- Ubuntu or Windows
- Python 3.9.5
- matplotlib
- ImagickMagic
- FFMpeg
As Introduction to Algorithms introduces, Bubble Sort is a popular, but inefficient, sorting algorithm. It works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements that are out of order.
BUBBLE-SORT(A)
// A[1..n]
1 for i = 1 to n - 1
2 for j = n downto i + 1
3 if A[j] < A[j - 1]
4 exchange A[j] with A[j - 1]
Download src/visual_bubble_sort.py and run it in Linux. You will see how Bubble Sort works.
Run the command python visual_bubble_sort.py -n 50, you will get the animation as follow.
If you want to save the animation into *.gif file, please run python visual_bubble_sort.py -n 50 -o outputfile. Then, you will get outputfile.gif.
Insertion Sort is an efficient algorithm for sorting a small number of elements. It separate a sequence as sorted part and unsorted one. Get an element from unsorted sequence and insert the element into the correct position in the sorted part. Do not stop until there is no element in unsorted part.
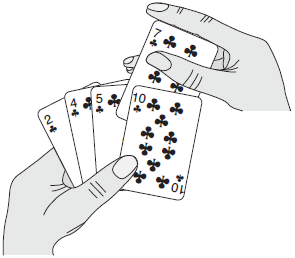
Introduction to Algorithms gives an excellent example to explain this, Insertion sort works the way many people sort a hand of playing cards. We start with an empty left hand and the cards face down on the table. We then remove one card at a time from the table and insert it into the correct position in the left hand. To find the correct position for a card, we compare it with each of the cards already in the hand, from right to left. At all times, the cards held in the left hand are sorted, and these cards were originally the top cards of the pile on the table.
Figure is taken from Introduction to Algorithms (Page 17 Figure 2.1).
INSERTION-SORT(A)
// A[1..n]
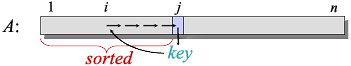
1 for j = 2 to n
2 key = A[j]
3 // Insert A[j] into the sorted sequence A[1..j - 1].
4 i = j - 1
5 while i > 0 and A[i] > key
6 A[i + 1] = A[i]
7 i = i - 1
8 A[i + 1] = key
Download src/visual_insertion_sort.py and run it in Linux. You will see how Insertion Sort works.
Run the command python visual_insertion_sort.py -n 50, you will get the animation as follow.
Run python visual_insertion_sort.py -n 50 -o outputfile to save the animation into a output.gif file.
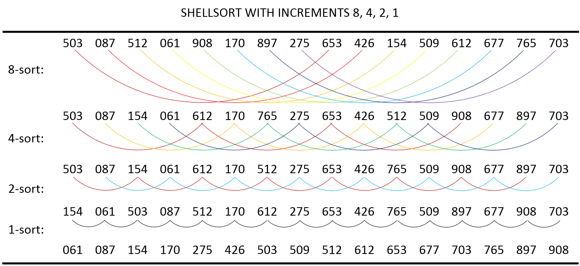
Shell Sort was proposed in 1959 by Donald L. Shell, which uses Insertion Sort on periodic subsequences of the input to produce a faster sorting algorithm.
This figure is a duplicate of a table from The Art of Computer Programming: Volume 3 (page 84 Table 3).
Shell Sort is also known as the "diminishing increment sort". It uses Insertion Sort on the large interval of elements to sort. Then the interval of sorting keeps on decreasing in a sequence until the interval reaches 1. These intervals are known as gap sequence (increment sequence). Shell’s original gap sequence: N/2, N/4, …, 1 (repeatedly divide by 2), but any sequence can be use, so long as the last gap equals 1. The Art of Computer Programming: Volume 3 (page 85) made a detailed description for how to choose a good sequence of increments for use in Shell Sort.
