Simplify Flutter pagination with Super Paging — A super package providing efficient data management, in-memory caching, configurable widgets and built-in error handling for a seamless pagination experience.
Live Demo: https://xsahil03x.github.io/super_paging
Show some ❤️ and star the repo to support the project
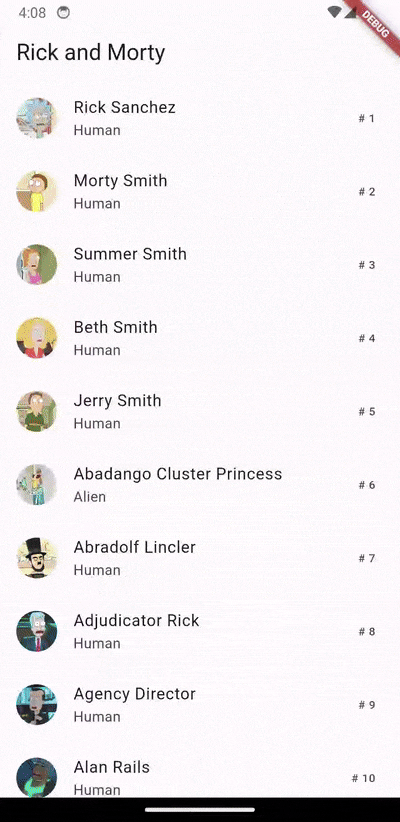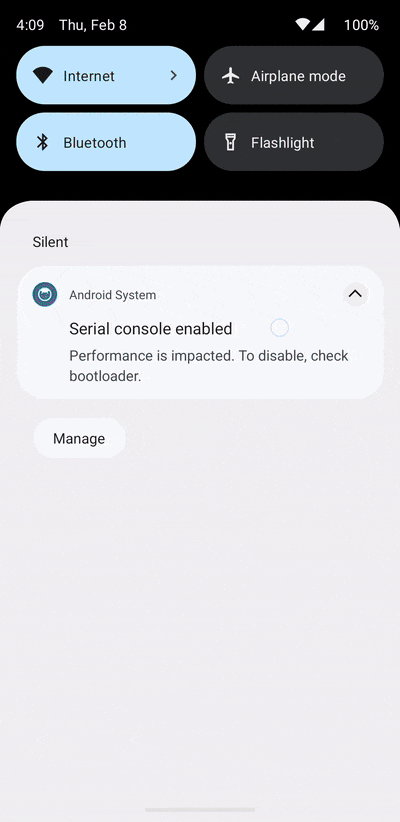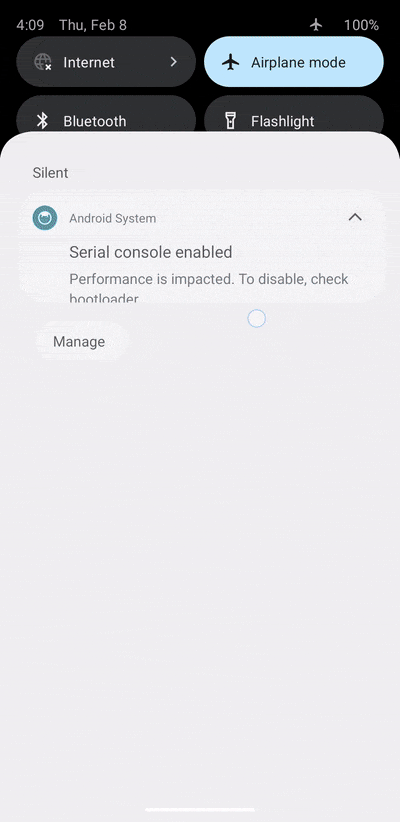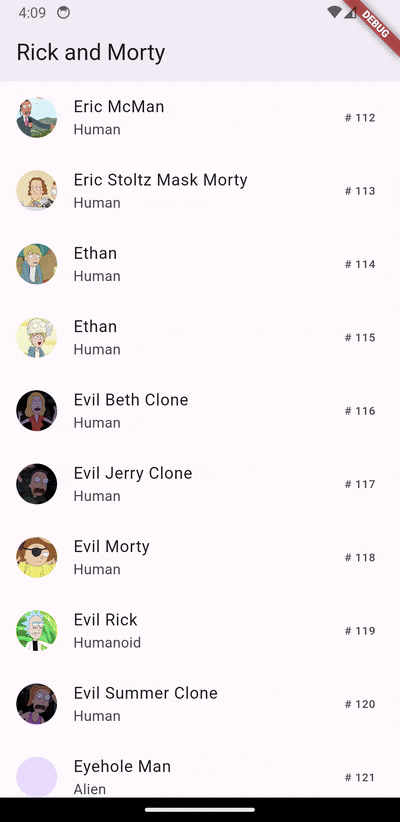
- In-memory Caching: Intelligently caches frequently accessed data, minimizing network requests and significantly improving performance.
