ISlash is a dynamically typed, interpreted programming language with no real use that I created for fun, which runs on top of Golang. The language somewhat resembles Assembly but it is simpler to understand and more high-level.
My main goal when creating ISlash was learning Golang (Go), as I had never used that language before. The name 'ISlash' is a pun with my last name 'Ibarra', because 'barra' means 'slash' in portuguese, which is my native language.
- Example Programs
- Language Support in VSCode
- Data Types
- Instructions
- Language Features
- Things to Notice
- Try ISlash - Playground
- Install ISlash Locally
- ISlash Docker Hub Image
- Possible Future Features
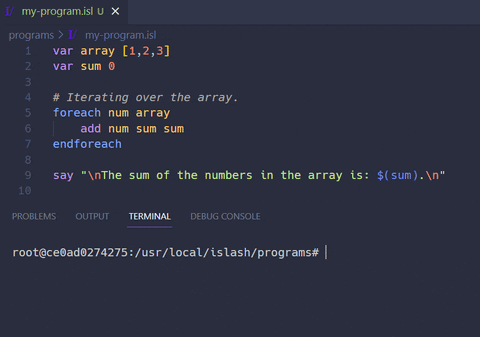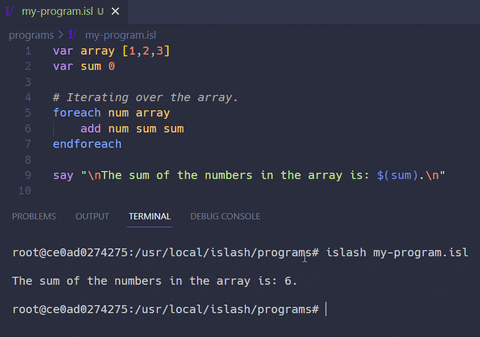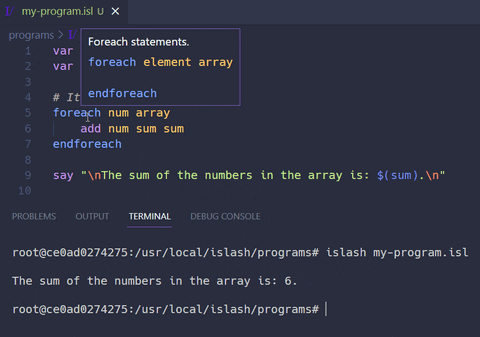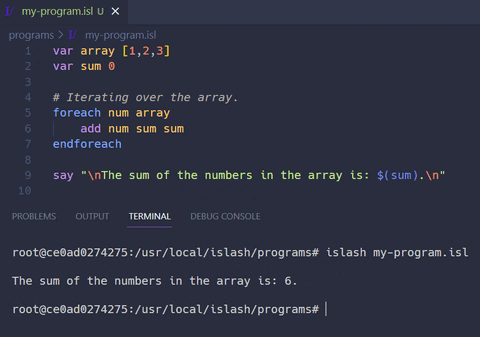
Example programs using the ISlash language can be found inside the example programs folder. There you'll find simple scripts showcasing the instructions of the language, as well as more advanced ones, such as a bubblesort, hangman, tic-tac-toe game and a csv reader script.
In the example below, we are multiplying numbers inputed by the user.
Download the ISlash Language Support Visual Studio Code extension to get syntax highlighting, code snippets, hovering tips and language icon.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| string | Strings are declared with double quotes. Ex: "Hello!" |
| number | Numbers may or may not have decimal places. Ex: 1, 2.3 |
| array | Arrays are declared with square brackets. Ex: [1,2,3], ["Hi","Hello"]. Do not put spaces between commas. |
In ISlash, although there is not a boolean data type, numbers can be used to represent boolean values:
| Boolean Value | Numbers Range |
|---|---|
| true | numbers ≥ 1 |
| false | numbers < 0 |
Instructions are not case sensitive.
