ConfigServer Security & Firewall (CSF) is a popular and powerful firewall solution for Linux servers. It provides a user-friendly interface and a wide range of security features to protect your server from various threats. In this article, we will guide you through the process of installing and configuring CSF on your Linux server.
- Summary
- Download
- References
- Features
- Install CSF
- Enable CSF Firewall Web UI
- Install Docker Patch
This guide will take you through the following steps:
- Install CSF (ConfigServer Firewall)
- Install CSF WebUI interface
- Install docker patch (pre and post)
- docker.sh script will be placed in
/usr/local/include/csf/post.d/docker.shand runs each time you restart CSF.
- docker.sh script will be placed in
The latest version of csf can be downloaded here:
Use the following pages for installation help:
- Chapter 1: How to Install and Configure CSF Firewall on Linux
- Chapter 2: How to Enable CSF Firewall Web UI
- Straight-forward SPI iptables firewall script
- Daemon process that checks for login authentication failures for:
- Courier imap, Dovecot, uw-imap, Kerio
- openSSH
- cPanel, WHM, Webmail (cPanel servers only)
- Pure-ftpd, vsftpd, Proftpd
- Password protected web pages (htpasswd)
- Mod_security failures (v1 and v2)
- Suhosin failures
- Exim SMTP AUTH
- Custom login failures with separate log file and regular expression matching
- POP3/IMAP login tracking to enforce logins per hour
- SSH login notification
- SU login notification
- Excessive connection blocking
- UI Integration for cPanel, DirectAdmin, InterWorx, CentOS Web Panel (CWP), VestaCP, CyberPanel - and Webmin
- Easy upgrade between versions from within the control panel
- Easy upgrade between versions from shell
- Pre-configured to work on a cPanel server with all the standard cPanel ports open
- Pre-configured to work on a DirectAdmin server with all the standard DirectAdmin ports open
- Auto-configures the SSH port if it’s non-standard on installation
- Block traffic on unused server IP addresses – helps reduce the risk to your server
- Alert when end-user scripts sending excessive emails per hour – for identifying spamming scripts
- Suspicious process reporting – reports potential exploits running on the server
- Excessive user processes reporting
- Excessive user process usage reporting and optional termination
- Suspicious file reporting – reports potential exploit files in /tmp and similar directories
- Directory and file watching – reports if a watched directory or a file changes
- Block traffic on a variety of Block Lists including DShield Block List and Spamhaus DROP List
- BOGON packet protection
- Pre-configured settings for Low, Medium or High firewall security (cPanel servers only)
- Works with multiple ethernet devices
- Server Security Check – Performs a basic security and settings check on the server (via cPanel/- DirectAdmin/Webmin UI)
- Allow Dynamic DNS IP addresses – always allow your IP address even if it changes whenever you connect to the internet
- Alert sent if server load average remains high for a specified length of time
- mod_security log reporting (if installed)
- Email relay tracking – tracks all email sent through the server and issues alerts for excessive usage (cPanel servers only)
- IDS (Intrusion Detection System) – the last line of detection alerts you to changes to system and application binaries
- SYN Flood protection
- Ping of death protection
- Port Scan tracking and blocking
- Permanent and Temporary (with TTL) IP blocking
- Exploit checks
- Account modification tracking – sends alerts if an account entry is modified, e.g. if the password is changed or the login shell
- Shared syslog aware
- Messenger Service – Allows you to redirect connection requests from blocked IP addresses to preconfigured text and html pages to inform the visitor that they have been blocked in the firewall. This can be particularly useful for those with a large user base and help process support requests more efficiently
- Country Code blocking – Allows you to deny or allow access by ISO Country Code
- Port Flooding Detection – Per IP, per Port connection flooding detection and mitigation to help block DOS attacks
- WHM root access notification (cPanel servers only)
- lfd Clustering – allows IP address blocks to be automatically propagated around a group of servers running lfd. It allows allows cluster-wide allows, removals and configuration changes
- Quick start csf – deferred startup by lfd for servers with large block and/or allow lists
- Distributed Login Failure Attack detection
- Temporary IP allows (with TTL)
- IPv6 Support with ip6tables
- Integrated UI – no need for a separate Control Panel or Apache to use the csf configuration
- Integrated support for cse within the Integrated UI
- cPanel Reseller access to per reseller configurable options Unblock, Deny, Allow and Search IP address blocks
- System Statistics – Basic graphs showing the performance of the server, e.g. Load Averages, CPU Usage, Memory Usage, etc
- ipset support for large IP lists
- Integrated with the CloudFlare Firewall
- …lots more!
- A Linux server running CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu, or any other compatible Linux distribution.
