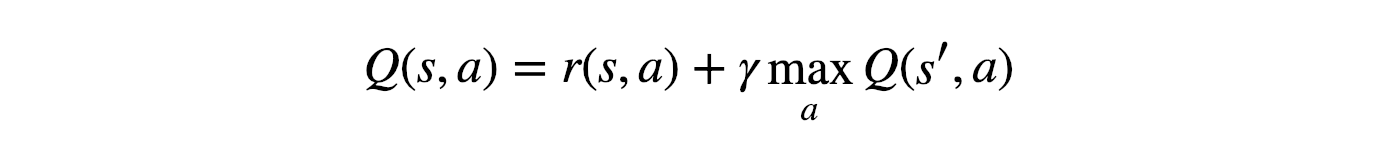The goal of the project is to create an algorithm capable of generating an infinite number of 4x4 mazes. We will use reinforcement learning, more precisely the Q-learning algorithm to generate different levels of maps. This is where the difficulty of this project lies. In the game design literature, it is common to use the BFS or DFS algorithm to generate a maze and/or use reinforcement learning to solve it, but I have only found one article that talks about reinforcement learning for generating a maze (Ahmed Khalifa, Philip Bontrager & al. PCGRL: Procedural Content Generation via Reinforcement Learning 2021). According to the authors: "To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time reinforcement learning is brought to bear on this problem. This is probably because it is not immediately obvious how to cast a level generation problem as a reinforcement learning problem".
This is exactly where the challenge lies. A common practice for a programmer, when one has a coding project that one has never encountered before, is, after reading and understanding the project, to do some research in google, StackOverflow, etc. We are not reinventing the wheel, it is important to not waste time on mistakes already made by programmers who have worked on this type of project before us. It also gives us more information and more understanding of possible future problems. I had never worked on a real RL project before. I only had some theoretical notions from my master's degree. So naturally, as a programmer who knows his best practices, I googled "RL to generate a map" :). After some research, I found the article I mentioned above, it's a very interesting paper, it gave me some ideas about the training process, the reward function, etc.. but this was the only article that talked about RL to generate a map and their project was quite different in some important aspects.
I knew then I'd have to "invent the wheel". I started by reading articles and theoretical papers about RL to understand how it works in depth. Moreover, I bought two very good courses on Udemy from well-known teachers. The first one is the acclaimed course of Lazy programmer and the second comes from Phil Tabor. This is a very good starting point for those interested in reinforcement learning.
After taking these theoretical and practical courses on reinforcement learning, I felt ready to start my project. Quickly, I was confronted with some problems: What are the optimal actions space, the state space, and so on? Thus began the headaches. The instructions were to use Q-learning but I figured out that I was going to have almost 1e10 elements in my Q-table and this was just impossible to manage. I had to think of another way. My first idea was to use DeepQ-learning but the instructions were to use Q-learning and since I have never used DeepQN, I didn't want to complicate the task. Then I thought of reducing the dimensionality by using symmetry and grouping similar states. And at this moment a new idea came to my mind, a hash table! During my blockchain startup experience, hashing was ubiquitous, so I worked a lot with hash functions and dictionaries. I'm pretty sure the idea came from there.
To summarize:
there are 24 binary editable walls Either there is here or there are not => 2^24 possible combinaisons of walls.
There are 16 boxes, either empty or filled with one of the three key points = > 16P3 = 3360 possible combinations of boxes.
I decided to use an actions space with 11 actions: addStart, AddEnd, addTreasure, EditTopwall, EditBotwall, EditEastWall, EditWestWall, goUp, goBot, goLeft, goRight (they are self-explanatory).