| Instruction | Description |
|---|---|
| VAR | Sets/declares variables. |
| ADD | + operator. |
| SUB | - operator. |
| MULT | * operator. |
| DIV | / operator. |
| MOD | % operator. |
| POWER | ^ operator. |
| ROOT | Square roots, cubic roots... |
| INCREMENT | ++ operator (Adds 1). |
| DECREMENT | -- operator (Subtracts 1). |
| RANDOM | Generates a random integer value within a range. |
| GREATER | > operator. |
| GREATEREQUAL | >= operator. |
| LESS | < operator. |
| LESSEQUAL | <= operator. |
| NOT | NOT operator |
| AND | AND operator. |
| OR | OR operator. |
| IF | If statements. |
| ELSEIF | Else if statements. |
| ELSE | Else statements. |
| ENDIF | Closes if blocks. |
| EQUAL | == operator. |
| NOTEQUAL | != operator. |
| CONCAT | Concatenates strings. |
| LENGTH | Gets the length of a string or an array. |
| UPPER | Turn strings into uppercase. |
| LOWER | Turn strings into lowercase. |
| SPLIT | Splits a string using a pattern, produces a string[] variable. |
| REPLACE | Replaces a pattern in a string by another pattern. |
| CHARAT | Gets the nth char of a string. |
| SAY | Prints to screen. |
| INPUT | Gets user input. |
| WHILE | While statements. |
| BREAK | Exits out of while blocks. |
| ENDWHILE | Closes while blocks. |
| FOREACH | Use to iterate over arrays. |
| ENDFOREACH | Closes foreach blocks. |
| APPEND | Appends an element to an array. |
| PREPEND | Preppends an element to an array. |
| REMOVEFIRST | Removes the first element of an array. |
| REMOVELAST | Removes the last element of an array. |
| SWAP | Swaps arrays positions. |
| GET | Gets the nth element of an array. |
| SETINDEX | Changes the element at an index. |
| CONTAINS | Checks if a string contains a character or if an array contains an element. |
| READFILE | Reads a file, produces a string variable. |
| READFILELINES | Reads a file line by line, produces a string[] variable. |
| WRITEFILE | Writes to a file, overrides previous content. |
| EXIT | Exits the program with a status code. |
Basic example programs using each of the instructions listed above can be found here.
Below, some ISlash language features will be explained:
Comments can be made using the # character at the beginning of lines:
# This is a comment!
say "Cool!"
ISlash allows the interpolation of Strings using the $() symbol:
var name "Arthur"
var age 20
say "My name is $(name) and I am $(age) years old."
To represent new lines, use the \n symbol:
say "Hi!\nThis is in a new line!"
Here are some important things to notice about the ISlash language:
- All variables are global and can be accessed from anywhere, as there are no scopes. If you create a variable inside an if block, you will be able to reference it outside of the if block. The only exception to this rule are foreach element variables, which only exists inside the foreach block.
Example:
foreach element [1,2,3]
# element exists here!
endforeach
# element does not exist here!
- The VAR command will create new variables if they don't exist yet. If they do, the previous value will be replaced by the new one.
- Even though ISlash is a dynamically typed language, arrays cannot contain values of different types. Because of that, when creating an empty array, you must specify if it will contain numbers or strings.
Example:
# OK!
var array [1,2,3]
var array ["Hello","Bye"]
var array []number
var array []string
# NOT OK!
var array []
If you're curious and want to try out the ISlash language, the steps below will teach you how to setup a playground Docker container with ISlash installed and a collection of example programs for you to run.
-
Download Docker.
-
Clone this repository.
git clone https://github.com/ArthurSudbrackIbarra/ISlash-Programming-Language.git- Go to the repository directory.
cd ISlash-Programming-Language- Start the playground Docker container:
docker compose up -d- Enter inside the Docker container that you started:
docker exec -it islash-playground-container sh- Run the ISlash programs you wish with:
islash <PATH_TO_MY_PROGRAM>
# Example:
islash my-program.islNOTE: All files inside the 'example-programs' directory are shared between your host machine and the Docker container using a bind mount volume, so you can modify the .isl files or create new ones in your host machine and then run them from inside the container.
TIP: You can automatize steps 4-5 using the scripts inside the automation-scripts folder: start-container.bat and start-container.sh, depending on your OS.
To completely delete all the resources created in your machine, use the following commands:
- Stop the container.
docker compose down- Delete the container.
docker rm islash-playground-container- Delete the container image.
docker rmi islash-programming-language_islash-playgroundTo install ISlash locally in your machine instead of using Docker, perform the following steps:
-
Download Go ^1.19.
-
Clone this repository.
git clone https://github.com/ArthurSudbrackIbarra/ISlash-Programming-Language.git- Go to the repository directory.
cd ISlash-Programming-Language- Build the ISlash executable, the command below will generate an 'islash.exe' file on Windows or an 'islash' file on unix based operating systems.
go build -o islash- Add the executable to your PATH.
-
(Windows) Add the repository directory to your PATH environment variable.
-
(Unix) Move the created executable 'islash' to /usr/bin.
sudo mv islash /usr/binISlash has an official Docker Hub image that you can pull and use in your projects. See the example below:
Directory Structure:
My-ISlash-Project/
├─ Dockerfile
├─ main.isl
Dockerfile Example:
FROM magicmanatee/islash:1.0
WORKDIR /home/my-islash-project
COPY . .
CMD ["islash", "main.isl"]
These are some of the features that I might implement in the future:
- Functions
- Switch/Case
- Foreach with indexes, not only elements.
- 'continue' instruction to be used inside while loops.