- Root access or a user account with sudo privileges.
- Perl installed on your server. If Perl is not installed, you can install it by running the following commands:
-
For CentOS/RHEL:
sudo yum install perl
-
For Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install perl
-
To download and install CSF, follow these steps:
- Log in to your server via SSH.
- Download the latest version of CSF using the wget command:
wget https://download.configserver.com/csf.tgz
- Extract the downloaded archive:
tar -xzf csf.tgz
- Navigate to the extracted directory:
cd csf - Run the installation script:
sudo sh install.sh
CSF will now be installed on your server, along with its Web UI (ConfigServer Firewall & Security) if you have a control panel like cPanel or DirectAdmin installed.
Before enabling and configuring CSF, it is crucial to test whether it is compatible with your server. Run the following command to initiate the test:
sudo perl /usr/local/csf/bin/csftest.plThe test will check for any potential issues or conflicts. If the test completes successfully, you will see the message “RESULT: csf should function on this server.” If there are any problems, the test will provide information on how to resolve them.
Now that CSF is installed, you can start configuring it to suit your server’s requirements. The main configuration file for CSF is located at /etc/csf/csf.conf. You can use your preferred text editor to modify the file, such as nano or vim:
sudo nano /etc/csf/csf.confSome essential settings you may want to modify include:
TESTING: Set this value to 0 to disable testing mode and activate the firewall.TCP_INandTCP_OUT: These settings define the allowed incoming and outgoing TCP ports, respectively. Add or remove ports as required, separated by commas.UDP_INandUDP_OUT: These settings define the allowed incoming and outgoing UDP ports, respectively. Add or remove ports as required, separated by commas.DENY_IP_LIMIT: This setting defines the maximum number of IP addresses that can be listed in the /etc/csf/csf.deny file. Adjust this limit as needed.CT_LIMIT: This setting controls the number of connections from a single IP address that are allowed before the IP is temporarily blocked. Adjust this value according to your server’s requirements.
These are just a few of the numerous configuration options available in CSF. Make sure to review the configuration file and adjust the settings to suit your server’s needs. After making changes to the configuration file, save and exit the text editor.
Once you have configured the CSF firewall, it is time to enable it. To do so, run the following command:
sudo csf -eThis command will restart the CSF and LFD (Login Failure Daemon) services, applying your configuration changes and activating the firewall.
CSF provides several commands to manage the firewall, such as:
sudo csf -ssudo csf -fsudo csf -rsudo csf -lsudo csf -a IP_ADDRESSsudo csf -ar IP_ADDRESSsudo csf -d IP_ADDRESSsudo csf -dr IP_ADDRESSsudo csf -td IP_ADDRESSsudo csf -tr IP_ADDRESSThese commands can help you manage your server’s security and monitor incoming and outgoing traffic.
If you decide to uninstall CSF for any reason, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the CSF directory:
cd /etc/csf - Run the uninstallation script:
sudo sh uninstall.sh
The script will remove CSF and its associated files from your server.
ConfigServer Security & Firewall (CSS) is an iptables based firewall for Linux systems. In our previous tutorial read installation tutorial of CSF on Linux system. CSF also provides in-built web UI for the managing firewall from the web interface. In this tutorial, you will find how to enable CSF Firewall Web UI on your system.
CSF UI required some of Perl modules to be installed on your system. Use the following commands to install required modules as per your operating system.
Debian based systems:
sudo apt-get install libio-socket-ssl-perl libcrypt-ssleay-perl \
libnet-libidn-perl libio-socket-inet6-perl libsocket6-perlRedhat based systems:
sudo yum install perl-IO-Socket-SSL.noarch perl-Net-SSLeay perl-Net-LibIDN \
perl-IO-Socket-INET6 perl-Socket6To enable CSF web UI edit /etc/csf/csf.conf file in your favorite text editor and update the following values.
sudo vim /etc/csf/csf.conf# 1 to enable, 0 to disable web ui
UI = "1"
# Set port for web UI. The default port is 6666, but
# I change this to 1025 to easy access. Default port create some issue
# with popular chrome and firefox browser (in my case)
UI_PORT = "1025"
# Leave blank to bind to all IP addresses on the server
UI_IP = ""
# Set username for authetnication
UI_USER = "admin"
# Set a strong password for authetnication
UI_PASS = "admin"
Change the following values to your own:
UI_PORTUI_USERUI_PASS
After making changes, edit /etc/csf/ui/ui.allow configuration file and add your public IP to allow access to CSF UI. Change YOUR_PUBLIC_IP_ADDRESS with your public IP address.
sudo echo "YOUR_PUBLIC_IP_ADDRESS" >> /etc/csf/ui/ui.allowWeb UI works under lfd daemon. So restart the lfd daemon on your system using the following command.
