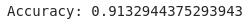Food image recogniton is one of the promising applicatons of visual object recogniton in computer vision.
In this study, a Food 11 dataset consistng of 13296 images of eleven categories.
Here we implemented 3 diferent Algorithms Decision Tree,CNN and DNN.
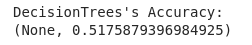
The Decision tree was frst tested as comparison, resulting in an overall accuracy of 51.75%; while the CNN performed much beter with an overall accuracy of 91%, but when implementng DNN with a much more parameters in the network (more than 80 million) we get an accuracy of 77%. Further improvement is within reach by collectng more images and optmizing the network architecture and relevant hyper-parameters.
Due to the widespread use of low-cost imaging devices like smartphone cameras, more and more applicatons are being developed in computer vision to facilitate automatc object recogniton, among which food image recogniton has recently gained much atenton.
Nowadays, people, especially diabetes patents, are increasingly cautous about their diet for improved health care. Food image recogniton provides a simple means to estmate the dietary caloric intake and evaluate people’s eatng habits, by using cameras to keep track of their food consumpton.
In recent years, Convoluton neural networks (CNN) have enjoyed great popularity as a means for image classifcatonocategorizaton since Krizhevsky et al won the ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recogniton Challenge (ILSVRC) 2012 competton.
CNN, as a variant of the standard deep neural network (DNN), is characterized by a special network architecture consistng of alternatng convoluton and pooling layers, to extract and combine local features from a two-dimensional input. Compared to conventonal hand-crafed feature extracton based approaches, CNN is advantageous since it is able to learn optmal features from images adaptvely.
In implementng CNN for image classifcaton, researchers have to collect such a large-scale dataset as the ILSVERC that contains more than one million images, for network training because of the need for learning a large number of parameters involved in the network, which, however, is not a trivial task. One simple way to deal with the situaton is to apply the CNN model that has been pre-trained based on a large-scale image data , which is so-called transfer learning.
Another way one can choose is to algorithmically expand the existng training data, e.g., by performing afne transformatons to the raw images. This study was aimed to apply CNNs aided with data expansion techniques to an eleven- class small-scale food image data.
As comparison, a conventonal a Decision tree was also employed for food image recogniton.
Experimental results demonstrated the superior performance of CNN and the efectveness of data expansion techniques in training small-scale data.
We had to choose between 2 datasets of Food Images :
- Food 11 : This is a dataset containing 16643 food images grouped in 11 major food
For each image : ID 0-10 refers to the 11 food categories respectvely.
- ImageNet : An image database organized according to the WordNet hierarchy in which each node of the hierarchy is depicted by hundreds and thousands of images. We will choose which categories we need and download its images then combine.
We preferred to choose the Food 11 dataset because of it is more realizable and well classifed and organized and we can extract the labels much easier. This dataset is divided into 3 types : Training set Images Evaluaton set Images Validaton set Images
To Read the dataset of images we upload the images on the drive and read it from it.
Afer accessing the folder of images we customize this images to be suitable for train.
Then we start to visualize sample of images.
Decision tree learning used to go from observatons about an item (represented in the branches) to conclusions about the item's target value (represented in the leaves). It is one of the predictve modeling approaches used in statstcs and machine learning. Tree models where the target variable can take a discrete set of values are called classifcaton trees; in these tree structures, leaves represent class labels and branches represent conjunctons of features that lead to those class labels. Decision trees where the target variable can take contnuous values (typically real numbers) are called regression trees. We frst create a classifer to train the model and then ft the train images.
A deep neural network is a neural network with a certain level of complexity, a neural network with more than two layers. Deep neural networks use sophistcated mathematcal modeling to process data in complex ways.
In general, is a technology built to simulate the actvity of the human brain – specifcally, patern recogniton and the passage of input through various layers of simulated neural connectons.
