${{\color{red}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂱}}}}$ ${{\color{black}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂡}}}}$ $\mathbb{\color{green}\Huge\ {0x1B.C-} \ \color{teal}{Sorting \ Algorithms} \ \color{green}{And} \ \color{teal}{Big O}}$ ${{\color{black}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂮}}}}$ ${{\color{red}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂾}}}}$
0x1B. C - Sorting algorithms & Big O is a project to be done in teams of 2 people or alone (solo)
- Done by: Bereket Dereje Mekonnen
- This project is meant to be done by groups of two students. Each group of two should pair program for at least the mandatory part.
- File_name: 📋 README.md file
- Created: 📅 On December 13, 2023
- Author: 💻 Bereket Dereje Mekonnen
- Project Title: 📖 0x1B. C - Sorting algorithms & Big O
- GitHub repository: 🗂 sorting_algorithms
- Directory: 📂 sorting_algorithms
- Project Tasks: Mandatory 📕 and Advanced 📗
- Tasks in number: 🔢 13 Tasks (4-Mandatory & 9-Advanced)
- Mandatory_Tasks: 📕 From Task 0 to 3
- Advanced_Tasks: 📗 From Task 4 to 12
PROJECT_TITLE: 🔠 0x1B. C - Sorting algorithms & Big O
GITHUB_REPOSITORY: 💾 sorting_algorithms 🗂
DIRECTORY: 📀 sorting_algorithms 📂
- print_array.c : is a C function that prints an array of integers.
- print_list.c : is a C function that prints a listint_t doubly-linked list.
- sort.h : is a Header file containing definitions and prototypes for all types and functions written for the project.
- deck.h : is a Header file containing definitions and prototypes for all types and functions written for the task 1000-sort_deck.c .
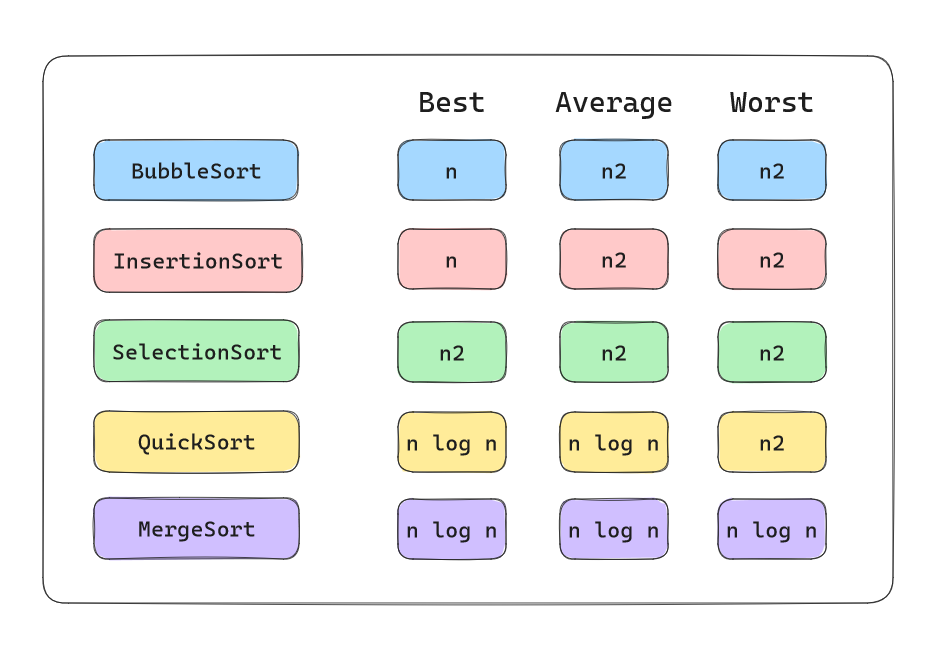
| 0 | Bubble sort | 0-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 1 | Insertion sort | 1-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 2 | Selection sort | 2-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 3 | Quick sort | 3-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 5 | Cocktail shaker sort |
101-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 6 | Counting sort | 102-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 7 | Merge sort | 103-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 8 | Heap sort | 104-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 10 | Bitonic sort | 106-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
| 11 | Quick Sort - Hoare Partition scheme |
107-O | 🟢 best case 🟡 average case 🔴 worst case |
- tests : Folder is a folder of test folders and files.