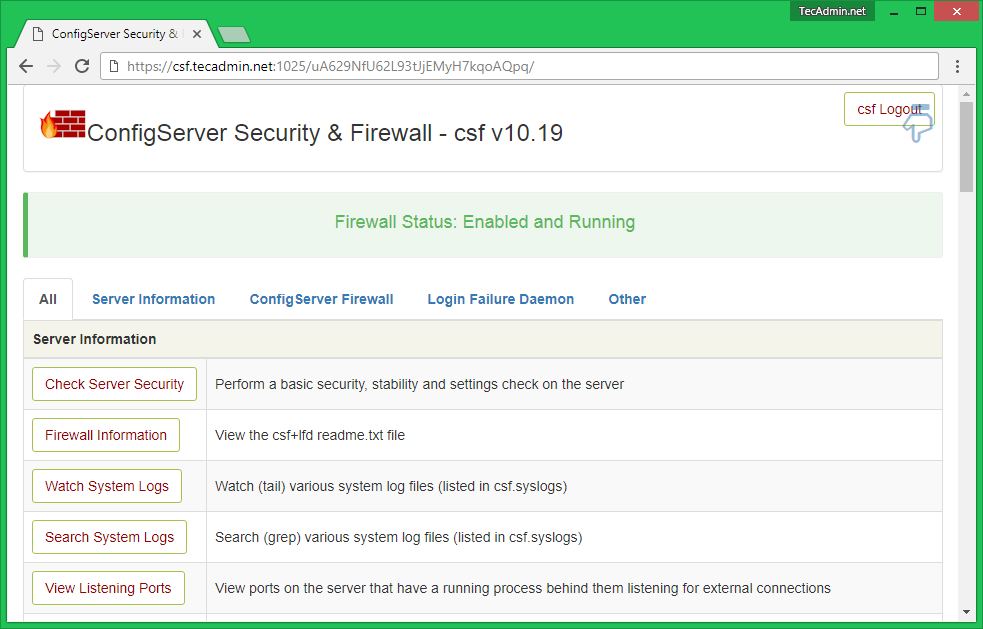
sudo service lfd restartNow, access CSF UI on your browser with the specified port. For this tutorial, I have used 1025 port. This will prompt for user authentication first. After successful login, you will find the screen like below.
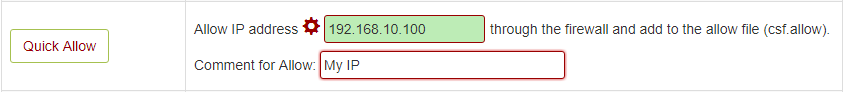
Allow IP Address – You can use below option to allow any IP quickly. This add the entry in /etc/csf/csf.allow file.
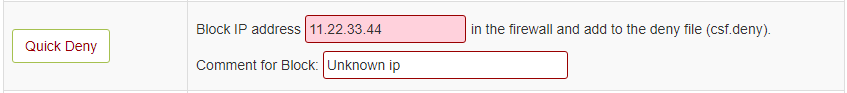
Deny IP Address – You can use below option to deny any IP quickly. This add the entry in /etc/csf/csf.deny file.
Unblock IP Address – You can use below option to quickly unblocked any IP which is already blocked by CSF.
After you have installed CSF and enabled the WebUI, you need to now install the docker patch if you run docker on your machine. This patch allows for docker to bypass CSF and not block traffic.
The docker patch allows for you to restart CSF without having to restart your docker containers.
Within your server, change to whatever directory where you want to download everything (including patch):
cd /home/$USER/DocumentsClone the repo
git clone https://github.com/Aetherinox/csf-firewall.gitSet the permissions (if needed)
sudo chmod +x /2-patch-docker/1-patch-pre/install.shRun the Pre Script first:
cd /2-patch-docker/1-patch-pre/
./install.shYou can also try:
sh install.shThe post script has a few settings you may need to adjust. Open docker.sh and check the following:
NETWORK_MANUAL_MODE: If you have manually set a static local IP address for each container, set this totrue.NETWORK_ADAPT_NAME: IfNETWORK_MANUAL_MODE = true, specify the network name you added to yourdocker-compose.ymlfile. Your container's docker-compose.yml would need to have the following:networks: traefik: name: traefik external: true
Set the permissions (if needed)
sudo chmod +x /2-patch-docker/2-patch-post/install.shRun the Post Script first:
cd /2-patch-docker/2-patch-post/
./install.shYou can also try:
sh install.shThe docker.sh file will be installed to /usr/local/include/csf/post.d