sshfortress is an open source openssh auditing software, will record sftp transfer records, ssh operation command records, scp transfer records and records with similar script terminal replay.
Most of the fortresses that exist on the market today either do a web interface to connect to the terminal, or a springboard machine to jump again, imagine if you are using a command line tool how to use a web terminal, and how to batch operations using a springboard machine, which is undoubtedly redundant, files can not be transferred to each other and other restrictions, which is why sshfortress appears, it does not change the user's original efficient use of habits.
SSHfortress Code is fully open source, source code from web front-end programming Java + JavaScript language | back-end programming language C .
This description is to introduce how to install the sshfortress system. It has a web management interface, greatfortress, which is implemented in java to visually increase functions such as accounts and assets. The backend sshfortress is a function developed on the basis of openssh. Let's see how to install and configure it.
- Product introduction
- Features
- Notice
- Depend
- Installation
- Source_code_compilation
- Video
- How to use
- Upgrade
The ssh fortress machine integrates various functions such as operation and maintenance identity authentication, account management and control, and system operation audit. Based on the implementation of the protocol Reverse Proxy, the data flow of the SSH, SCP, and SFTP protocols is recorded through Reverse Proxy. Unified operation and maintenance entrances, unified permissions between users and hosting accounts to prevent internal data leakage.

The bastion machine has functions such as operation audit, authority management and control, safety certification, and efficient operation and maintenance.Power group management: Establish authorization management of personnel responsibilities and resource allocation according to personnel, departmental organizations, and resource groups.
- Operational audit
Multi-faceted operation and maintenance personnel's operation behavior is used as the basis for incident traceability and accident analysis.
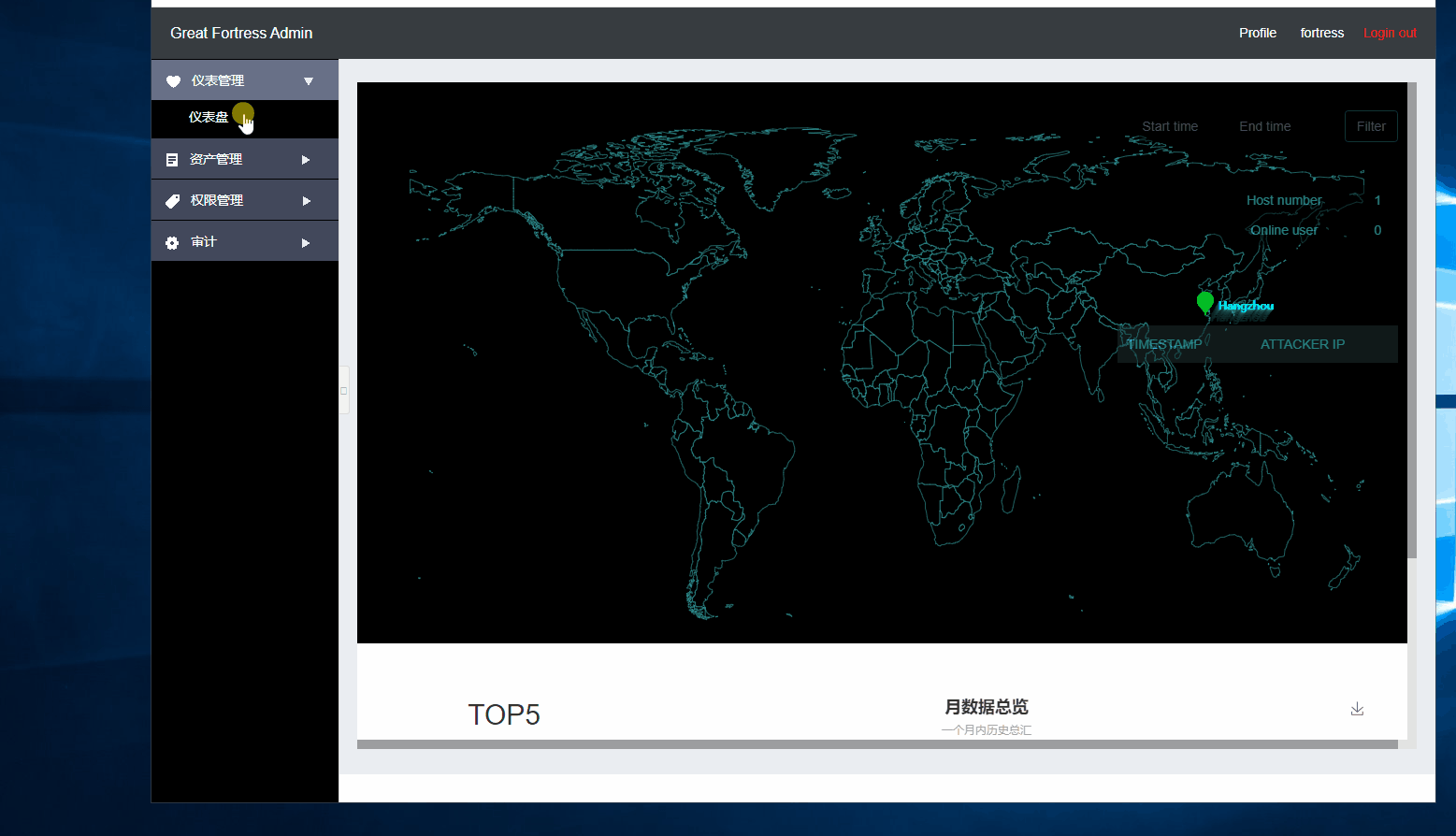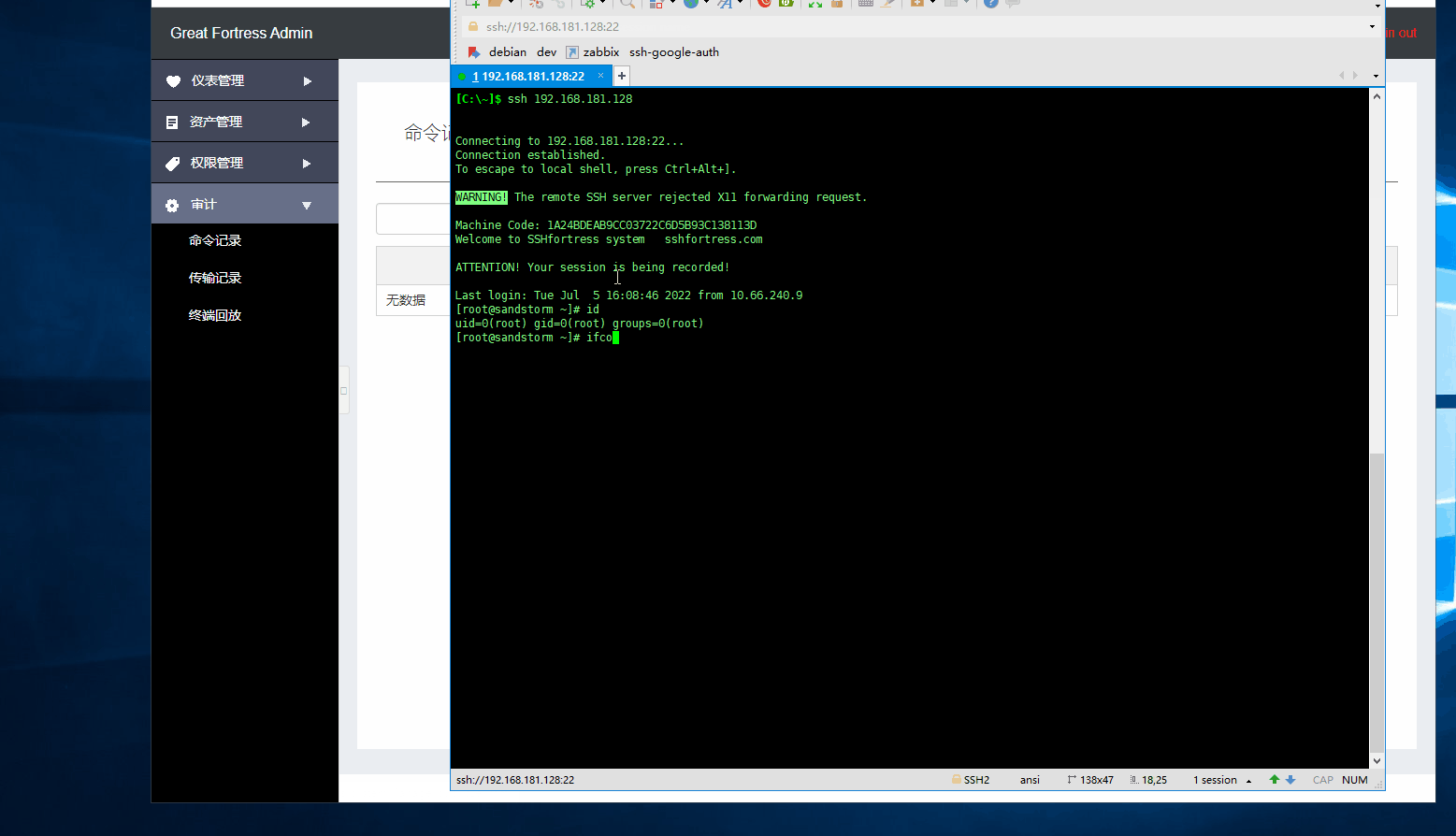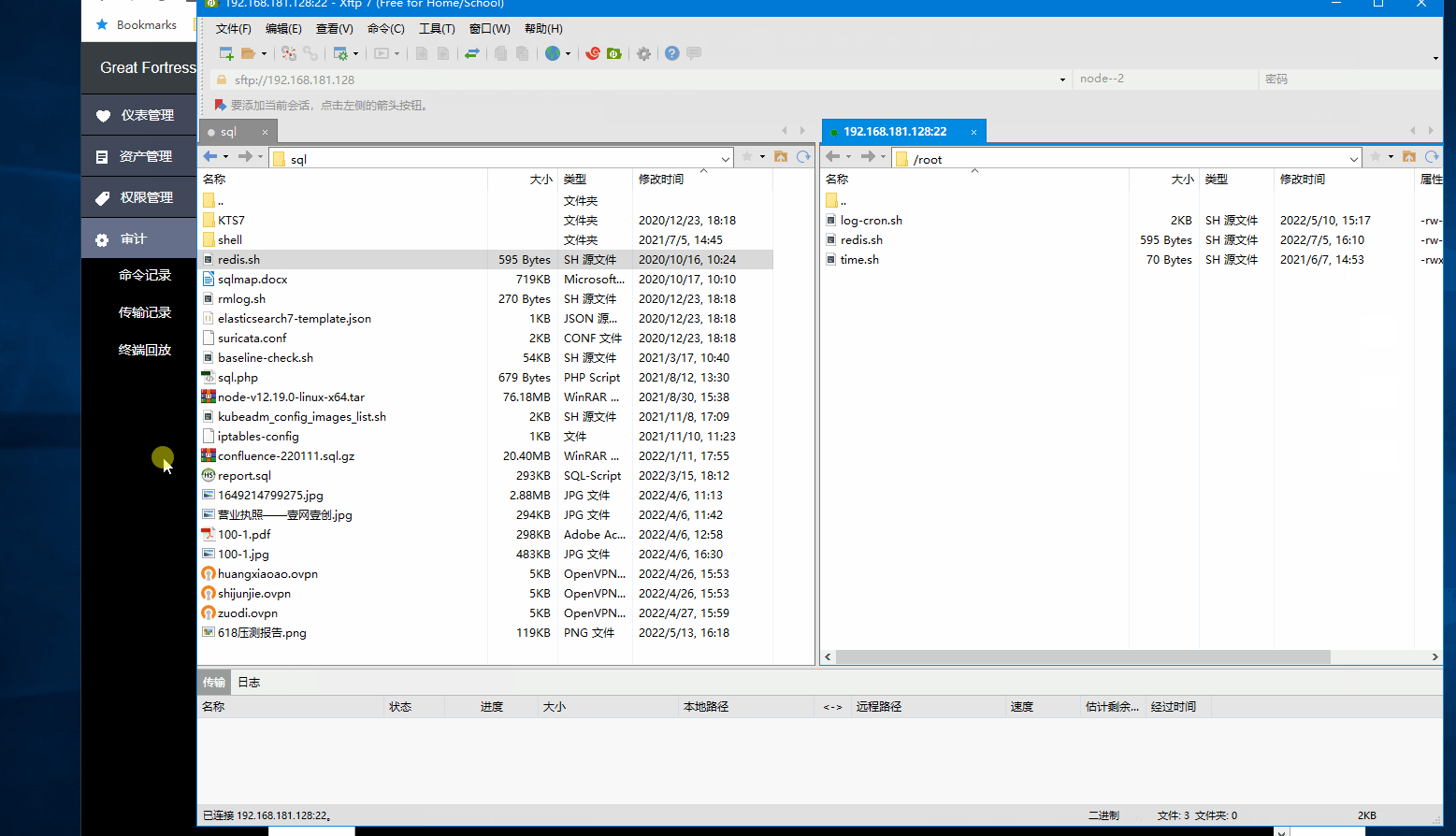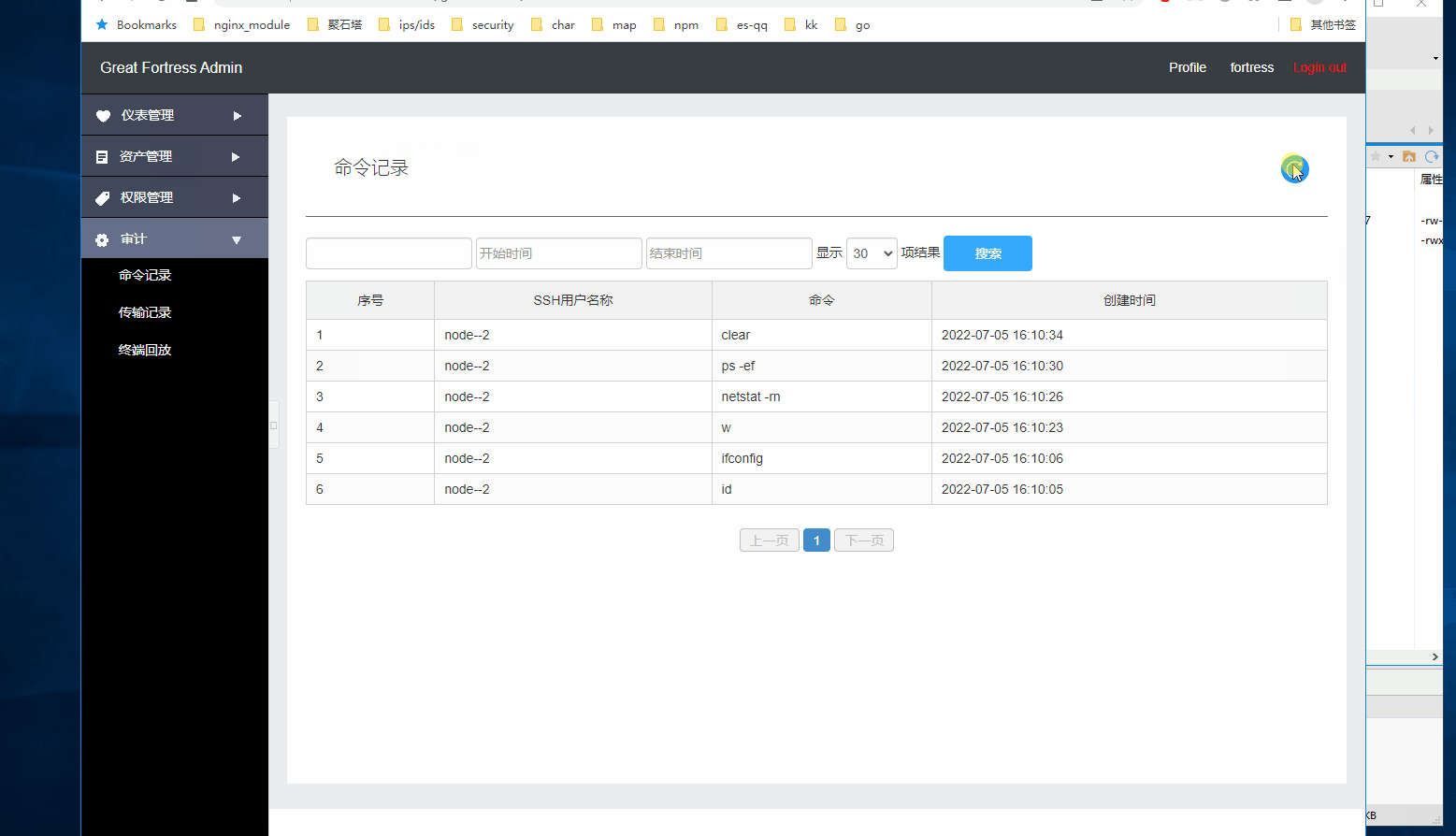
Operation and maintenance operation records: Detailed records of operation errors, malicious operations, and unauthorized operations.
Linux command auditing: Extractable command character auditing.
File transfer audit: Support remote desktop file transfer, SFTP original file audit.
Terminal recording playback: Support terminal recording ssh operation process, fully compatible with the scriptreplay tool that comes with Linux for playback. Playback file storage path /var/log/sshfortress_playback, classified by year, month, and day.
example:
#cd /var/log/sshfortress_playback/2020/03/24
# scriptreplay test-10.13.49.time test-10.13.49.log
If you don't have much space on your hard drive, it's recommended that you only keep it for 30 days, which can be cleaned using crontab
echo "00 00 * * * root find /var/log/sshfortress_playback/ -mtime +30 -exec rm -rf {} \;" >> /etc/crontab
- Authority control
Through account management and authority group management, the division of powers to manage personnel and assets is achieved.
Account management and control: There is only one operation and maintenance account, which solves problems such as shared accounts, temporary accounts, and abuse of permissions.
- Efficient
Native implementation, does not change user usage habits as if no bastion machine was used.
C/S architecture operation and maintenance access: Supports SSH, SCP, SFTP protocols. Multi-operation and maintenance tools: Support PuTTY, SecureCRT, Xshell and other tools.
