brief extra description is provided.
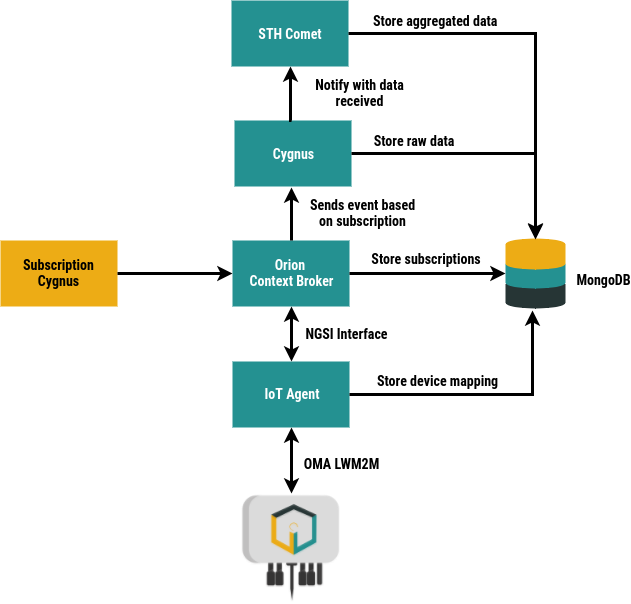
In order to be able to map the OMA LWM2M information model to OMA NGSI entities, atributes and metadata a configuration file is created reflecting the correspondence. config.js in the docker-compose/ directory contains two blocks:
- LwM2M server configuration, specifying aspects like server port, content-format used or the log level of the service.
- NGSI configuration, where information about the http server, the storage and the mapping between the protocols are specified. On the other hand, a dynamic configuration can be carried out using the service API. The postman collection of this service provides a skeleton template.
More information about the component can be found in the LWM2M IoT Agent Guide.
agent.conf In order to configure the channels and databases in which the information will persist,
it is necessary to configure the agent.conf file in the docker-compose/ directory.
This file will be loaded into the docker container as a configuration file.
An example of the file that is loaded by default can be found in this url.
In the previous example we can see how to initialize each of the different connectors to databases.
To simplify the debug better add only the necessary ones.
Orion-Cygnus Communication In order to get the information that reaches Orion to be persistent, it is necessary to create subscriptions on Orion by setting Cygnus as the url of the callback. An example of the subscription to create can be found in the postman collection within the main directory.
More information about the component can be found in the Cygnus Guide.
These three components work jointly to accomplish a visual representation of the information in Orion Context Broker. QuantumLeap is a library that receives Orion information through subcriptions and stores the information in a Crate database. Last, the grafana container launchs a web services with user interface in which the Crate database deployed can be configured as data source. A more detailed guide of this services interaction can be found in the use-cases/ directory.
Perseo CEP is a Complex Event Processing (CEP) module. In this module, Perseo-core is the back-end of Perseo CEP, the rule-engine. It checks incoming events and, if any action must be done, it call to Perseo-fe through a POST request. Perseo-fe refresh the set of Perseo-core rule periodically. When Perseo-core send an action to Perseo-fe, it is responsible of send an action vía SMS, e-mail or HTTP. A more detailed guide of this services interaction can be found in the use-cases/ directory. docker-compose.yml In order for Perseo CEP can send a notification, it must have configured the following servers: SMPP, SMTP and HTTP in docker-compose.yml file contained in the docker-compose/ directory. The environment variables available for Perseo configuration can be foun in this url.
The architecture building and execution must contains using docker-compose must contains a previous step, the IoT Agent container building. This is due to the LWM2M IoT Agent madurity state. Currently some modifications in its code are needed and, for this reason, the modified source code is provided to ensure the interopeability between devices and Orion.
Within the IoT Agent folder execute:
$ docker build -t "iotagent:latest" $(pwd)
In order for the iotagent to receive its configuration, a config.js file must exist in the docker-compose directory. This directory will include the information that must be mapped between the devices and the orion.
Launch infrastructure:
$ docker-compose up
Launch infrastructure in background:
$ docker-compose up -d
Stop infrastructure:
$ docker-compose down
The docker-compose service description do not use version tag in the majority of the services. That implies the use of the service last version at the time of perform the pull. There are some exceptions like the MongoDB version or the IoT Agent that must be build in the host machine.
- Add FIWARE security stack
- Create different docker-composes adapting the components to the user case required.
- Change diagrams and add perseo documentation
From HOP Ubiquitous we are pretty interested in the extension of the services ready to be deployed. If you have experience with any other FIWARE component do not hesitate to contact us.
- Currently a IoT Agent memory issue has been discovered. The error implies the service stop and for this reason a restart condition is provided in the docker-compose file.