- Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform used by thousands of companies for high-performance data pipelines, streaming analytics, data integration, and mission-critical applications.
- Kafka is based on Publish-Subscriber Model. And can be used for Event-Driven Architecture.
- Kafka can process a large amount of data in a short amount of time (1 million messages/sec).
- It also has low latency, making it possible to process data in real-time.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Message broker (PubSub model) in Event-Driven Architecture | Use Kafka when your application has a high throughput i.e. application has to process a large volume of messages, event driven services etc. |
| Data Ingestion - Real-time events, analytics etc. | If we want to build our own Google Analytics or Amplitude (to track app activities, events etc.), we can use Kafka as a broker. |
| Distributed Logging - Logs Aggregation, Metrics | Various systems in the IT infrastructure can push events/messages/logs in the Kafka. (example - ELK stack) |
| Stream Processing - Data Pipelines, Microservices etc. | Kafka Streams can be helpful in stream processing the events (map/reduce, aggregation, counts etc.). |
| Data Pipelines - CDC of DBs | Kafka connectors can be helpful to migrate from one DB to another, i.e. handle CDC. |
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability - Horizontal scalability | Kafka can be horizontally scaled easily across the cluster. - A cluster of brokers is used to partition and streamline the data thereby, scaling up the storage capacity. |
| Performance - High Throughput | Each Kafka broker can serve more than 1 million messages per second and can hold TBs of data. - Default configured message size in Kafka is 1MB. |
| High Volume | Large amount of data can be stored in the Kafka pool. |
| Durability | The data is kept persistent (as per retention policy) and tolerant to any hardware failures by copying the data in the clusters. |
| High Availability, Fault Tolerance | The distributed, partitioned, replicated, and fault-tolerant nature of Kafka makes it very reliable. - Kafka connector can handle failures with three strategies summarised as fast-fail, ignore and re-queue (sends to another topic). |
| Extensibility | Allows multiple ways for applications to plugin and make use of Kafka. - Also, it has provisions for new connectors that you can write as needed. |
| Data Processing/Transformation | Using Kafka Stream API, Kafka allows for deriving new data streams using the existing data streams from producers. |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Topic | Topic is a category or feed where messages (or events) would be saved and published. |
| Producer | Producer writes data into the topics (1 or more) in the Kafka. |
| Consumer | A consumer can subscribe (listen) to the topics (1 or more) and read data from those in the Kafka. |
| Consumer Group | A consumer group in Kafka is a collection of consumers who work together to ingest data from the same topic or range of topics. |
| Consumer Offset | Consuming a partition sequentially makes it easy to tell which messages have been processed. - All messages with an offset less than a consumer’s current offset have already been processed - And all messages with a greater offset have not yet been seen. - Thus, the broker does not need to track acknowledgments for every single message— it only needs to periodically record the consumer offsets. - The reduced bookkeeping overhead and the opportunities for batching and pipelining in this approach help increase the throughput of log-based systems. |
| Broker (i.e. Server) | A Kafka cluster is made up of a number of brokers (servers), which provides load balancing, reliable redundancy & fail-over. - Without sacrificing performance, each broker instance can handle read and write volumes of hundreds of thousands per second (and gigabytes of messages). |
| Kafka Controller | The Kafka controller is brain of the Kafka cluster. - It monitors the liveliness of the brokers and acts on broker failures. - Kafka Controller does leader election for the topic & in-charge of partition leaders and replication (if leader goes down). |
| Partitioning | Topics can be parallelized via partitions, which split data into a single topic among numerous brokers. |
| Partition Key | Partition key helps in deciding partition and maintaining the order of the messages. |
| Partition - Replication | Each partition would be replicated across the brokers/servers in the cluster (as per configured replication factor). |