sshfortress will take over port 22, so before this you need to compile and install another openssh and listen to other ports (other than port 22) so that you can connect remotely https://openbsd.hk/pub/OpenBSD/OpenSSH/portable/
# wget https://openbsd.hk/pub/OpenBSD/OpenSSH/portable/openssh-8.1p1.tar.gz
# tar zxvf openssh-8.1p1.tar.gz
# cd openssh-8.1p1/
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/openssh2233
# make -j4; make install
# sed -i '1i\Port 2233' /usr/local/openssh2233/etc/sshd_config
# sed -i '2i\PermitRootLogin yes' /usr/local/openssh2233/etc/sshd_config
# /usr/local/openssh2233/sbin/sshd
You can create a boot startup item rc-local was loaded before centos7, and then no longer loaded at boot time, now we open it
[root@centos8 tmp]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service
[Unit]
Description=/etc/rc.local
ConditionPathExists=/etc/rc.local
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start
TimeoutSec=0
StandardOutput=tty
RemainAfterExit=yes
SysVStartPriority=99
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable rc-local
# chmod +x /etc/rc.local
# echo "/usr/local/openssh2233/sbin/sshd" >> /etc/rc.local
Friendly reminder centos8 starts to enable nftables instead of iptables. If you are not familiar with the addition of rules, it is best to clear the rules
# nft flush ruleset
- glibc 2.17+
- mysql 5.6+ or MariaDB
- jdk 1.8
- tomcat 8
- sshfortress
sshfortress source code compilation is dependent on several libraries, for convenience I put libfuse3, glib-2.0, libcharset static compilation in the static_lib directory, just compile the mysql, openssl can be completed openssh compilation, of course, if you are afraid to add private goods can also compile their own, you can see how to compile in static_link.sh, of course, you can also download the compiled binary version. You can see how to compile it in static_link.sh, and of course you can download the compiled binary version.
https://github.com/libfuse/libfuse
https://download.gnome.org/sources/glib/2.0/
https://ftp.gnu.org/pub/gnu/libiconv
https://www.openssl.org/source
https://www.mysql.com/downloads/ or https://mariadb.org/
`ssl-fips` build openssl-fips-2.0.16.tar.gz
# ./config ; make; make install
`openssl` build openssl-1.0.1t.tar.gz
# ./config shared -fPIC
# make depend; make -j4; make install
`mysql` There is space below to explain
`openssh` build
# ./configure --sysconfdir=/etc/ssh --sbindir=/usr/sbin --bindir=/usr/bin --with-ssl-dir=/usr/local/ssl
# make; make install
Enter the resource page and download as needed, https://sshfortress.com/downloads/ or https://github.com/sshfortress/sshfortress/releases to download
apache-tomcat-8.5.31.tar.gz 09-Jan-2020 11:21 9M
audit_sec.sql 09-Jan-2020 16:07 10M
greatfortress.tar.gz 10-Jan-2020 09:52 65M
jdk-8u172-linux-x64.tar.gz 09-Jan-2020 11:22 182M
sshfortress-1.6.1.sha256 09-Jan-2020 16:14 155
sshfortress-1.6.1.tar.gz 09-Jan-2020 15:58 10M
# tar zxvf jdk-8u172-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
# ln -s /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_172/ /usr/local/jdk
# echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk" >> /etc/profile
# echo "export JRE_HOME=/usr/local/jdk/jre" >> /etc/profile
# echo "export CLASSPATH=.:\${JAVA_HOME}/lib:\${JRE_HOME}/lib:\${CLASSPATH}" >> /etc/profile
# echo "export PATH=\${JAVA_HOME}/bin:\${JRE_HOME}/bin:/usr/local/mysql/bin:\${PATH}" >> /etc/profile
# source /etc/profile
Database support custom configuration, you can modify the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, the default connection to this It can be configured to other addresses such as rds (tomcat connection pool should also be modified), so you don't need to install mysql.
....
sshfortress_host localhost
sshfortress_user audit
sshfortress_password audit
sshfortress_database audit_sec
sshfortress_port 3306
.....