- There are two Folder inside tests folder, this are
- tests-main.c Folder
- tests-output Folder
- There are two Folder inside tests folder, this are
-
tests-main.c Folder is a folder of main.c files.
- main.c files are a files we can use them to test our functions.
-
Files📚 inside tests-main.c Folder 📂
-
tests-output Folder is a folder of output files.
- output files are a compiled files output on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Using gcc, Using the options -Wall -Werror -Wextra -pedantic -std=gnu89 plus using tests-main.c files.
-
Files📚 inside tests-output Folder 📂 are
- Sorting algorithm
- Big O notation
- Sorting algorithms animations
- 15 sorting algorithms in 6 minutes (WARNING: The following video can trigger seizure/epilepsy. It is not required for the project, as it is only a funny visualization of different sorting algorithms)
- CS50 Algorithms explanation in detail by David Malan
- All about sorting algorithms
- At the end of this project, You are expected to be able to explain to anyone, Without the help of Google:
- At least four different sorting algorithms.
- What is the Big O notation, and how to evaluate the time complexity of an algorithm.
- How to select the best sorting algorithm for a given input.
- What is a stable sorting algorithm.
- You are tasked to come up with solutions for the tasks below yourself to meet with the above learning objectives.
- You will not be able to meet the objectives of this or any following project by copying and pasting someone else’s work.
- You are not allowed to publish any content of this project.
- Any form of plagiarism is strictly forbidden and will result in removal from the program.
- Allowed editors: vi, vim, emacs.
- All your files will be compiled on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Using gcc, Using the options -Wall -Werror -Wextra -pedantic -std=gnu89
- All your files should end with a new line
- A README.md file🧾, at the root of the folder 📂 of the project is mandatory.
- Your code should use the Betty style. It will be checked using betty-style.pl, and betty-doc.pl.
- You are not allowed to use global variables.
- No more than 5 functions per file.
- **Unless specified otherwise,**You are not allowed to use the standard library. Any use of functions like printf, puts, … is totally forbidden.
- In the following examples, the main.c files are shown as examples. You can use them to test your functions, but you don’t have to push them to your repo (if you do we won’t take them into account). We will use our own main.c files at compilation. Our main.c files might be different from the one shown in the examples.
- The prototypes of all your functions should be included in your header file called sort.h
- Don’t forget to push your header file .
- All your header files should be include guarded
- A list/array does not need to be esorted if its size is less than 2.
There should be one project repository per group. If you clone/fork/whatever a project repository with the same name before the second deadline, you risk a 0% score.
- For this project you are given the following print_array, and print_list functions:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/**
* print_array - Prints an array of integers
*
* @array: The array to be printed
* @size: Number of elements in @array
*/
void print_array(const int *array, size_t size)
{
size_t i;
i = 0;
while (array && i < size)
{
if (i > 0)
printf(", ");
printf("%d", array[i]);
++i;
}
printf("\n");
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* print_list - Prints a list of integers
*
* @list: The list to be printed
*/
void print_list(const listint_t *list)
{
int i;
i = 0;
while (list)
{
if (i > 0)
printf(", ");
printf("%d", list->n);
++i;
list = list->next;
}
printf("\n");
}- Our files print_array and print_list (containing the print_array and print_list functions) will be compiled with your functions during the correction.
- Please declare the prototype of the functions print_array, and print_list in your sort.h header file.