The architecture of DNN used here is as follow :
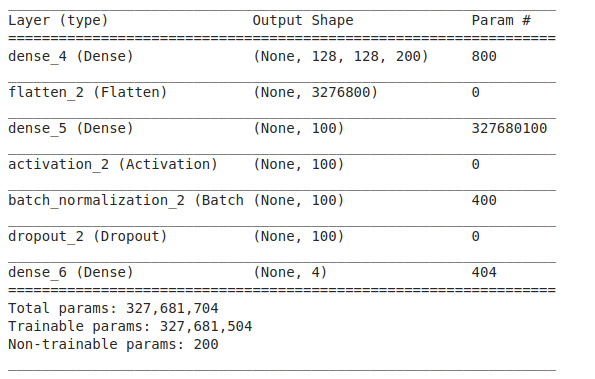
which the input layer consists of 200 unit with the shape of the image (128 x 128) and the next layer consists of 100 unit which generate about 327 million parameters and drop out of 0.
The architecture of the CNN used in this study is schematcally illustrated in this fg.
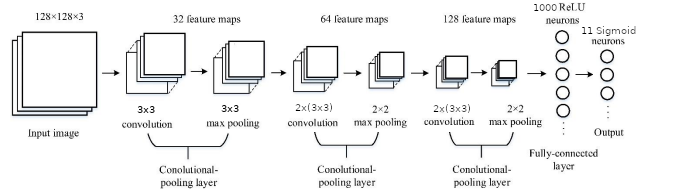
The network has four layers of hidden neurons (three convoluton-pooling and one fully-connected), apart from a fnal layer of output neurons (the input is not considered as a layer). The input contains 128 ×128× neurons, representng the RGB values for a 128 ×128×3 image. The first convolutonal-pooling layer uses a local receptve feld (also known as convolutonal kernel) of size 3x3 with a stride length of 1 pixel to extract 32 feature maps, followed by a max pooling operaton conducted in a 3×3 region; the second and third convolutonal-pooling layers use four 3×3 (2 for each convolutonal-pooling) local receptve felds, resultng in 64 and 128 feature maps, respectvely, and the other parameters remain unchanged. The fourth layer is a fully-connected layer with 1000 rectfed linear units (ReLU) neurons, and the output layer has 11 sigmoid neurons that correspond to the eleven categories of food. The three convolutonal-pooling layers also use ReLU actvaton functons. The network was trained with the SDG algorithm with a cross-entropy cost functon. The dropout that randomly eliminate a porton of neurons from the network was used to reduce possible overfing. The dropout rates of 0.25 and 0.5 were set for the third convolutonal- pooling layer and the fully-connected layer, respectvely. A fxed learning rate over the entre training process seems suboptmal, since it does takes account of the dynamical training behavior. The CNN was implemented by using the keras package which was confgured to use GPU for training.
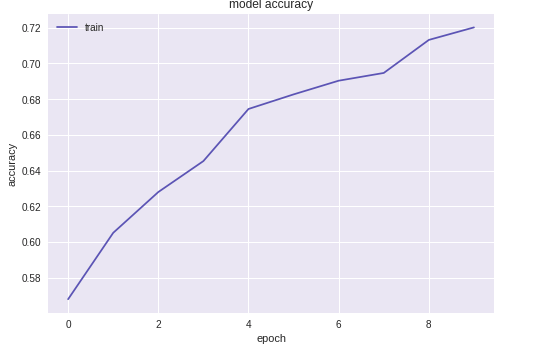
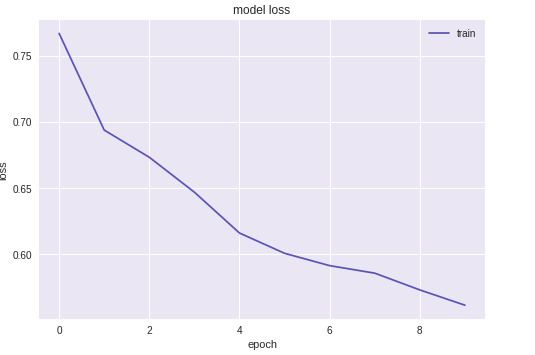
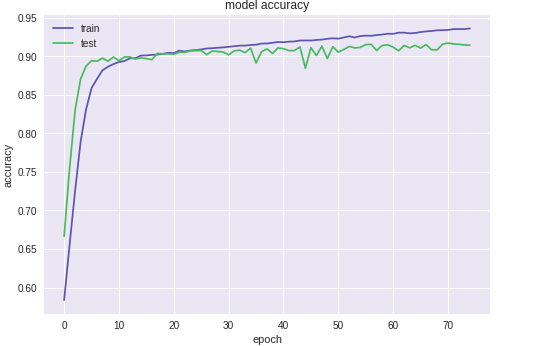
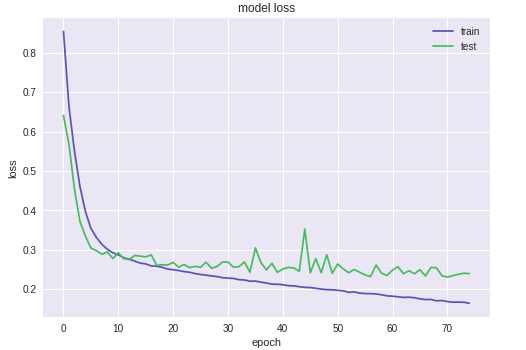
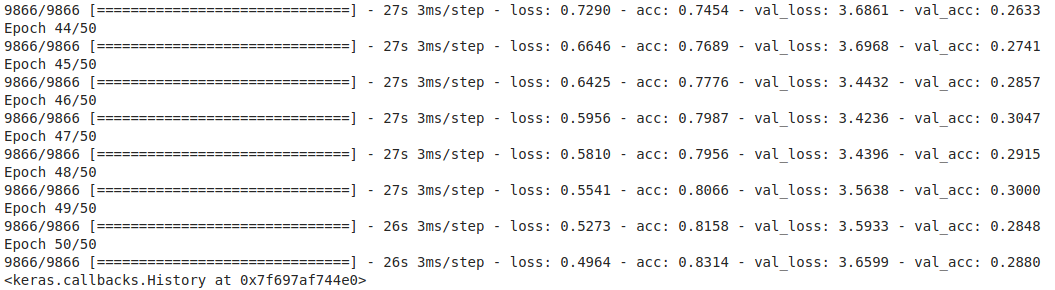
the Training results
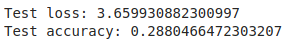
 The Test result
The Test result