- option 1: Source compilation
# yum -y install make gcc-c++ cmake bison-devel bison ncurses-devel libgnomeui-devel perl-Module-Install bzip2 libtirpc-devel
# wget https://github.com/sshfortress/sshfortress/releases/download/1.6.1/mysql-5.7.16.tar.gz
# wget https://github.com/sshfortress/sshfortress/releases/download/1.6.1/boost_1_59_0.tar.bz2
# tar jxvf boost_1_59_0.tar.bz2 -C /tmp
# tar zxvf mysql-5.7.16.tar.gz
# groupadd mysql;useradd -r -g mysql -s /bin/false -M mysql
# cd mysql-5.7.16/
# cmake . -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql \
-DINSTALL_DATADIR=/usr/local/mysql/data \
-DSYSCONFDIR=/usr/local/mysql/etc \
-DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8mb4 \
-DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8mb4_general_ci \
-DEXTRA_CHARSETS=all \
-USER=mysql \
-DWITH_MYISAM_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DWITH_ARCHIVE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DWITH_BLACKHOLE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DWITH_MEMORY_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DWITH_BOOST=/tmp/boost_1_59_0
# make -j4; make install
# chown -R mysql.mysql /usr/local/mysql
# cp -f support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
# mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data
# /etc/init.d/mysqld start
# Initial password, which can be seen during initialization <temporary password 'NiBMcstse9!i'>
# mysql -uroot -p'NiBMcstse9!i' --connect-expired-password -e "alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'SSHfortress123@';CREATE USER 'sshfortress'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'SSHfortress123@';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'sshfortress'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'SSHfortress123@' WITH GRANT OPTION MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS 0;flush privileges;"
# mysql -uroot -p'SSHfortress123@' -e "create database audit_sec; use mysql;create user 'audit'@'127.0.0.1' identified by 'audit'; grant all privileges on audit_sec.* to 'audit'@'127.0.0.1';"
# mysql -uroot -p'SSHfortress123@' -e "set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=1; set global explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=1;set global sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION';"
# mysql -uroot -p'SSHfortress123@' audit_sec <audit_sec.sql
To prevent it from failing every restart, write it to the configuration file as follows:
#[root@centos8 local]# cat /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
log_bin_trust_function_creators=on
explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=on
sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
# systemctl enable mysqld
# /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
- Option 2: YUM install , Here take centos8 mysql8.0 as an example
# yum install mysql-server
# echo "skip_ssl" >> /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
# echo "log_bin_trust_function_creators=on" >> /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
# echo "explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=on" >> /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
# echo "sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES" >> /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
# systemctl enable mysqld
# systemctl restart mysqld
# mysql -e "create user audit@'127.0.0.1' identified by 'audit'; grant all privileges on *.* to audit@'127.0.0.1' with grant option;"
# mysql -e "create database audit_sec;"
# mysql audit_sec < audit_sec.sql
- Option 3: APT install , Here take Debian 9.9.0 MariaDB 10.1.41 as an example
# apt-get install mysql-server
# systemctl enable mariadb
# mysql -e "create user audit@'127.0.0.1' identified by 'audit'; grant all privileges on *.* to audit@'127.0.0.1' with grant option;"
# mysql -e "create database audit_sec;"
# mysql audit_sec < audit_sec.sql
# tar zxvf apache-tomcat-8.5.31.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
# ln -s /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.31/ /usr/local/tomcat
# rm -rf /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/*
# tar zxvf greatfortress.tar.gz -C /usr/local/tomcat/webapps
# sed -i 's/192.168.7.3/x.x.x.x/g' /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/greatfortress/common/layui/layui.js
# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/catalina.sh start
# If tomcat doesn't show the CAPTCHA, you can add it to catalina.sh JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.awt.headless=true"
x.x.x.x Is your listening address
http://x.x.x.x:8080/greatfortress
Account: fortress
password hilookhere
After starting tomcat, the first login is a bit slow
# tar zxvf sshfortress-x.x.x.tar.gz
# cd sshfortress-x.x.x
# ./install.sh
# setenforce 0
`If selinux is enabled on the system, you need to disable it`
Login name plus two minus signs plus asset number Example:
ssh name--ID@x.x.x.x
scp ll.jpg name--ID@x.x.x.x:/tmp
sftp name--ID@x.x.x.
https://sshfortress.com/en/video.html

The sshfortress upgrade just needs to replace the files with changes, it doesn't need to upgrade all of them, it usually just needs to upgrade the sshd,ssh files and restart the service afterwards. /etc/init.d/sshd.init restart
If you have suggestions for improving sshfortress or joining us in doing something interesting, you can submit a PR and ISSUE to sshfortress