- Please use the following data structure for doubly linked list:
/**
* struct listint_s - Doubly linked list node
*
* @n: Integer stored in the node
* @prev: Pointer to the previous element of the list
* @next: Pointer to the next element of the list
*/
typedef struct listint_s
{
const int n;
struct listint_s *prev;
struct listint_s *next;
} listint_t;-
Please, note this format is used for Quiz and Task questions.
-
Please use the “short” notation (don’t use constants). Example: O(nk) or O(wn) should be written O(n). If an answer is required within a file, all your answers files must have a newline at the end.
- Here is a quick tip to help you test your sorting algorithms with big sets of random integers: Random.org
PROJECT_TITLE: 🔠 0x1B. C - Sorting algorithms & Big O
GITHUB_REPOSITORY: 💾 sorting_algorithms 🗂
DIRECTORY: 📀 sorting_algorithms 📂
- File_name: 📋 README.md file
- Created: 📅 On December 13, 2023
- Author: 💻 Bereket Dereje Mekonnen
- Project Title: 📖 0x1B. C - Sorting algorithms & Big O
- GitHub repository: 🗂 sorting_algorithms
- Directory: 📂 sorting_algorithms
- Project Tasks: Mandatory 📕 and Advanced 📗
- Tasks in number: 🔢 13 Tasks (4-Mandatory & 9-Advanced)
- Mandatory_Tasks: 📕 From Task 0 to 3
- Advanced_Tasks: 📗 From Task 4 to 12
- File:
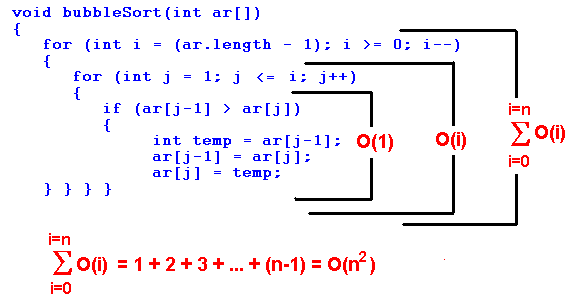
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Bubble sort algorithm
- Prototype: void bubble_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 0-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Bubble sortalgorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 0-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
bubble_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 0-bubble_sort.c 0-main.c print_array.c -o bubble
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./bubble
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 99, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 99, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 99, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 99, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7, 99
19, 48, 13, 71, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7, 99
19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 96, 73, 86, 7, 99
19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 73, 96, 86, 7, 99
19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 7, 99
19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 73, 86, 7, 96, 99
19, 13, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 7, 96, 99
19, 13, 48, 52, 71, 73, 7, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 7, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 7, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 7, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 7, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 7, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 7, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts a doubly linked list of integers in ascending order using the Insertion sort algorithm
- Prototype: void insertion_sort_list(listint_t **list);
- You are not allowed to modify the expected to print the integer n of a node. You have to swap the nodes themselves.
- You’re expected to print the list after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 1-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Insertion sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 1-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* create_listint - Creates a doubly linked list from an array of integers
*
* @array: Array to convert to a doubly linked list
* @size: Size of the array
*
* Return: Pointer to the first element of the created list. NULL on failure
*/
listint_t *create_listint(const int *array, size_t size)
{
listint_t *list;
listint_t *node;
int *tmp;
list = NULL;
while (size--)
{
node = malloc(sizeof(*node));
if (!node)
return (NULL);
tmp = (int *)&node->n;
*tmp = array[size];
node->next = list;
node->prev = NULL;
list = node;
if (list->next)
list->next->prev = list;
}
return (list);
}
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
listint_t *list;
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
list = create_listint(array, n);
if (!list)
return (1);
print_list(list);
printf("\n");
insertion_sort_list(&list);
printf("\n");
print_list(list);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 1-main.c 1-insertion_sort_list.c print_list.c -o insertion
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./bubble
./insertion
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 99, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 13, 71, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 13, 48, 71, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 71, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 71, 52, 99, 96, 73, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 99, 96, 73, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 96, 99, 73, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 96, 73, 99, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 96, 99, 86, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 96, 86, 99, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99, 7
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 7, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 7, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 7, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 7, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 52, 7, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 48, 7, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 7, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 7, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Selection sort algorithm
- Prototype: void selection_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 2-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Selection sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 2-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
selection_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89
2-main.c 2-selection_sort.c print_array.c -o select
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./select
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
7, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 19
7, 13, 99, 71, 48, 52, 96, 73, 86, 19
7, 13, 19, 71, 48, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 71, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 96, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Quick sort algorithm
- Prototype: void quick_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You must implement the Lomuto partition scheme.
