- Binary Storage is a write once read many data structure stored on the hard drive. It should provide persistent storage for arbitrary binary content (stream of bytes).
- When adding new data to the storage client provides a string key that will be associated with this data. Once added to the storage the data cannot be modified through storage API. Storage should be able to identify corruption and unauthorized modification of the data.
- After data has been successfully added to the storage client could request it for reading by key and it should be returned as a stream of bytes.
- The storage should be thread-safe and should support multi-threaded addition of new data and reading of existing data.
- Logical organization of the Binary Storage is presented on the picture below:
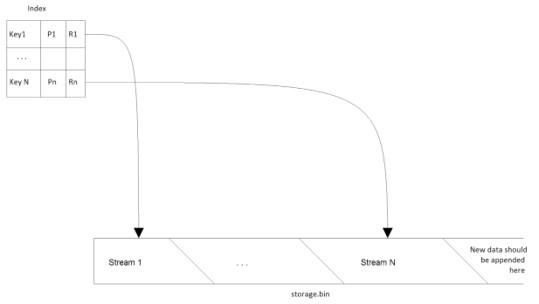
It consists of two logical parts Index and Storage File.
- Storage File is a plain file on the disk (storage.bin) where all binary streams are stored. New data should be appended to the end of the storage file. To save disk space some streams of data might be stored in a compressed form in the Storage File.
- Index is a persistent data structure that is used to associate keys (Ki) with streams by means of references (Ri). The reference is simply a pair of byte offset within the Storage File and size of data also in bytes. All information (Pi) required for a normal operation of the Binary Storage should also be stored in the Index. (Pi) can be hash value of the content, CRC code or a combination of any other properties.
The task is to implement the Binary Storage that satisfies all requirements listed below and passes acceptance criteria.
The solution should be accompanied with a short description and performance measurements.
If any optional requirement is implemented, it should be mentioned in the description.
Limitations, important design decisions and usage of 3rd party components should be described.
For 3GB data, with 25030 files, extracted from RandomData2.7z and 12 concurrent threads, here are the results:
| Version | Time | Memory |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | ||
| 2.0 | ||
| 3.0 | ||
| 4.0 | ||
| 5.0 |
Notes: In case the tests don't run on VS 2017, please disable the "For improved performance..." checkbox in VS (Tools > Options > Test > General)
| Id | Description |
|---|---|
| #1 | The solution should be implemented in C# language using .NET 4 or higher in Visual Studio 2015 or higher. Use of 3rd party libraries should be minimal and limited to open source public libraries. All sources should be provided. Solution should be standalone and should not require any additional software installed on the host machine like MS SQL Server, MS Message Queue, etc. |
| #2.1 | IBinaryStorage interface should be implemented in a class called BinaryStorage. See attached Visual Studio solution. |
| #2.2 | In the attached solution, TestApp project should not be modified. It will be used to test the code against the large set of files. |
| #3 | The solution can use as much memory as the host system provides. But it should work on the systems with 1GB of RAM and should not fail with OutOfMemory exceptions. |
| #4 | It should be possible to configure the maximum amount of hard disk space that can be allocated for Storage File. |
| #5 | Index structure should have compact representation on the disk and in the memory. It should support arbitrary amount of records and might keep frequently used records in the memory to achieve the best performance during lookups for information. |
| #6 | It should be possible to add a new data to the Binary Storage by providing a string key, an instance that implements stream and optional storage parameters (see IBinaryStorage). Optional storage parameters: • Hash of the data (MD5). If provided implementation should hash input stream while saving and verify hash match. If hashes don't match the data should not be added to binary storage and exception should be thrown. • Compression flag. If this flag is present, the data is already compressed and therefore there is no benefit of compressing it again. • Length. If present indicates the length of the input stream. When storage file is full or disk is full a proper exception should be thrown during attempt to add new data. If data with the same key is already present in the storage a proper exception should be thrown. |
| #7 | Adding data to the Binary Storage should be transactional. If any error occurs during the addition, changes should be rolled back (records removed form Index, etc).After Add method returns, the data should be saved to the disk and ready for consumption. |
| #8 | It should be possible to retrieve binary data as stream from the Binary Storage by providing a key. The data retrieved from the storage should be exactly the same as the data previously added to the storage for persistence.If stream was compressed during persistence (see also requirement #102) it should be transparently decompressed prior to sending it to the client. It there is no data for a given key a proper exception should be thrown.If the Binary Storage is in the process of persisting data for a given key, the read operation should wait until persisting process complete and then return data on success or exception otherwise. |
| #9 | The Binary Storage should cache frequently accessed data in the main memory to minimize the number of read requests to hard drive. |
| #10 | Adding and reading data from the Binary Storage should be thread-safe and multi-threaded. Thread-safe means that many threads might try to add data to the storage at the same time. Multi-threaded means that adding data distributed among 2 or more threads should be generally faster than adding the same data using only one thread. |
| #11 | It should be possible to check if a given key is present in the Index. |
| Id | Description |
|---|---|
| #101 | Duplicate binary data should be stored only once in the Storage File. Hash value should be used to check for duplicates. |
| #102 | Storage should compress an input stream during persistence (if it is not already compressed, see #6) to save disk space. However it might not be reasonable to compress a small stream. It should be possible to configure compression based on stream length (compress all streams with length greater than specified threshold).It might be reasonable to store hashes of compressed and raw data to support de-duplication (#101). |
| #103 | It should be possible to configure the maximum amount of hard disk space that can be allocated for storing Index. |
The test application will be used to run a number of tests against provided solution. Therefore it is very important to implement API exactly as described in this document.
The solution will be judged based on the outcome from the test as well as the source code review and supporting materials (description of the solution).
The decision will be made based on the following criteria:
- Conformance to API, requirements
- Code and design quality
- Performance
- Support for concurrency
- RAM consumed (less for the same performance is better)
- HDD space consumed for persisting data (less is better)