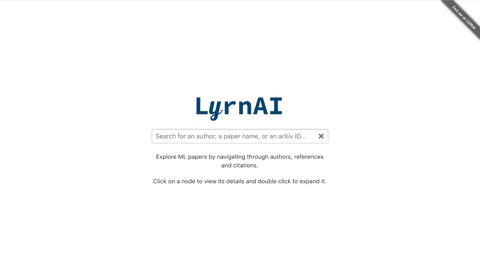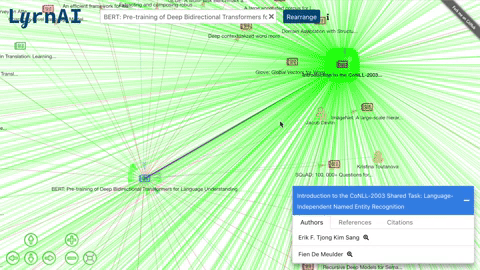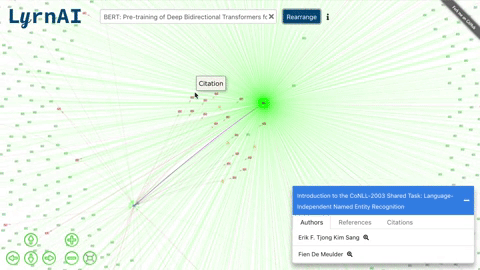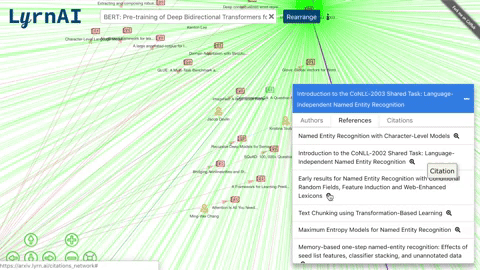
MLG (Machine Learning Graph) is a visual representation of ML researchers and papers, and the connections between them. Each node in the graph (/citations_network) is an author or a paper, and an edge can represent a citation, a reference or a authorship.
Note: There is an old version of the graph (/network) in which edges represent co-authorship of papers, based solely on arXiv.org.
Live demo is available at Lyrn.ai.
MLG allows you to:
- Search for papers or authors.
- Navigate between related papers and authors.
- Click on a node to view its list of papers and double click to expand its connections.
- Re-organize the network after expanding.
The backend is based on arxiv-sanity but with a lot of modifications:
- The papers data is collected from arxiv.org and semanticscholar.org. Everything is stored on MongoDB.
- Rebuilt the Twitter daemon - it now collects tweets from a list of prominent ML accounts, in addition for searching arxiv.org links on Twitter.
The project includes three parts:
- / - arXiv text explorer.
- /citations_network - The new visual network graph explorer.
- /network - The old arXiv visual graph explorer.
Example of the old version:
$ virtualenv env # optional: use virtualenv
$ source env/bin/activate # optional: use virtualenv
$ pip install -r requirements.txtThere is still some legacy code from arxiv-sanity that require some of the packages in the requirement.
- Install and start MongoDB
- Optional - Run
fetch_papers.pyto collect all paper from arXiv. Runfetch_citations_and_references.pyto collect data from semanticScholar.org. - Create
twitter.txtwith your Twitter API credentials (values of consumer key and secret, in separate lines). You can also add accounts to thetwitter_users.jsonfile. - Run
run_background_tasks.pyto start background tasks scheduler. - Run the flask server with
serve.py.
After fetching papers from arXiv you can build the network graph by running the notebook graph_generator.ipynb.
It will overwrite the static/network_data.json.
Note: Calculating the physics of the network (nodes' position) is very slow. The current hack is to run it once (by changing the physics settings in network.js) and store the calculated positions. I tried using networkX to calculate the positions, however, the results weren't pleasing...
If you'd like to run the flask server online (e.g. AWS) run it as python serve.py --prod.
You also want to create a secret_key.txt file and fill it with random text (see top of serve.py).