- The pivot should always be the last element of the partition being sorted.
- You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 3-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Quick sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case-,Average,-performance)
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 3-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
quick_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 3-main.c 3-quick_sort.c print_array.c -o quick
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./quick
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
7, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 19
7, 13, 99, 71, 48, 52, 96, 73, 86, 19
7, 13, 19, 71, 48, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 71, 48, 52, 73, 96, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 71, 48, 52, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 71, 52, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Shell sort algorithm, using the Knuth sequence
- Prototype: void shell_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You must use the following sequence of intervals (a.k.a the Knuth sequence):
- You’re expected to print the array after each time you decrease the interval (See example below).
No big O notations of the time complexity of the Shell sort (Knuth sequence) algorithm needed - as the complexity is dependent on the size of array and gap.
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 100-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
shell_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 100-main.c 100-shell_sort.c print_array.c -o shell
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./shell
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
13, 7, 96, 71, 19, 48, 99, 73, 86, 52
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- Write a function that sorts a doubly linked list of integers in ascending order using the Cocktail shaker sort algorithm
- Prototype: void cocktail_sort_list(listint_t **list);
- You are not allowed to modify the integer n of a node. You have to swap the nodes themselves.
- You’re expected to print the list after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 101-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Cocktail shaker sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case-,Average%20performance,-%EF%BF%BD)
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 101-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* create_listint - Creates a doubly linked list from an array of integers
*
* @array: Array to convert to a doubly linked list
* @size: Size of the array
*
* Return: Pointer to the first element of the created list. NULL on failure
*/
listint_t *create_listint(const int *array, size_t size)
{
listint_t *list;
listint_t *node;
int *tmp;
list = NULL;
while (size--)
{
node = malloc(sizeof(*node));
if (!node)
return (NULL);
tmp = (int *)&node->n;
*tmp = array[size];
node->next = list;
node->prev = NULL;
list = node;
if (list->next)
list->next->prev = list;
}
return (list);
}
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
listint_t *list;
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
list = create_listint(array, n);
if (!list)
return (1);
print_list(list);
printf("\n");
cocktail_sort_list(&list);
printf("\n");
print_list(list);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 101-main.c 101-cocktail_sort_list.c print_list.c -o cocktail
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./cocktail
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 99, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 99, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 99, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 99, 86, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99, 7
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7, 99
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 7, 86, 99
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 7, 73, 86, 99
19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 7, 96, 73, 86, 99
19, 48, 71, 13, 7, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
19, 48, 71, 7, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
19, 48, 7, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
19, 7, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 19, 48, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 19, 48, 13, 71, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 73, 96, 86, 99
7, 19, 48, 13, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 19, 13, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Counting sort algorithm
- Prototype: void counting_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You can assume that array will contain only numbers >= 0 .
- You are allowed to use malloc and free for this task.
- You’re expected to print your counting array after once it is set up (See example below).
- Write in the file 102-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Counting sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 102-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
counting_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 102-main.c 102-counting_sort.c print_array.c -o counting
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./counting
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Merge sort algorithm
- Prototype: void merge_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You must implement the top-down merge sort algorithm.