-
the dataset size is 1.1884 GB so it is very difcult to read it every time from the disk so we decided to upload the images on the drive.
-
Each image size was 512 x 512 which considered a very large image on any device to calculate so we use (htps:oobulkresizephotos.como) to resize the images to 128 x 128 to be easy to handle , this operaton takes about a day and a half to do so.
-
because of the huge amount of images (16 thousands) it is taking to long to read from drive to colab framework so we upload the images as a 3 zip fles (Train, Validaton, Evaluaton) and accessing the images from them without extractng them at all.
-
the images wasn’t suitable for training so we scale the pixels of images intensites to the range [0 , 1].
-
To Visualize the image we got some help from Anime or Cartoon Team.
- We couldn’t take all the 9863 image to train on because the Colab memory wasn’t enough (It need more than 12 GB to train and ft) so we made the train only on the half of the dataset.
- We had to reshape the images to vectorize the images matrix.
- When creatng a simple DNN model that results a 327,681, parameters which consider a very big heavy on the memory and couldn’t to handle the 9863 image nor half of them so we made the train only on 1/8 of them to made it run without any runtme or memory leak.
- This study reported on the applicatons of CNNs to a eleven-class small- scale food image data. A fve-layer CNN model was constructed achieved the best test accuracy of 91% without data expansion (in paper the accuracy without data expansion was 74%), which was beter than the accuracy of 51% achieved by the Decision tree approach and 76 % achieved by the DNN approach.
- Training the CNN with diferent epochs showed the limited room for further improvement in test accuracy, which could be achieved by collectng more training data or by optmizing the architecture and hyper-parameters of the network, rather than by increasing the training epochs in the current framework, which, otherwise, would aggravate the overtraining problem.
- The Big deal in data expansion was the dataset is already big so when generate more data that was a big heavy on memory and we coudn’t even train 200 image of the dataset.