SHELL-SORT(A)
// A[1..n]
1 gap = n / 2
2 while gap >= 1
3 for i = 1 to gap
4 for j = i + gap to n step = gap // Insertion Sort
5 key = A[j]
6 k = j - gap
7 while k > 0 and A[k] > key
8 A[k + gap] = A[k]
9 k = k - gap
10 A[k + gap] = key
11 gap = gap / 2
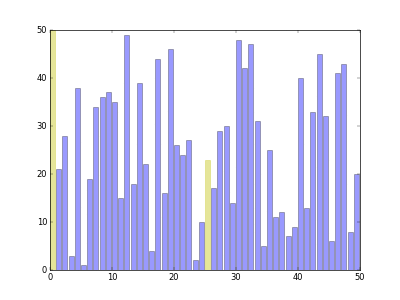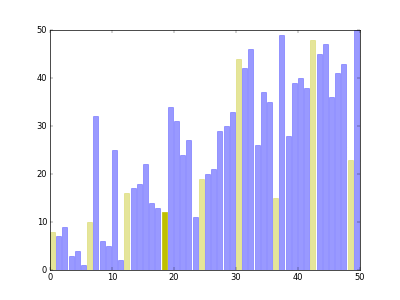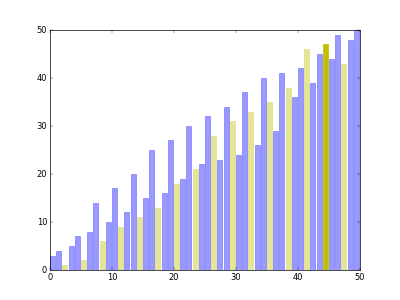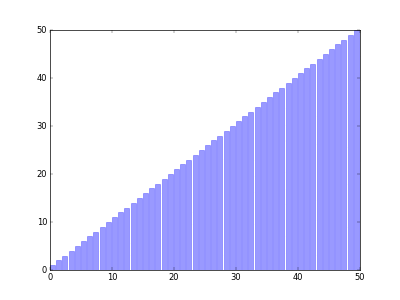
Download src/visual_shell_sort.py and run it in Linux. You will see how Shell Sort works.
Run the command python visual_shell_sort.py -n 50, you will get the animation as follow.
Run python visual_shell_sort.py -n 50 -o outputfile to save the animation into a output.gif file.
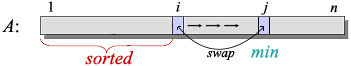
Selection Sort is similar to Insertion Sort. They both separate a sequence as two sequences, sorted one and unsorted one. Selection Sort selects a smallest element from unsorted sequence and exchange the smallest element with the element just behind sorted sequence, while Insertion Sort get the first element from unsorted sequence and insert it into the correct position of sorted sequence.
SELECTION-SORT(A)
// A[1..n]
1 for i = 1 to n - 1
2 indexOfMinElement = i
3 for j = i + 1 to n
4 if A[j] < A[indexOfMinElement]
5 indexOfMinElement = j
6 exchange A[i] with A[indexOfMinElement]
Download src/visual_selection_sort.py and run it in Linux. You will see how Selection Sort works.
Run the command python visual_selection_sort.py -n 50, you will get the animation as follow.
Run python visual_selection_sort.py -n 50 -o outputfile to save the animation into a output.gif file.
Merge Sort is an effective algorithm which builds on merging operation. It closely follows the divide-and-conquer paradigm (Check Introduction to Algorithms page 30 2.3.1 to know The divide-and-conquer approach).
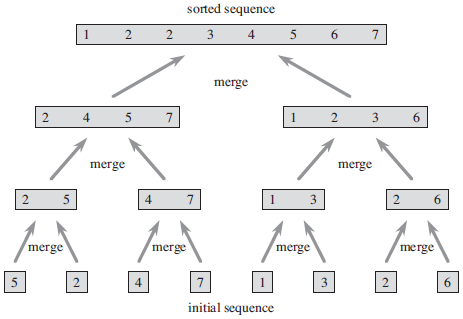
First divide an array A into two new subarrays L and R, then separately divide L and R into another two new subarrays (four subarrays total), and so on. By recursively calling MERGE-SORT(A, p, r) itself, the n-element sequence can be divided into n subsequences of 1 element each. Then call MERGE(A, p, q, r) to combine n subsequences into a sorted sequence.
Figure is taken from Introduction to Algorithms (Page 35 Figure 2.4). The operation of merge sort on the array A = [5, 2, 4, 7, 1, 3, 2, 6]. The length of the sorted sequences being merged increase as the algorithm progresses from bottom to top.
The procedure MERGE-SORT(A, p, r) sorts the elements in the subarray A[p .. r]. If p >= r, the subarray has at most one element and is therefore already sorted. Otherwise, the divide step simply computes an index q that partitions A[p .. r] into two subarrays: A[p .. q], containing n/2 elements, and A[q + 1 .. r], containing n/2 or n/2 + 1 elements.