- When you divide an array into two sub-arrays, [the size of the left array should always be] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort#:~:text=i%2B%2B)-,A%5Bi%5D%20%3D%20B%5Bi%5D%3B,-%7D) <= [the size of the right array] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort#:~:text=i%2B%2B)-,A%5Bi%5D%20%3D%20B%5Bi%5D%3B,-%7D) i.e. {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} -> {1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}
- Sort the left array before the right array
- You are allowed to use printf.
- You are allowed to use malloc and free only once (only one call)
- Output: see example
- Write in the file 103-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Merge sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 103-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
merge_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 103-main.c 103-merge_sort.c print_array.c -o merge
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./merge
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
Merging...
[left]: 19
[right]: 48
[Done]: 19, 48
Merging...
[left]: 71
[right]: 13
[Done]: 13, 71
Merging...
[left]: 99
[right]: 13, 71
[Done]: 13, 71, 99
Merging...
[left]: 19, 48
[right]: 13, 71, 99
[Done]: 13, 19, 48, 71, 99
Merging...
[left]: 52
[right]: 96
[Done]: 52, 96
Merging...
[left]: 86
[right]: 7
[Done]: 7, 86
Merging...
[left]: 73
[right]: 7, 86
[Done]: 7, 73, 86
Merging...
[left]: 52, 96
[right]: 7, 73, 86
[Done]: 7, 52, 73, 86, 96
Merging...
[left]: 13, 19, 48, 71, 99
[right]: 7, 52, 73, 86, 96
[Done]: 7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Heap sort algorithm
- Prototype: void heap_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 104-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Heap sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 104-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
heap_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 104-main.c 104-heap_sort.c print_array.c -o heap
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./heap
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
19, 48, 99, 86, 13, 52, 96, 73, 71, 7
19, 86, 99, 48, 13, 52, 96, 73, 71, 7
19, 86, 99, 73, 13, 52, 96, 48, 71, 7
99, 86, 19, 73, 13, 52, 96, 48, 71, 7
99, 86, 96, 73, 13, 52, 19, 48, 71, 7
7, 86, 96, 73, 13, 52, 19, 48, 71, 99
96, 86, 7, 73, 13, 52, 19, 48, 71, 99
96, 86, 52, 73, 13, 7, 19, 48, 71, 99
71, 86, 52, 73, 13, 7, 19, 48, 96, 99
86, 71, 52, 73, 13, 7, 19, 48, 96, 99
86, 73, 52, 71, 13, 7, 19, 48, 96, 99
48, 73, 52, 71, 13, 7, 19, 86, 96, 99
73, 48, 52, 71, 13, 7, 19, 86, 96, 99
73, 71, 52, 48, 13, 7, 19, 86, 96, 99
19, 71, 52, 48, 13, 7, 73, 86, 96, 99
71, 19, 52, 48, 13, 7, 73, 86, 96, 99
71, 48, 52, 19, 13, 7, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 48, 52, 19, 13, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
52, 48, 7, 19, 13, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 48, 7, 19, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
48, 13, 7, 19, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
48, 19, 7, 13, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 19, 7, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
19, 13, 7, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
13, 7, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Radix sort algorithm
- Prototype: void radix_sort(int *array, size_t size);
- You must implement the LSD Radix sort algorithm.
- You can assume that array will contain only numbers >= 0 .
- You are allowed to use malloc and free for this task.
- You’re expected to print the array each time you increase your significant digit (See example below).
