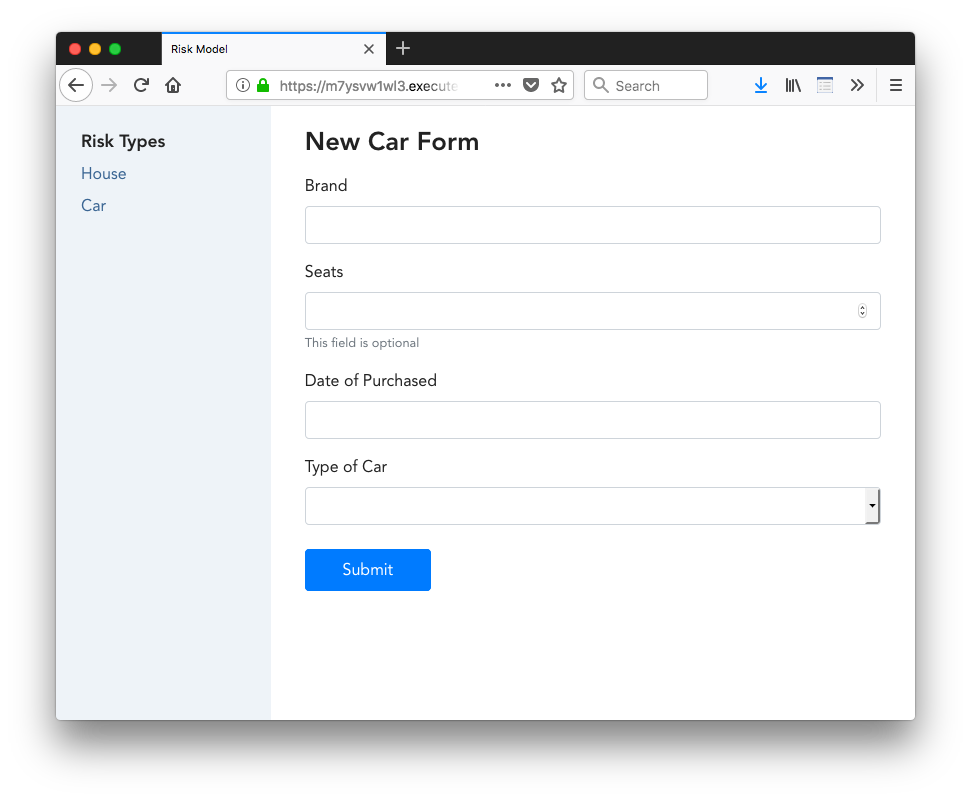
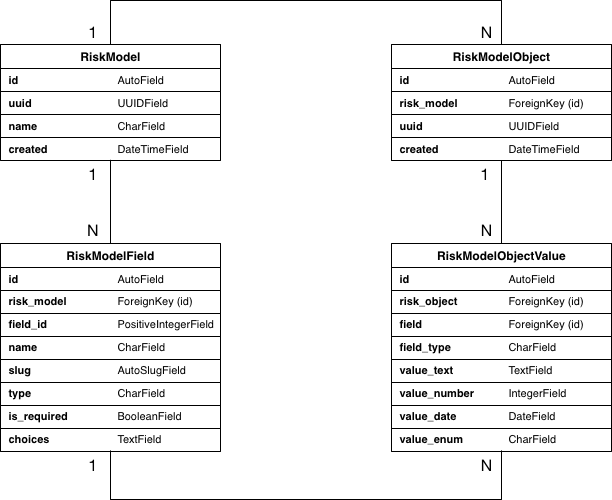
This web application project was created for test assignment
- Django
- SQLite (The reason I chose this over PostgreSQL or MySQL is because this project is database-agnostic and performance or compatibility is not an issue here)
- VueJS
- Webpack
- Docker (Used in development only)
- AWS Lambda using Zappa
-
RiskModel is something that can be insured e.g. House, Automobiles, Health. In each model, apart from
namethat user will specify,iduuidandcreatedwill be auto-generated. -
RiskModelField is a property definition of RiskModel e.g. purchased date, person age, market value.
-
field_idis auto-generated in a sequence starting from 1 for each RiskModel object (it will be unique if combined withrisk_model). It's mainly used as a reference to existing fields in REST API (as realidshould not be exposed) -
nameis a name of property -
slugis a url-friendly text generated fromname. It will be used in REST API to set properties of RiskModelObject. -
typeis a data type of property. There're 4 available types in this project. text, number, date, and enum. -
is_requiredis a flag to check if this property is mandatory. -
choicesis a choice of enum property type. Using comma-separated to keep data.
-
-
RiskModelObject is an entry of RiskModel e.g. car insurance number 1234567, health insurance of John Snow.
-
RiskModelObjectValue is a property value of RiskModelObject.
