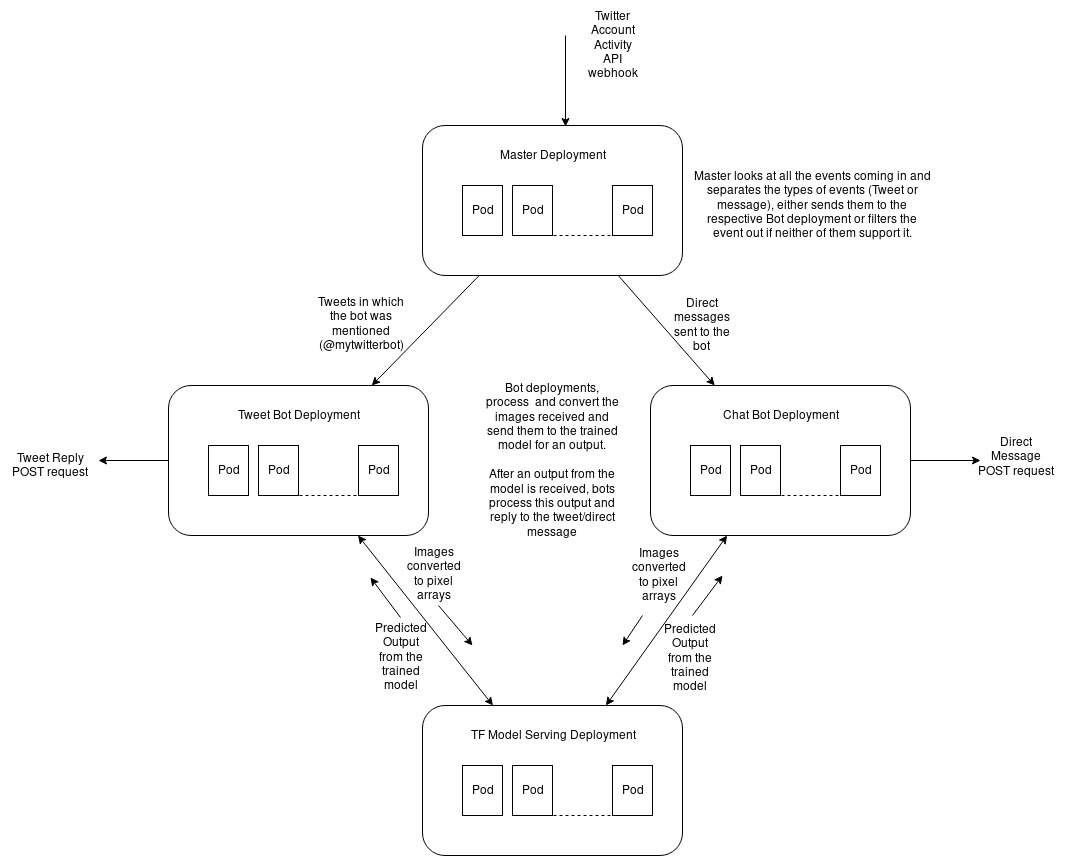
This application is a twitter bot that replies to direct messages and tweets in which the bot is mentioned. This bot is divided into 4 different openshift deployments.
- Tensorflow model serving
- Twitter Chatbot Workers
- Twitter Tweetbot Workers
- Twitter Master Workers
Each of them is a separate deployment because that makes them individually scalable, so if more users are interacting with the chatbot (using direct messages), the number of chatbot workers can be increased easily.
This will help with automatically getting CA certificates for your public routes.
make oc_deploy_acme
This will download your stored model from github and deploy it on openshift (Make sure this is done before the chatbot and tweetbot deployment)
make oc_deploy_tf_serving
This is the deployment of worker pods, that reply to direct messages
make oc_deploy_chatbot_worker
This is the deployment of worker pods, that reply to tweet mentions (@MYTWITTERNAME)
make oc_deploy_tweetbot_worker
This is the deployment of master pods, master pods create a webhook, which receives events like direct messages and tweet mentions using the twitter Account Activity API.
make oc_deploy_master
To deploy all of them, run:
make oc_deploy_all
This will deploy the tensorflow-serving first, then the chatbot/tweetbot workers, then finally the master deployment.
make oc_delete_all
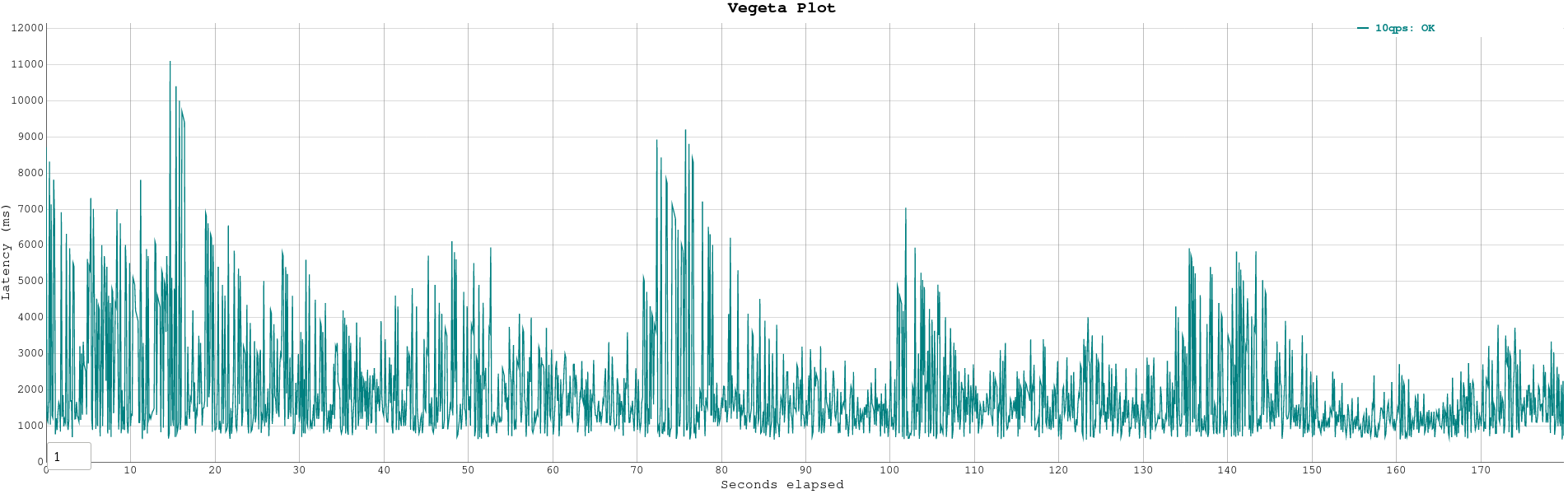
To load test the deployments, we use vegeta.
** Before beginning to load test, set the env variable FLT_LOAD_TESTING_MODE=True, this will prevent the response to reach the twitter servers. This is important because if you send to many requests too fast to the twitter server, your app might get disabled by twitter
In the load_test directory of this repo, you will see a fake_dm.json, targets.txt and vegeta_attack.sh.
- fake_dm.json is a dummy message that includes a url to an image which will be processed by the bot.
- targets.txt includes the POST request configuration that vegeta will bombard the webhook with. This also points to the fake_dm.json as that json will act as the body for the POST request (Update the location for the json file before load testing).
- vegeta_attack.sh is a very simple example script which shows how to attack the webhook with 10 requests per second and plot the latency graph for these requests in an html file (For more info go here).