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 105-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
radix_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 105-main.c 105-radix_sort.c print_array.c -o radix
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./radix
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
71, 52, 13, 73, 96, 86, 7, 48, 19, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Bitonic sort algorithm
- Write in the file 106-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Bitonic sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 106-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {100, 93, 40, 57, 14, 58, 85, 54, 31, 56, 46, 39, 15, 26, 78, 13};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
bitonic_sort(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 106-main.c 106-bitonic_sort.c print_array.c -o bitonic
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./bitonic
100, 93, 40, 57, 14, 58, 85, 54, 31, 56, 46, 39, 15, 26, 78, 13
Merging [16/16] (UP):
100, 93, 40, 57, 14, 58, 85, 54, 31, 56, 46, 39, 15, 26, 78, 13
Merging [8/16] (UP):
100, 93, 40, 57, 14, 58, 85, 54
Merging [4/16] (UP):
100, 93, 40, 57
Merging [2/16] (UP):
100, 93
Result [2/16] (UP):
93, 100
Merging [2/16] (DOWN):
40, 57
Result [2/16] (DOWN):
57, 40
Result [4/16] (UP):
40, 57, 93, 100
Merging [4/16] (DOWN):
14, 58, 85, 54
Merging [2/16] (UP):
14, 58
Result [2/16] (UP):
14, 58
Merging [2/16] (DOWN):
85, 54
Result [2/16] (DOWN):
85, 54
Result [4/16] (DOWN):
85, 58, 54, 14
Result [8/16] (UP):
14, 40, 54, 57, 58, 85, 93, 100
Merging [8/16] (DOWN):
31, 56, 46, 39, 15, 26, 78, 13
Merging [4/16] (UP):
31, 56, 46, 39
Merging [2/16] (UP):
31, 56
Result [2/16] (UP):
31, 56
Merging [2/16] (DOWN):
46, 39
Result [2/16] (DOWN):
46, 39
Result [4/16] (UP):
31, 39, 46, 56
Merging [4/16] (DOWN):
15, 26, 78, 13
Merging [2/16] (UP):
15, 26
Result [2/16] (UP):
15, 26
Merging [2/16] (DOWN):
78, 13
Result [2/16] (DOWN):
78, 13
Result [4/16] (DOWN):
78, 26, 15, 13
Result [8/16] (DOWN):
78, 56, 46, 39, 31, 26, 15, 13
Result [16/16] (UP):
13, 14, 15, 26, 31, 39, 40, 46, 54, 56, 57, 58, 78, 85, 93, 100
13, 14, 15, 26, 31, 39, 40, 46, 54, 56, 57, 58, 78, 85, 93, 100
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$- File:
- Write a function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Quick sort algorithm
- Prototype: void quick_sort_hoare(int *array, size_t size);
- You must implement the Hoare partition scheme.
- The pivot should always be the last element of the partition being sorted.
- You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below).
- Write in the file 107-O, the big O notations of the time complexity of the Quick sort algorithm, with 1 notation per line:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 107-main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
/**
* main - Entry point
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
int main(void)
{
int array[] = {19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7};
size_t n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
print_array(array, n);
printf("\n");
quick_sort_hoare(array, n);
printf("\n");
print_array(array, n);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 107-main.c 107-quick_sort_hoare.c print_array.c -o quick
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./quick
19, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 7
7, 48, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 19
7, 19, 99, 71, 13, 52, 96, 73, 86, 48
7, 19, 13, 71, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 48
7, 13, 19, 71, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 48
7, 13, 19, 48, 99, 52, 96, 73, 86, 71
7, 13, 19, 48, 71, 52, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 96, 73, 86, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 86, 73, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
7, 13, 19, 48, 52, 71, 73, 86, 96, 99
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$Another example of output:
alex@/tmp/sort$ ./quick_2
87, 65, 28, 63, 93, 52, 39, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 11, 16, 21, 75, 36, 71, 8, 45, 38