-
field_typeis a cached value of itsfield.type. Since we always need to check field type before setting or getting a value, keep cached value offield_typehere will cut down on database joins. -
value_text,value_number,value_date,value_enumis where the value of property will be kept in one of these columns based on data type. I separate each data type into its own column because I want to be able to use native data type for query.
-
All API send and received application/json data
GET /api/models/
Parameters
limitLimit number of results. Default is 20. If you want to get all data in one request, set limit to 0.
POST /api/models/
Example request body in application/json format
{
"name": "Car",
"fields": [
{
"name": "Brand",
"type": "text"
},
{
"name": "Seats",
"type": "number"
},
{
"name": "Date of Purchased",
"type": "date",
"is_required": true
},
{
"name": "Type of Car",
"type": "enum",
"choices": "Sedan,SUV,Eco",
"is_required": true
},
{
"name": "Paint Color",
"type": "text"
}
]
}
In each field that submitted, field_id and slug will be auto-generated. is_required is default to False, but user can override it.
If field type is enum, you must provide choices data in comma-separated text format.
GET /api/models/{model uuid}/
PUT /api/models/{model uuid}/
Example request body in application/json format
{
"name": "Automobiles",
"fields": [
{
"field_id": 1,
"slug": "manufacturer",
"name": "Manufacturer",
"type": "text",
"is_required": true
},
{
"field_id": 2,
"slug": "seats",
"name": "Seats",
"type": "number"
"is_required": false
},
{
"field_id": 3,
"slug": "date-of-purchased",
"name": "Date of Purchased",
"type": "date",
"is_required": true
},
{
"field_id": 4,
"slug": "type-of-car",
"name": "Type of Car",
"type": "enum",
"choices": "Sedan,SUV,Eco",
"is_required": true
},
{
"name": "Owner",
"type": "text",
"is_required": true
}
]
}
From above example,
- I will change field name from
BrandtoManufacturerand make it mandatory. - I will add a new field
Owner. - I will delete a field
Paint Coloras I haven't include this field to the request.
Note on update behavior
- Field that has
field_idwill be updated with its existing field. - Field that doesn't have
field_idwill be considered as a new field. - Important! Existing field that doesn't appear in the request will be deleted. User should always include field data to an update request, even that field doesn't have a change.
DELETE /api/models/{model uuid}/
GET /api/models/{model uuid}/objects/
Parameters
limitLimit number of results. Default is 20. If you want to get all data in one request, set limit to 0.
POST /api/models/{model uuid}/objects/
Example request body in application/json format
{
"manufacturer": "Toyota",
"seats": 4,
"date-of-purchased": "2015-04-02",
"type-of-car": "Sedan",
"owner": "Panu Tangchalermkul"
}
Use field's slug as a key to set object's values.
GET /api/models/objects/{object uuid}/
PUT /api/models/objects/{object uuid}/
Example request body in application/json format
{
"manufacturer": "Ford",
"seats": 6,
"date-of-purchased": "2015-04-02",
"type-of-car": "SUV",
"owner": "Panu Tangchalermkul"
}
DELETE /api/models/objects/{object uuid}/
-
Install Docker
-
Build Docker images
docker-compose -f dev-compose.yml build -
Start Docker containers
docker-compose -f dev-compose.yml up
1.1 Open AWS Console, goto IAM service under Security, Identity & Compliance
1.2 Create a new user & group with following permissions
AWSLambdaFullAccess
IAMFullAccess
AmazonS3FullAccess
AmazonAPIGatewayInvokeFullAccess
AmazonAPIGatewayPushToCloudWatchLogs
AmazonAPIGatewayAdministrator
Also create Inline Policies as following
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1449904348000",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:CreateChangeSet",
"cloudformation:ListStacks",
"cloudformation:UpdateStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DescribeChangeSet",
"cloudformation:ExecuteChangeSet",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackResource"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
I know that above permissions is too broad (e.g. some that end with FullAccess). Let's find some more time to experiment with narrower permission in the future.
1.3 Install AWS CLI and setup credentials on the machine
2.1 Install Python 3
2.2 Install Node and Yarn
3.1 Create a new virtualenv (don't use existing development virtualenv)
3.2 Install Python packages
pip install -r ./requirements/production.txt
3.3 Install Node packages
cd ./client && yarn
3.4 Build VueJS app
cd ./client && yarn run build
4.1 Edit environment file using template from env.example file
`cp env.example .env`
- Generate new DJANGO_SECRET_KEY
- Enter AWS configurations
4.2 Collect static files and upload it to AWS S3
python manage.py collectstatic
4.4 Delete node_modules
rm -rf ./client/node_modules
Note: We should delete node_modules here because later it won't be uploaded by Zappa
4.5 If this is the first time, run
zappa deploy production
If you've already deployed it, run
zappa update
If there's something wrong, use zappa tail to display log on server.
Phew... actually all these steps for deployment should be automated in CI.