Module 5 (Shortest Path)
In graph problems, the Shortest Path Problem is a path finding of 2 vertices in a graph that has the minimum sum of weights. This problem can be solved easily using BFS if all edges have a weight of 1. However, in this problem, weight can be of any value. There are many implementations for solving the Shortest Path Problem, but what we will discuss now is Dijkstra's Algorithm.
Dijkstra's algorithm itself has many variations, but the most common is to find the shortest path from the source vertex to all other vertices.
- Set all vertex distances to infinity (can be replaced with very large values or values that will not be used) except the distance from the source which will be set to 0.
- Push vertex source to min-priority queue (priority queue with the order from small to large) with format (distance, vertex), for comparison of min-priority queue will use distance from vertex.
- Pop the vertex with the minimum distance from the priority queue
- Update the distance of the connected vertex to the popped vertex (the vertex from the result of step 3) with the case “current vertex distance + edge weight < next vertex distance”, then push the vertex.
- If the results of the pop vertex have been visited previously, then do continue.
- Perform steps 3 to 5 until the priority queue is empty.
Find the shortest path from vertex A to all other vertices.

Inisial:

Step 1:

Step 2:
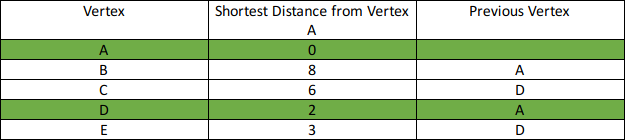
Step 3:

Step 4:
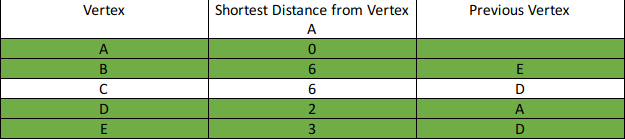
Step 5:

-
// pii pair of integer, integer typedef pair <int, int> pii; int dist[10]; vector <pii> v[10]; void dijkstra(int s, int n) { priority_queue <pii, vector <pii>, greater <pii> > pq; set <int> seen; memset(dist, -1, sizeof(dist)); dist[s] = 0; pq.push({0, s}); while(!pq.empty()) { pii now = pq.top(); pq.pop(); if(seen.find(now.second) != seen.end()) continue; seen.insert(now.second); for(int i = 0; i < v[now.second].size(); i++) { int next = v[now.second][i].second; int cost = v[now.second][i].first; if(now.first + cost < dist[next] || dist[next] == -1) { dist[next] = now.first + cost; pq.push({dist[next], next}); } } } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << "from " << s << " to " << i << " : " << dist[i] << endl; } return; }
Modul Struktur Data
Ditulis oleh tim Asisten Struktur Data 2020 - Teknik Informatika ITS
Modul 0
- Pengenalan Struktur Data IND | ENG
- Dynamic Array IND | ENG
- Linked List IND | ENG
- Soal Latihan IND | ENG
Modul 1
- Stack IND | ENG
- Queue IND | ENG
- Deque IND | ENG
- Priority Queue (List Based) IND | ENG
- Soal Latihan IND | ENG
Modul 2
- Pengenalan Tree IND | ENG
- Binary Search Tree IND | ENG
- Traversal BST IND | ENG
- Soal Latihan IND | ENG
Modul 3
Modul 4
- Melangkah Menuju C++ | ENG
- Standard Template Library Container | ENG
- Pengenalan Graf | ENG
- Traversal Graf | ENG
Modul 5