38, 65, 28, 63, 93, 52, 39, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 11, 16, 21, 75, 36, 71, 8, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 63, 93, 52, 39, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 11, 16, 21, 75, 36, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 93, 52, 39, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 11, 16, 21, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 21, 52, 39, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 11, 16, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 21, 16, 39, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 11, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 21, 16, 11, 59, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 26, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 21, 16, 11, 26, 27, 30, 24, 83, 69, 62, 13, 6, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 21, 16, 11, 26, 27, 30, 24, 6, 69, 62, 13, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
38, 8, 28, 36, 21, 16, 11, 26, 27, 30, 24, 6, 13, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
13, 8, 28, 36, 21, 16, 11, 26, 27, 30, 24, 6, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
13, 8, 6, 36, 21, 16, 11, 26, 27, 30, 24, 28, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
13, 8, 6, 11, 21, 16, 36, 26, 27, 30, 24, 28, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
11, 8, 6, 13, 21, 16, 36, 26, 27, 30, 24, 28, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
6, 8, 11, 13, 21, 16, 36, 26, 27, 30, 24, 28, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
6, 8, 11, 13, 21, 16, 28, 26, 27, 30, 24, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
6, 8, 11, 13, 21, 16, 28, 26, 27, 24, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
6, 8, 11, 13, 21, 16, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 88, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 87
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 87, 58, 92, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 45, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 87, 58, 45, 59, 42, 39, 52, 93, 75, 63, 71, 65, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 83, 87, 58, 45, 59, 42, 39, 52, 65, 75, 63, 71, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 71, 87, 58, 45, 59, 42, 39, 52, 65, 75, 63, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 69, 71, 63, 58, 45, 59, 42, 39, 52, 65, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 65, 71, 63, 58, 45, 59, 42, 39, 52, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 62, 65, 52, 63, 58, 45, 59, 42, 39, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 65, 52, 63, 58, 45, 59, 42, 62, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 62, 52, 63, 58, 45, 59, 42, 65, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 62, 52, 42, 58, 45, 59, 63, 65, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 59, 52, 42, 58, 45, 62, 63, 65, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 45, 52, 42, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 45, 42, 52, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 42, 45, 52, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 71, 69, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 42, 45, 52, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 69, 71, 75, 87, 83, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 42, 45, 52, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 69, 71, 75, 83, 87, 93, 92, 88
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 42, 45, 52, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 69, 71, 75, 83, 87, 88, 92, 93
6, 8, 11, 13, 16, 21, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 36, 38, 39, 42, 45, 52, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 69, 71, 75, 83, 87, 88, 92, 93
alex@/tmp/sort$ - File:
- Write a function that sorts a deck of cards.
- Prototype: void sort_deck(deck_node_t **deck);
- You are allowed to use C standard library function qsort
- Please use the following data structures:
typedef enum kind_e
{
SPADE = 0,
HEART,
CLUB,
DIAMOND
} kind_t;
/**
* struct card_s - Playing card
*
* @value: Value of the card
* From "Ace" to "King"
* @kind: Kind of the card
*/
typedef struct card_s
{
const char *value;
const kind_t kind;
} card_t;
/**
* struct deck_node_s - Deck of card
*
* @card: Pointer to the card of the node
* @prev: Pointer to the previous node of the list
* @next: Pointer to the next node of the list
*/
typedef struct deck_node_s
{
const card_t *card;
struct deck_node_s *prev;
struct deck_node_s *next;
} deck_node_t;- You have to push you deck.h header file, containing the previous data structures definition.
- Each node of the doubly linked list contains a card that you cannot modify. You have to swap the nodes.
- You can assume there is exactly 52 elements in the doubly linked list.
- You are free to use the sorting algorithm of your choice.
