Pygmalion in the greek mythologie is a sculptor that fell in love with one of his creations. In the myth, Aphrodite gives life to Galatea, the sculpture he fell in love with. This package is a python machine learning library that implements models for some common machine learning tasks. Everything that you need to give a mind of their own to inanimate silicon-based objects that are computers.
pygmalion can be installed through pip.
python -m pip install pygmalion
Architectures for several common machine learning tasks (regression, image classification, machine translation ...) are implemented in this package.
The inputs and outputs of the models are common python objects (such as numpy array and pandas dataframes).
In this section we are going to see how to load a dataset, train a model, display some metrics, and save a model.
>>> import pygmalion as ml
>>> import pygmalion.neural_networks as nn
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as pltYou can download a dataset and split it with the split function.
>>> ml.datasets.boston_housing("./")
>>> df = pd.read_csv("./boston_housing.csv")
>>> df_train, df_val, df_test = ml.utilities.split(df, weights=(0.8, 0.1, 0.1))Creating and training a model takes few lines of code.
>>> inputs, target = [c for c in df.columns if c != "medv"], "medv"
>>> model = nn.DenseRegressor(inputs, target, hidden_layers=[32, 32])
>>> x_train, y_train = model.data_to_tensor(df_train[inputs], df_train[target])
>>> x_val, y_val = model.data_to_tensor(df_val[inputs], df_val[target])
>>> history = model.fit((x_train, y_train), (x_val, y_val), n_steps=1000, patience=100, learning_rate=1.0E-3)Some usefull metrics can easily be evaluated.
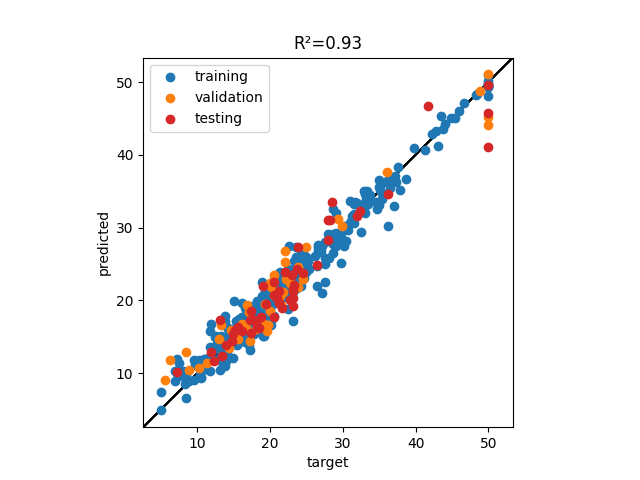
For a regressor model, the available metrics are MSE, RMSE, R2, and the correlation between target and prediction can be visualized with the plot_fitting function.
>>> f, ax = plt.subplots()
>>> ml.utilities.plot_fitting(df_train[target], model.predict(df_train), ax=ax, label="training")
>>> ml.utilities.plot_fitting(df_val[target], model.predict(df_val), ax=ax, label="validation")
>>> ml.utilities.plot_fitting(df_test[target], model.predict(df_test), ax=ax, label="testing", color="C3")
>>> R2 = ml.utilities.R2(model.predict(df_test), df_test[target])
>>> ax.set_title(f"R²={R2:.3g}")
>>> ax.set_xlabel("target")
>>> ax.set_ylabel("predicted")
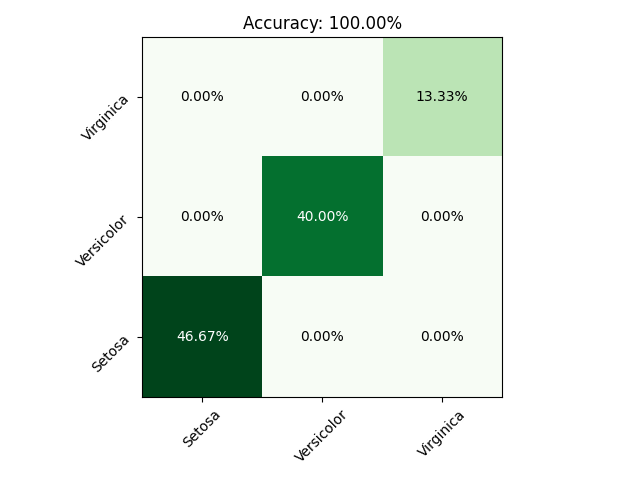
>>> plt.show()For a classifier model you can evaluate the accuracy, and display the confusion matrix.