MERGE-SORT(A, p, r)
1 if p < r
2 q = (p + r) / 2
3 MERGE-SORT(A, p, q)
4 MERGE-SORT(A, q + 1, r)
5 MERGE(A, p, q, r)
In Merge Sort algorithm, the key subroutine is MERGE(A, p, q, r). The figure below shows how to merge two sorted subarrays L[2, 4, 5, 7] and R[1, 2, 3, 6] to a sorted array A.
Figure is taken from Introduction to Algorithms (Page 32 Figure 2.3 and Page 33 Figure 2.3, continued).
A is an array and p, q, and r are indices into the array such that p <= q < r. The procedure assumes that the subarrays A[p .. q] and A[q + 1 .. r] are in sorted order. It merges them to form a single sorted subarray that replaces the current subarray A[p .. r].
Here we add ∞ behind both L[1 .. m] and R[1 .. n] subarrays as a sentinel value, so that whenever an element with ∞ is exposed, it cannot be the smaller element unless both subarrays have their sentinel values exposed. But once that happens, all the nonsentinel elements have already been placed onto the array A[p .. r]. And we can stop the procedure at that time.
MERGE(A, p, q, r)
1 m = q - p + 1
2 n = r - q
3 let L[1..m + 1] and R[1..n + 1] be new arrays
4 for i = 1 to m
5 L[i] = A[p + i - 1]
6 for j = 1 to n
7 R[j] = A[q + j]
8 L[m + 1] = ∞
9 R[n + 1] = ∞
10 i = 1
11 j = 1
12 for k = p to r
13 if L[i] <= R[j]
14 A[k] = L[i]
15 i = i + 1
16 else A[k] = R[j]
17 j = j + 1
There is not ∞ in programming language, such as Python, C and so on. Therefore, we rewrite the MERGE procedure so that it does not use sentinels, instead stopping once either array L or R has had all its elements copied back to A and then copying the remainder of the other array back into A.
MERGE(A, p, q, r)
// Not use sentinel value
1 m = q - p + 1
2 n = r - q
3 let L[1..m] and R[1..n] be new arrays
4 i = 1
5 j = 1
6 k = p
7 while i <= m and j <= n
8 if L[i] <= R[j]
9 A[k] = L[i]
10 i = i + 1
11 k = k + 1
12 else A[k] = R[j]
13 j = j + 1
14 k = k + 1
15 while i <= m
16 A[k] = L[i]
17 i = i + 1
18 k = k + 1
19 while j <= n
20 A[k] = R[j]
21 j = j + 1
22 k = k + 1
Here is an example to merge two sorted subarrays L[2, 3, 4, 5] and R[1, 2, 6, 7] to a sorted array A without using a sentinel value.
In (g), array L has all its elements copied back to A. Therefore, in (h), copy the remainder (6 and 7) of array R back into A without comparison with array L.
Download src/visual_merge_sort.py and run it in Linux. You will see how Merge Sort works.
Run the command python visual_merge_sort.py -n 50, you will get the animation as follow.
Run python visual_merge_sort.py -n 50 -o outputfile to save the animation into a output.mp4 file. Then you can convert it into output.gif file by ffmpeg -i output.mp4 output.gif.
Quick Sort was proposed by C.A.R. Hoare in 1962. It, like Merge Sort, applies the divide-and-conquer paradigm.
Quick Sort an n-element array:
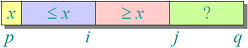
- Divide: Partition the array into two subarrays around a pivot x such that elements in lower subarray ≤ x ≤ elements in upper subarray.

- Conquer: Recursively sort the two subarrays.
- Combine: Trivial.
Introduction to Algorithms Page 171 gives the implementation of quicksort:
QUICK-SORT(A, p, r)
1 if p < r
2 q = PARTITION(A, p, r)
3 QUICK-SORT(A, p, q - 1)
4 QUICK-SORT(A, q + 1, r)
The key to the algorithm is the PARTITION procedure, which rearranges the subarray A[p .. q] in place.
PARTITION(A, p, q)
1 x = A[p]
2 i = p
3 for j = p + 1 to q
4 if A[j] <= x
5 i = i + 1
6 exchange A[i] with A[j]
7 exchange A[i] with A[p]
8 return i
Invariant:
Example of partitioning:
Download src/visual_quick_sort.py and run it in Linux. You will see how Quick Sort works.
Run the command python visual_quick_sort.py -n 50, you will get the animation as follow.
Run python visual_quick_sort.py -n 50 -o outputfile to save the animation into a output.gif file.