- Configurable Widgets: Customize the look and feel of your pagination with a variety of built-in widgets,
like
PagingListViewandBidirectionalPagingListView. - Error Handling: Gracefully handles potential errors during data loading and retrieval, ensuring a smooth user experience even in unexpected situations.
- Flexible Configuration: Tailor Pager's behavior to your specific needs by adjusting parameters like initial keys, page sizes, and caching strategies.
- Extensive Documentation: Clear and comprehensive documentation, making it easy for developers of all levels to understand and implement effectively.
Add the following to your pubspec.yaml and replace [version] with the latest version:
dependencies:
super_paging: ^[version]To get started, import the package:
import 'package:super_paging/super_paging.dart';Create a PagingSource:
class RickAndMortySource extends PagingSource<int, Character> {
final RickAndMortyApi api;
RickAndMortySource({required this.api});
@override
Future<LoadResult<int, Character>> load(PagingConfig<int> config, int key) async {
try {
final characters = await api.getCharacters(page: key);
return LoadResult.page(nextKey: key + 1, items: characters);
} catch (e) {
return LoadResult.error(e);
}
}
}Create a Pager Instance:
final pager = Pager(
initialKey: 1,
config: const PagingConfig(pageSize: 20, initialLoadSize: 60),
pagingSourceFactory: () => RickAndMortySource(api: RickAndMortyApi()),
);Integrate with UI:
PagingListView(
pager: pager,
itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
final item = pager.items.elementAt(index);
return ListTile(
title: Text(item.name),
subtitle: Text(item.species),
trailing: Text('# ${item.id}'),
leading: CircleAvatar(backgroundImage: NetworkImage(item.image)),
);
},
emptyBuilder: (BuildContext context) {
return const Center(
child: Text('No characters found'),
);
},
errorBuilder: (BuildContext context, Object? error) {
return Center(child: Text('$error'));
},
loadingBuilder: (BuildContext context) {
return const Center(
child: CircularProgressIndicator.adaptive(),
);
},
);Handle Refresh and Retry:
// Refresh the data
await pager.refresh();
// Retry failed loads
await pager.retry();Dispose Resources:
@override
void dispose() {
pager.dispose();
super.dispose();
}Pager(
// Defines the initial key to use for the first load.
//
// By default, the initial key is null.
initialKey: null,
// Configuration for pagination behavior.
config: PagingConfig(
// Defines the number of items to load in a single page.
pageSize: 20,
// Defines the number of items to load in the first page.
//
// By default, the initial load size is 3 times the page size.
initialLoadSize: 60,
// Defines how far from the edge of loaded content an access
// must be to trigger further loading.
//
// By default, the pager will start loading when the user scrolls
// within 3 items of the end of the loaded content.
//
// If set to null, the pager will not start loading more content until
// they are specifically requested by the user.
prefetchIndex: 3,
// @Experimental
//
// Defines the maximum number of items to keep in memory before
// pages should be dropped.
//
// If set to null (Default), pages will never be dropped.
maxSize: null,
),
// Defines the initial state to use for the first load.
//
// By default, [PagingState.initial()] state is used.
initialState: PagingState.initial(),
// Defines the source from which to load the paginated data.
pagingSourceFactory: () => MyPagingSource(),
);PagingListView<int, String>(
// Defines the pager to use for loading data.
pager: myPager,
// Defines the builder that is called to build items in the ListView.
//
// The builder is called once for each item in the list.
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final item = myPager.valueList.elementAt(index);
return ListTile(
title: Text(item),
);
},
// Defines the builder that is called to build the empty state of the list.
emptyBuilder: (context) {
return const Center(
child: Text('No items found'),
);
},
// Defines the builder that is called to build the error state of the list.
//
// [error] is the error that caused the state to be built.
errorBuilder: (context, error) {
return Center(child: Text('Error: $error'));
},
// Defines the builder that is called to build the loading state of the list.
loadingBuilder: (context) {
return const Center(
child: CircularProgressIndicator.adaptive(),
);
},
// Defines the builder that is called to build the prepend state of the list.
//
// [state] is the current state of the pager and [pager] is the pager instance.
//
// Optional. If not provided, the list will show the default prepend loading state.
prependStateBuilder: (context, state, pager) {
// Return a widget based on the state. For example, a button to load the previous page.
// Use the [pager] instance to call [pager.load()] or [pager.retry] based on the state.
},
// Defines the builder that is called to build the append state of the list.
//
// [state] is the current state of the pager and [pager] is the pager instance.
//
// Optional. If not provided, the list will show the default append loading state.
appendStateBuilder: (context, state, pager) {
// Return a widget based on the state. For example, a button to load the next page.
// Use the [pager] instance to call [pager.load()] or [pager.retry] based on the state.
},
);