>>> ml.datasets.iris("./")
>>> df = pd.read_csv("./iris.csv")
>>> df_train, df_val, df_test = ml.utilities.split(df, weights=(0.7, 0.2, 0.1))
>>> inputs, target = [c for c in df.columns if c != "variety"], "variety"
>>> classes = df[target].unique()
>>> model = nn.DenseClassifier(inputs, target, classes, hidden_layers=[8, 8, 8])
>>> train_data = model.data_to_tensor(df_train[inputs], df_train[target])
>>> val_data = model.data_to_tensor(df_train[inputs], df_train[target])
>>> model.fit(train_data, val_data, n_steps=1000, patience=100)
>>> f, ax = plt.subplots()
>>> y_test, y_pred = df_test[target], model.predict(df_test)
>>> ml.utilities.plot_matrix(ml.utilities.confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, classes=classes), ax=ax, cmap="Greens", write_values=True, format=".2%")
>>> acc = ml.utilities.accuracy(y_pred, y_test)
>>> ax.set_title(f"Accuracy: {acc:.2%}")
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>> plt.show()All the models can be saved directly to the disk with the save method. A model saved on the disk can then be loaded back with the load_model function.
>>> model.save("./model.pth")
>>> model = ml.utilities.load_model("./model.pth")For examples of model training see the samples folder in the github page.
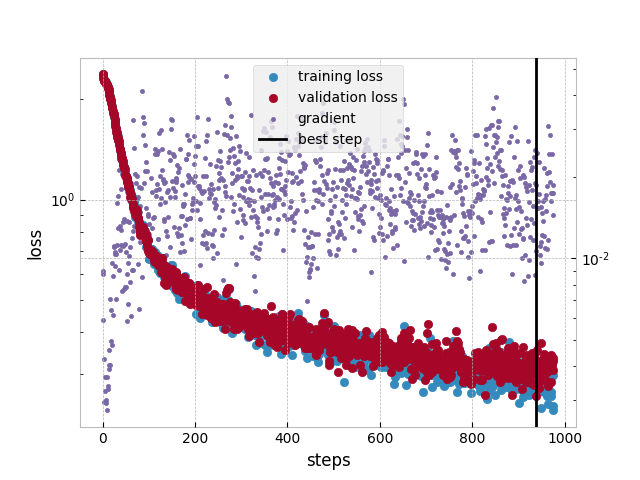
The neural networks are implemented in pytorch under the hood. Each model is a pytorch Module. The fit method of neural networks returns a train loss, validation loss, gradient scale history that can be ploted with the plot_loss functions.
>>> train_losses, val_losses, grad, best_step = model.fit(...)
>>> ml.utilities.plot_losses(train_losses, val_losses, grad, best_step)A DenseRegressor (or multi layer perceptron regressor) predicts a scalar value given an input of several variables. An example of DenseRegressor training was demonstrated in a previous section.
A DenseClassifier (or multi layer perceptron classifier) predicts a str class value given an input of several variables. An example of DenseClassifier training was presented in a previous section.
