ACM Research, Fall 2021
- Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Background
- Data Collection
- Model
- Results
- Web Demo
- Contributors
The advent of smartphones and the Internet has brought together a variety of communities and like-minded individuals. This has resulted in the creation of many different subcultures and the emergence of corresponding language patterns. By observing the linguistic diversity of Twitter users, we aim to analyze the language patterns of different groups of people and communities through a mobile keyboard next-word prediction model.
We chose to create an LSTM neural network because our reading and research suggested that this would be the best way forward. When reading from research papers, we found that the G-board team (developers of Google's mobile keyboard for Android) used a variant on LSTMs optimized for mobile devices. However, we found that such modification was not necessary for our model. Compared to other recurrent neural networks, we decided to implement LSTMs since they are very good at remembering ordered context, which is essential for accurately predicting the next word that a user might type on a keyboard. We chose Twitter for data because of the easy availability of very siloed users and communities for analysis.
We first created a "base model", trained on 1,600,000 tweets from Sentiment140's publicly available training set. We then fine-tuned the model by training copies of the base model on various sets of data representing various communities. From Twitter's topics list, we chose 5 different subtopics from various communities to analyze: K-pop, Cryptocurrency, Beauty, Technology and Gaming. We then created a separate data set for each subtopic. Since each topic has distinct word frequencies associated with it, we were able to ensure that fine-tuning our model with different data sets would yield dramatic and interesting results. We also created a "combined" model, beginning with the base model and fine-tuning it on the tweets from every subtopic combined.
We found users likely to tweet about each topic from Twitter's topic pages and then used the Twitter API to collect recent tweets from each user. Because most users frequently tweet about a limited number of topics, it is reasonable to assume that each user who appears a topic page tweets about the given topic regularly.
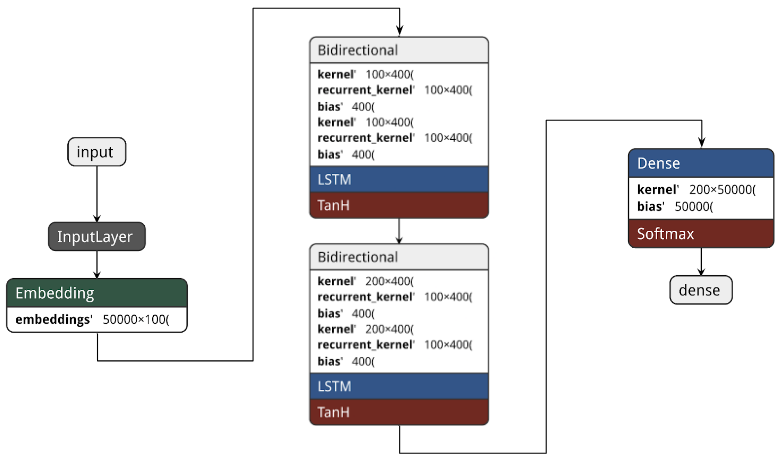
To implement the model, we drew on previous examples for inspiration on model structure and data setup, especially that of Gboard. We tokenized the input data, converting each word to a number, corresponding to the frequency of the word in the input dataset. The model is trained on examples with the prior four words in a string as the x vector and the current word as a y vector, for each word in each tweet (the x vector is padded with zeros if there are less than 4 previous words). We learned a 100-dimensional embedding vector as input to the two LSTM layers. Each LSTM layer is Bidirectional, and contains 100 neurons.
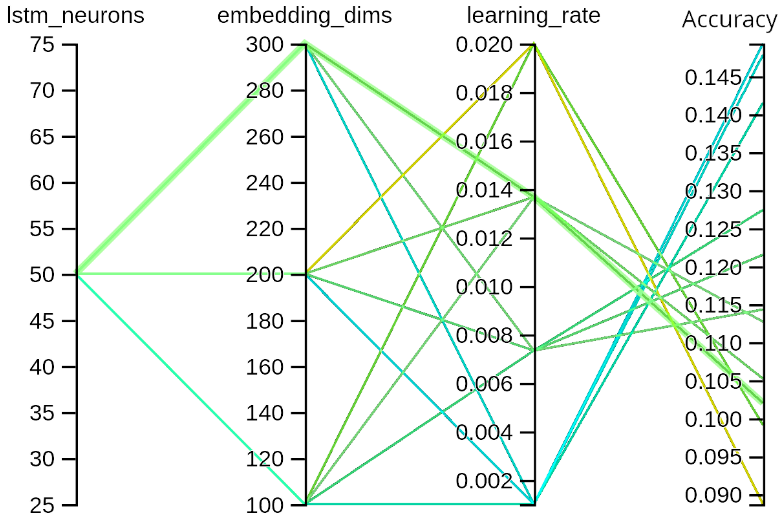
We found the optimal model structure and hyperparameter values through hyperparameter optimization. Finally, we used a dense layer of 50000 neurons (corresponding to 50000 words in our tokenizer vocabulary) to deliver predicted probabilities for the next word. We found that 50000 words in our vocabulary produced the best quantitative accuracy as well as qualitative prediction quality.
Pictured is a prediction tree given the initial text of "computer". To generate this tree, we refined our base model (initially trained on the base Twitter dataset) by training it on all the tweets from every subtopic. Our goal was to see how well the model would retain computer-related vocabulary knowledge given a prompt related to the tech subtopic. We take the three most "likely" next words as predicted by the model, and for each of those predict three more, etc.
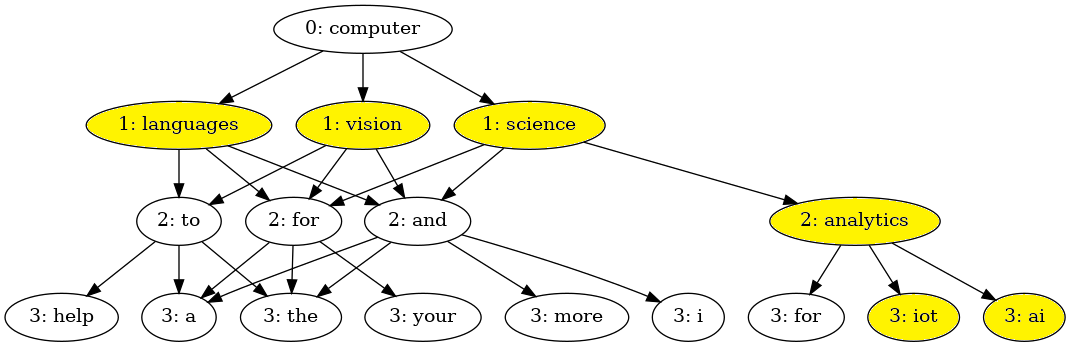
Highlighted is everything related to technology. It is important to note the model's ability to retain context and information about the subject several words later, showcasing the power of LSTM models.

Pictured below is a prediction tree given the initial text of "investing in". To generate this tree, we refined the base model by training it on the crypto subgroup data. Highlighted is everything related to crypto.
Try out the model yourself at mobilekeyboard.web.app
- Roman Hauksson-Neill
- Max Hogan
- Anh Nguyen
- Megan Vu
- Aditya Rathod - Research Lead
- Dr. Vincent Ng - Faculty Advisor
