-
AES was developed by NIST(National Institute of Standards and Technology) in 1997
-
It was developed for replacing DES which was slow and was vulnerable to various attacks
-
AES was then published on 26th November 2001
-
Best open source solutions for encryption today
-
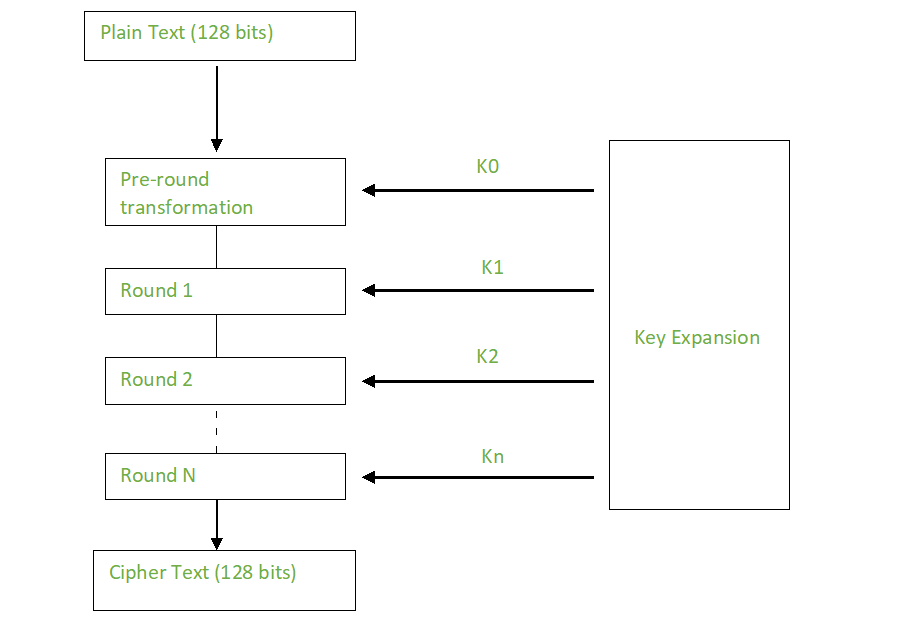
The key size can be 128/192/256 bits
-
For 128 bits, it encrypts data in blocks of 128 bits each, which means it takes 128 bits as input and outputs 128 bits of encrypted cipher text as output
-
AES relies on substitution-permutation network principle which means it is performed using a series of linked operations which involves replacing and shuffling of the input data
AES performs operations on bytes of data rather than in bits. Since the block size is 128 bits, the cipher processes 128 bits (or 16 bytes) of the input data at a time.
The number of rounds depends on the key length as follows :
128 bit key – 10 rounds
192 bit key – 12 rounds
256 bit key – 14 rounds
AES considers each block as a 16 byte (4 byte x 4 byte = 128 ) grid in a column major arrangement.
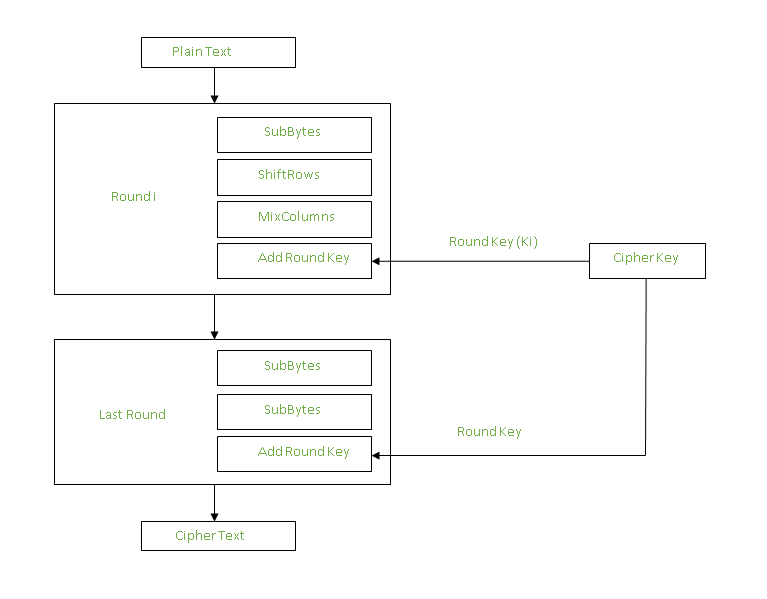
Each round comprises of 4 steps :
1. SubBytes
In this step each byte is substituted by another byte, This substitution is done in a way that a byte is never substituted by itself and also not substituted by another byte which is a compliment of the current byte
2. ShiftRows
- The first row is not shifted
- The second row is shifted once to the left
- The third row is shifted twice to the left
- The fourth row is shifted thrice to the left
3. MixColumns
This step is basically a matrix multiplication Each column is multiplied with a specific matrix and thus the position of each byte in the column is changed as a result
4. Add Round Key
Now the resultant output of the previous stage is XOR-ed with the corresponding round key
Here, the 16 bytes is not considered as a grid but just as 128 bits of data
The stages in the rounds can be easily undone as these stages have an opposite to it which when performed reverts the change Each 128 blocks goes through the 10, 12 or 14 rounds depending on the key size
The stages of each round in decryption is as follows :
- Add round key
- Inverse MixColumns
- ShiftRows
- Inverse SubByte
Before going further, we should have a library installed
-
os Already installed in standard python package for python 3.0 or above
-
pycryptodome (earlier pycryto) so, after some vulnerablities were found in the pycryto, the community suggested to better use pycryptodome
pip3 install pycryptodomeTo use AES Encryption and Decryption in Python, we have to follow the below steps.
from os import urandom
from crypto.cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import padTo generate a secret key, we will use Python os module’s urandom() method.
secret_key = urandom(16)The purpose of the iv is to produce different encrypted data so that an potential attacker will not be able to use cryptanalysis to decode the key data or message data We will generate the initialization vector using os.urandom() function.
iv = urandom(16)For successful decryption, the iv must be provided to the recipient, but it does not need to be kept secret. It is placed at the beginning of the output file (after the first 8 bytes of the original file size) so that the receiver may read it before decrypting the data.
To generate the AES cipher object, we will use AES.new() method AES.new() method takes three parameters - secret_key, AES.MODE.CBC, iv
obj = AES.new(secret_key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)CBC is one of the classic modes of Cipher Operations, below are some the other modes:
- Encrypt the message with AES
message = 'password is triplenine999'
paddedmessage=pad(message.encode(), 16, style='pkcs7')
encrypted_text = encr_obj.encrypt(paddedmessage)
print('The encrypted text: ', encrypted_text)Here, we have to encode the message (which is in str now) to "utf8"
PKCS #7 is one of the family of standards called Public-Key Cryptography Standards (PKCS) created by RSA Laboratories
- Decrypt the message
decr_obj = AES.new(secret_key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
decrypted_text = decr_obj.decrypt(encrypted_text)
print('The decrypted text: ', decrypted_text.decode())