The agent has a random initial position in the matrix with 16 box
We end up with almost 2^24 * 3360 * 11 * 16 possibles states
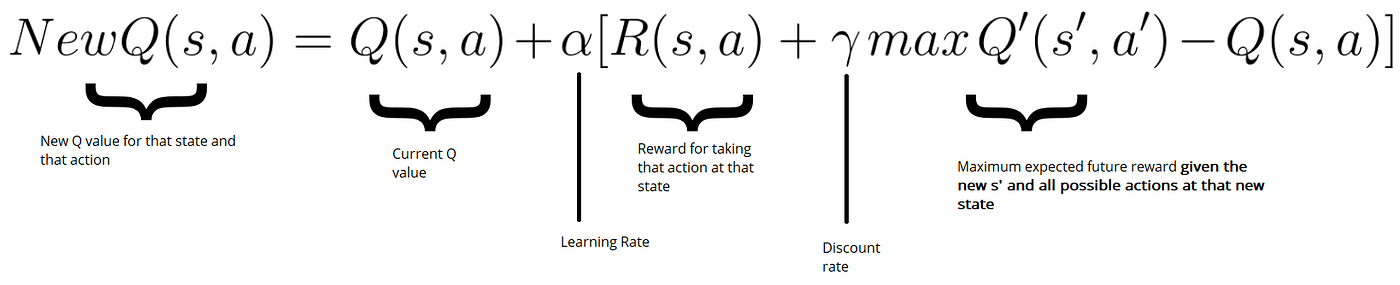
Solution? Instead of using a Q_table, use a Q_hash (with Q dict) where we store only the visited states. We also use a hash to store our state with python given hash function: We store it in self.state : hash(self.maze_map, self.start, self.end, self.treasure, self.ix, self.iy) where maze_map is the state of our maze, start, end, and treasure are the locations of your key points, self.ix and self.iy are the locations of our agent in the matrix. When we have the state, if it's a New state, We initialize Q[self.state] = [0] * len of actions space (=11 in our case). After setting up our Q_hash we just have to use the bellman equation and Q learning temporal difference to update our Q_hash.
our algorithm does not generate an infinite number of mazes since we always give the same labyrinth at the beginning with all the walls closed, only the position of the agent at the beginning differs from one game to another and there are only 16 possible different starting location for the agent. Thus, presented as follows our AI can generate only a small number of different mazes. But this is not a problem, we just need to make some little modifications to make him able to make an "infinite" number of mazes. One solution could be to randomly select a starting state in Q_hash.keys() (we can only start with a state already visited).
This IA most of the time gives good enough mazes but sometimes they are pretty "bad". To improve this we can "play" with the parameters of the agent or the environment like the gamma factor, discount factor, the number of games played, the number of steps by game, etc. But I think to make the algorithm much better we have to reduce the len of space states to 10 000 or 20 000 states using symmetry or similarity detection. Maybe DeepQN could give better results too since it handles the curse of dimensionality.
Belleman equation
Updating Q with temporal difference
AmT42, map_generator, ahmet-celebi-973b63197, Ahmet_Celebi@hotmail.fr, Q-learning map generator,
-
Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/AmT42/map_generator.git
-
Launches the .bat file : 'map_generator_run_script.bat', you must have anaconda env otherwise you'll have to run by yourself the scrip in the .py file 'map_generator_script.py'
-
A text file will appears "maze_sample.txt", copy past him here : Graphic Interphace the first element which is a sample of our matrix e.g. : {'(0, 0)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(0, 1)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(0, 2)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(0, 3)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(1, 0)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(1, 1)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(1, 2)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(1, 3)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '0'}, '(2, 0)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '1', 'S': '0'}, '(2, 1)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '1', 'S': '0'}, '(2, 2)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '1', 'S': '0'}, '(2, 3)': {'E': '0', 'W': '0', 'N': '1', 'S': '0'}, '(3, 0)': {'E': '1', 'W': '0', 'N': '0', 'S': '1'}, '(3, 1)': {'E': '1', 'W': '1', 'N': '0', 'S': '1'}, '(3, 2)': {'E': '1', 'W': '1', 'N': '0', 'S': '1'}, '(3, 3)': {'E': '0', 'W': '1', 'N': '0', 'S': '1'}} The last 3 elements are the location of the starting, ending and trasure point e.g. : (3, 2), (3, 0), (3, 3). and you'll have to add it manually in the Graphic Interphace website given above. Some other .svg files will appear in your folder direction e.g. "maze(2,2).svg" it's one example of a maze generated by the IA but the keypoints aren't displayed.
Contributions are what make the open source community such an amazing place to learn, inspire, and create. Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated.
If you have a suggestion that would make this better, please fork the repo and create a pull request. You can also simply open an issue with the tag "enhancement". Don't forget to give the project a star! Thanks again!
- Fork the Project
- Create your Feature Branch (
git checkout -b feature/AmazingFeature) - Commit your Changes (
git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature') - Push to the Branch (
git push origin feature/AmazingFeature) - Open a Pull Request
Ahmet CELEBI - @Linkedin - Ahmet_celebi@hotmail.fr
Project Link: https://github.com/AmT42/map_generator