| Partition - Leader | Only one partition (of the topic) would be active at the time, called Leader. - Write requests on the partition, would be handled by Leader. |
| Partition - Follower | Other partitions (of the topic) would only replicate message, called Followers. |
| Replication Factor | Based on configured replication factor (replication.factor), the number of followers would be decided. - Example - 3 replication factor means there would be 1 leader and 2 followers. |
| Log Compaction | Log compaction is a mechanism to give finer-grained per-record retention, rather than the coarser-grained time-based retention. |
| Core APIs - Producer, Consumer apis etc. | Kafka HTTP APIs can be integrated in the client apis, to push the message to the specific topic (& partition key). |
| In-Sync Replicas (ISR) | An in-sync replica (ISR) is a broker that has the latest data for a given partition. - A leader is always an in-sync replica. - A follower is an in-sync replica only if it has fully caught up to the partition it’s following. - Read requests on the partition, would be handled by in-sync replicas. |
| ACK levels | acks denotes the number of brokers that must receive the record before we consider the write as successful. |
| acks=0 - Ack level | With a value of 0, the producer won’t even wait for a response from the broker. |
| acks=1 - ACK level | With a setting of 1, the producer will consider the write successful when the leader receives the record. - The leader broker will know to immediately respond the moment it receives the record and not wait any longer. |
| acks=all - ACK level | When set to all, the producer will consider the write successful when all of the in-sync replicas receive the record. - This is achieved by the leader broker being smart as to when it responds to the request – it’ll send back a response once all the in-sync replicas receive the record themselves. |
| Security Considerations | All components (brokers, zookeeper, producers, consumers etc.) should authenticate each other and setup an encrypted (SSL) channel for communication. - Authorization - ACLs should be defined and enforced to control which users can perform what action? |
| Group co-ordinator | Role of group-coordinator is to manage a consumer group and specially partition rebalance. Read more |
| Config | Min. Value |
|---|---|
| Replication Factor | 3 |
In-sync replicas (min.insync.replicas) |
2 |
| Kafka Brokers (in different AZs) | 3 |
| Component | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Kafka Connect | Kafka Connect is a tool for scalably and reliably streaming data between Apache Kafka and other systems. |
| Schema Registry | Schema Registry holds schemas & ensures that schema used by producer and consumer, are identical. |
| Kafka Streams | Streams API is a client library for building applications and microservices, where the input and output data are stored in Kafka clusters. |
| kSQL | kSQL is a database purpose-built for stream processing applications. |
| Zookeeper | Zookeeper manages Kafka Cluster (new broker, new partition etc.), brokers coordination & election process (leader, Controller election etc.) |
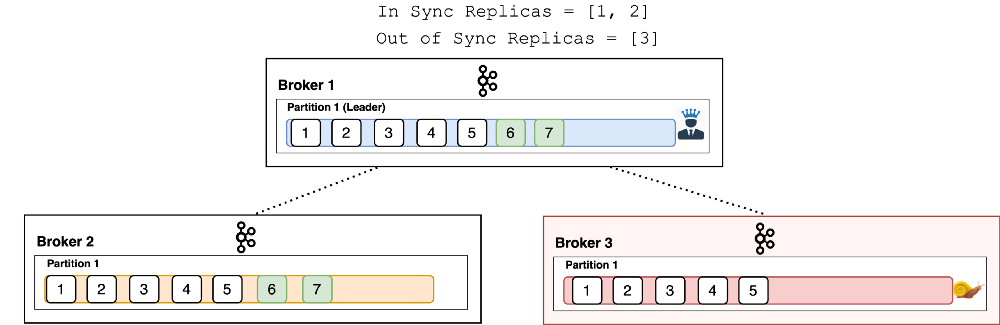
- Broker1 & Broker2 are in sync replicas (i.e. all messages are same in both the brokers).
- While Broker3 is out of sync replica.
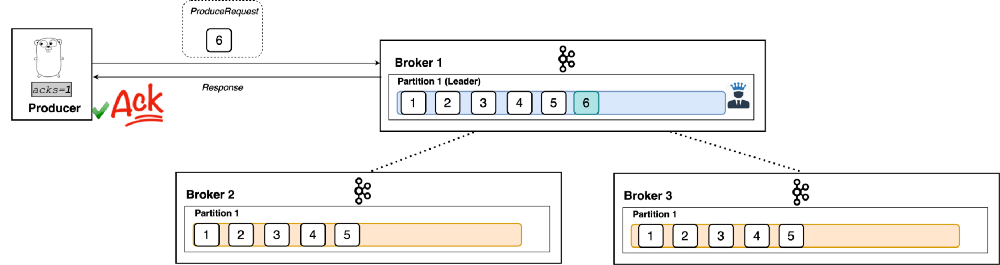
- If ack=1 is set as ack level, producer is acknowledged only when message (example message id - 6) is stored in one of the broker (Broker 1 in this case) successfully.
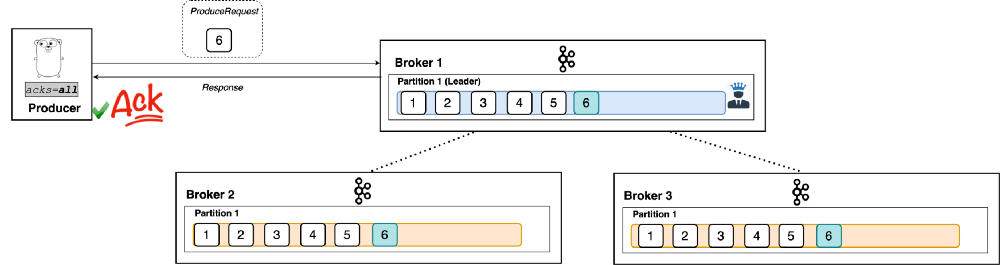
- If ack=all is set as ack level, producer is acknowledged only when message (example message id - 6) is stored in all the brokers successfully.
- Kafka vs Others
- Kafka Estimates
- Apache Kafka - Benchmarking@LinkedIn
- Why Kafka is so fast?
- Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (MSK) can be used to deploy Kafka on AWS.
- Kora: The Cloud Native Engine for Apache Kafka
- Kafka official documentation
- Martin Kleppmann | Kafka Summit London 2019 Keynote | Is Kafka a Database?
- Kafka Interview Question
- How to minimize the latency involved in kafka messaging framework?
- Apache Kafka on AWS using Amazon MSK
- Kafka Talk by Tri Hug
- Role of ZooKeeper in Kafka
- Replication in Kafka
- Swiggy - BehindTheBug — Kafka Under The Water
- Designing and testing a highly available Kafka cluster on Kubernetes (without zookeeper)
- ETL Is Dead, Long Live Streams: real-time streams w/ Apache Kafka