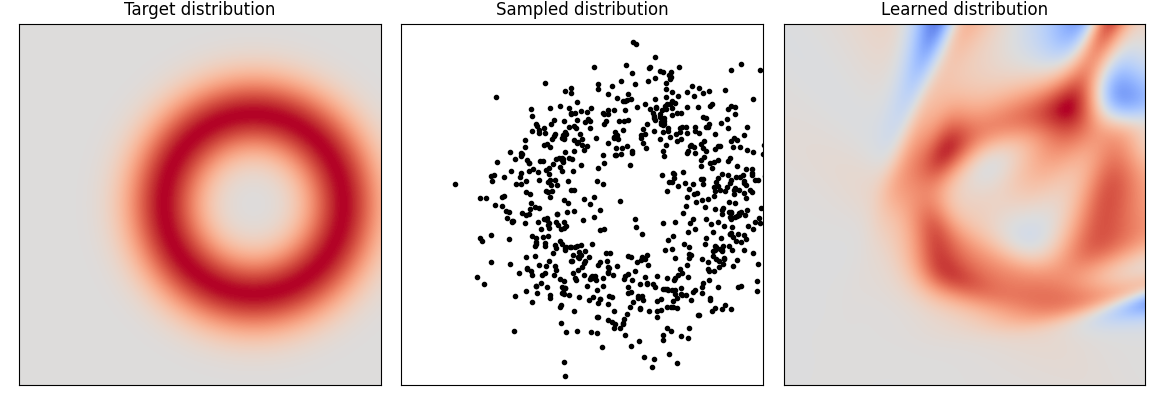
A ProbabilityDistribution is a multilayer perceptron used to learn the CDF (Cumulated Distribution Function) of tabular data in an unsupervised fashion. Countrary to gaussian mixture models it's PDF (Probability Density Function) is not constrained to beeing positive which makes it a degenerate distribution function. This model is usefull for anomaly detection, or training domain learning.
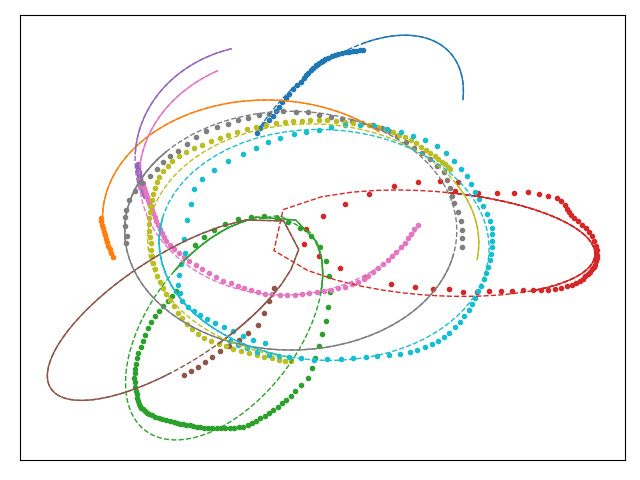
A TimeSeriesRegressor forecast future values of a time series. Here below a model trained to predict the next steps of random eliptical orbit trajectories.
It is implemented as an encoder/decoder Transformer.
An ImageClassifier predicts a str class given as input an image. Here below the predictions of a model trained on the fashion-MNIST dataset.
It is implemented as a Convolutional Neural Network similar to ResNet.
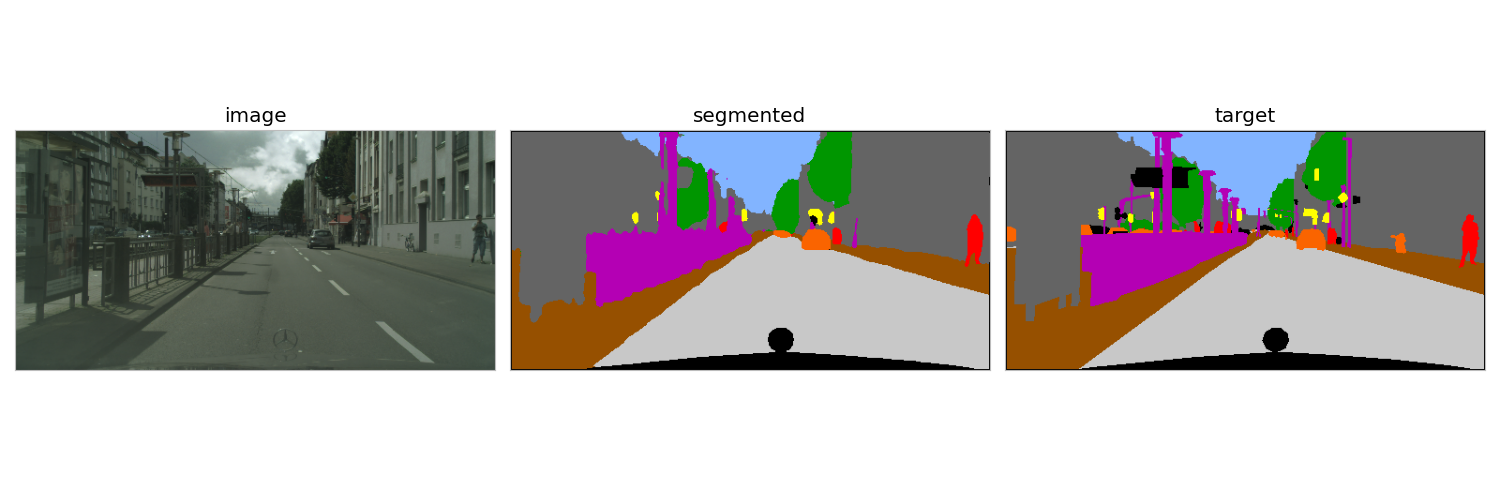
An ImageSegmenter predicts a class for each pixel of the input image (semantic segmentation). Here below the predictions of a model trained on the cityscape dataset.