- The deck must be ordered:
- From Ace
${{\color{red}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂱}}}}$ ${{\color{black}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂡}}}}$ 🅰️ to 🤴🏾${{\color{black}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂮}}}}$ ${{\color{red}\Huge{\textsf{ 🂾}}}}$ King - From Spades
♠️ to♦️ Diamonds - See example below
- From Ace
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms/tests/tests-main.c$ cat 1000-main.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "deck.h"
void print_deck(const deck_node_t *deck)
{
size_t i;
char kinds[4] = {'S', 'H', 'C', 'D'};
i = 0;
while (deck)
{
if (i)
printf(", ");
printf("{%s, %c}", deck->card->value, kinds[deck->card->kind]);
if (i == 12)
printf("\n");
i = (i + 1) % 13;
deck = deck->next;
}
}
deck_node_t *init_deck(const card_t cards[52])
{
deck_node_t *deck;
deck_node_t *node;
size_t i;
i = 52;
deck = NULL;
while (i--)
{
node = malloc(sizeof(*node));
if (!node)
return (NULL);
node->card = &cards[i];
node->next = deck;
node->prev = NULL;
if (deck)
deck->prev = node;
deck = node;
}
return (deck);
}
int main(void)
{
card_t cards[52] = {
{"Jack", CLUB}, {"4", HEART}, {"3", HEART}, {"3", DIAMOND}, {"Queen", HEART}, {"5", HEART}, {"5", SPADE}, {"10", HEART}, {"6", HEART}, {"5", DIAMOND}, {"6", SPADE}, {"9", HEART}, {"7", DIAMOND}, {"Jack", SPADE}, {"Ace", DIAMOND}, {"9", CLUB}, {"Jack", DIAMOND}, {"7", SPADE}, {"King", DIAMOND}, {"10", CLUB}, {"King", SPADE}, {"8", CLUB}, {"9", SPADE}, {"6", CLUB}, {"Ace", CLUB}, {"3", SPADE}, {"8", SPADE}, {"9", DIAMOND}, {"2", HEART}, {"4", DIAMOND}, {"6", DIAMOND}, {"3", CLUB}, {"Queen", CLUB}, {"10", SPADE}, {"8", DIAMOND}, {"8", HEART}, {"Ace", SPADE}, {"Jack", HEART}, {"2", CLUB}, {"4", SPADE}, {"2", SPADE}, {"2", DIAMOND}, {"King", CLUB}, {"Queen", SPADE}, {"Queen", DIAMOND}, {"7", CLUB}, {"7", HEART}, {"5", CLUB}, {"10", DIAMOND}, {"4", CLUB}, {"King", HEART}, {"Ace", HEART},
};
deck_node_t *deck;
deck = init_deck(cards);
print_deck(deck);
printf("\n");
sort_deck(&deck);
printf("\n");
print_deck(deck);
return (0);
}BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ gcc -Wall -Wextra -Werror -pedantic -std=gnu89 1000-main.c 1000-sort_deck.c -o deck
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$ ./deck
{Jack, C}, {4, H}, {3, H}, {3, D}, {Queen, H}, {5, H}, {5, S}, {10, H}, {6, H}, {5, D}, {6, S}, {9, H}, {7, D}
{Jack, S}, {Ace, D}, {9, C}, {Jack, D}, {7, S}, {King, D}, {10, C}, {King, S}, {8, C}, {9, S}, {6, C}, {Ace, C}, {3, S}
{8, S}, {9, D}, {2, H}, {4, D}, {6, D}, {3, C}, {Queen, C}, {10, S}, {8, D}, {8, H}, {Ace, S}, {Jack, H}, {2, C}
{4, S}, {2, S}, {2, D}, {King, C}, {Queen, S}, {Queen, D}, {7, C}, {7, H}, {5, C}, {10, D}, {4, C}, {King, H}, {Ace, H}
{Ace, S}, {2, S}, {3, S}, {4, S}, {5, S}, {6, S}, {7, S}, {8, S}, {9, S}, {10, S}, {Jack, S}, {Queen, S}, {King, S}
{Ace, H}, {2, H}, {3, H}, {4, H}, {5, H}, {6, H}, {7, H}, {8, H}, {9, H}, {10, H}, {Jack, H}, {Queen, H}, {King, H}
{Ace, C}, {2, C}, {3, C}, {4, C}, {5, C}, {6, C}, {7, C}, {8, C}, {9, C}, {10, C}, {Jack, C}, {Queen, C}, {King, C}
{Ace, D}, {2, D}, {3, D}, {4, D}, {5, D}, {6, D}, {7, D}, {8, D}, {9, D}, {10, D}, {Jack, D}, {Queen, D}, {King, D}
BekaHabesha@BekaHabesha:~/sorting_algorithms$