It is implemented as a Convolutional Neural Network similar to U-Net.
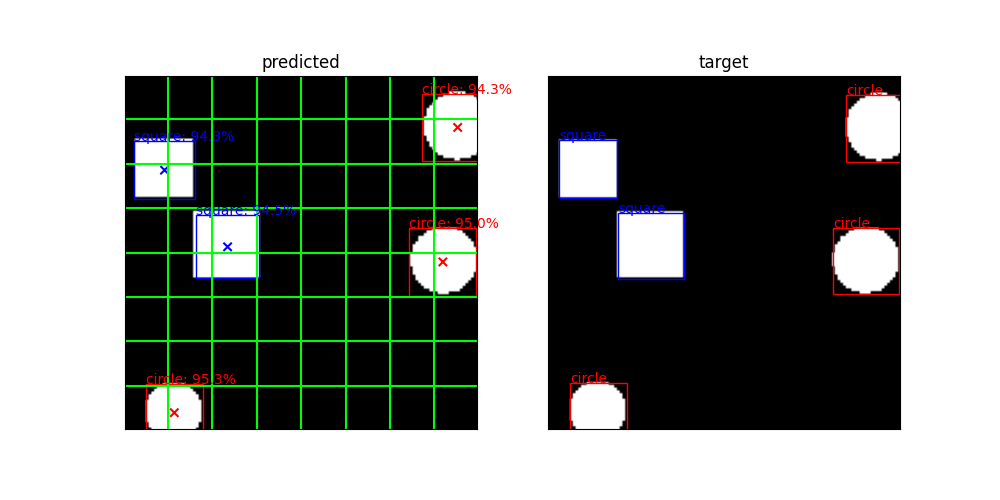
An ImageObjectDetector predict the presence and box coordinates of objects in an image. This model is an implementation of the YOLO convolutional neural network. Here below the prediction of a model trained to detect circles and squares in images generated on the fly:
A TextClassifier classifies text inputs. It is implemented as a transformer encoder. Here below some prediction of the model on a sentiment analysis task where tweets were to be classified as positive, neutral or negative.
@JetBlue Thanks! Her flight leaves at 2 but she's arriving to the airport early. Wedding is in VT in Sept. Grateful you fly to BTV!! :)
>>> positive
@united how are conditions in BOS today? I'm in UA994. Everything appears to be in time but I wanted to check.
>>> neutral
@AmericanAir it's been almost 3 days and it's still frozen. Thanks doll 😘😑
>>> negative
A TextTranslator model predicts a string outputs for a string inputs. It is implemented as an encoder/decoder transformer. Here below some predictions of a model trained to translate arabic numerals to roman numerals.
1411 >>> MCDXI
1132 >>> MCXXXII
1354 >>> MCCCLIV
1469 >>> MCDLXIX
1290 >>> MCCXC
1698 >>> MDCXCVIII
657 >>> DCLVII
132 >>> CXXXII
1662 >>> MDCLXII
1150 >>> MCL