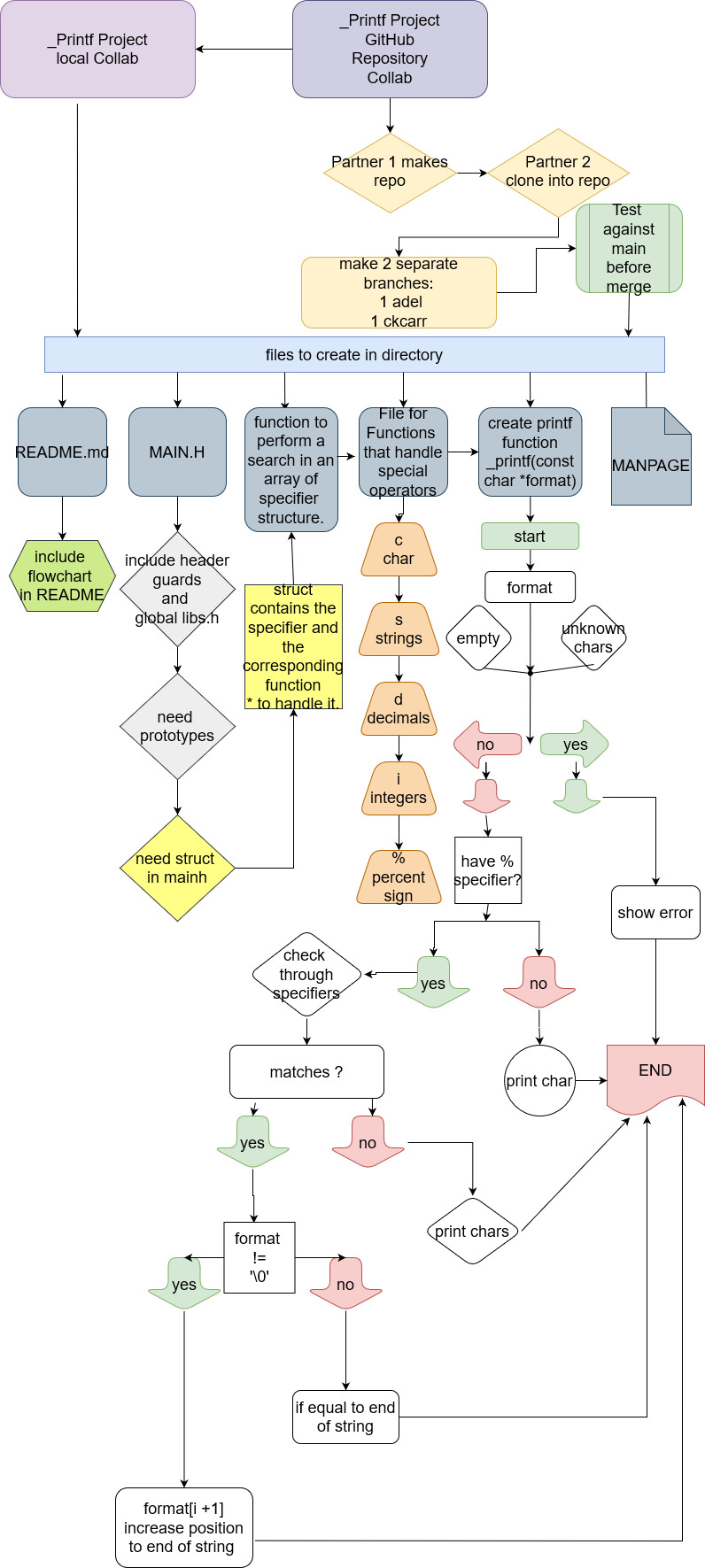
This project challenged us to recreate some of the functionallity of printf without global variables or switch / case statements. The only allowed functions or macros were:
write,
malloc,
free,
va_start,
va_arg,
va_copy, and
va_end.
With these tools we created a program that returns the number of characters printed (excluding the null byte used to end output to strings), writes to the standard output stream, and handles the following conversion specifier types:
c,
s,
d,
i.
In this project we did not handle:
flag characters,
field width,
precision,
length modifiers.
The _printf function was coded on an Ubuntu 20.04 LTS machine with gcc version 9.4.0.
Compilation was competed with the following gcc options -Wall -Werror -Wextra -pedantic -std=gnu89
To use the _printf function, assuming the above dependencies have been installed,
compile all .c files in the repository and include the header main.h with
any main function.
Example main.c:
#include "main.h"
int main(void)
{
_printf("Hello, World!");
return (0);
}
Compilation:
$ gcc *.c -o tester
Output:
$ ./tester
Hello, World!
$
The function _printf writes output to standard output under the control of a format string that specifies how subsequent arguments are
converted for output.
Prototype: int _printf(const char *format, ...);
Upon successful return, _printf returns the number of characters printed
(excluding the terminating null byte used to end output to strings). If an
output error is encountered, the function returns -1.
The format string argument is a constant character string composed of zero
or more directives:
ordinary characters (not %) which are copied unchanged
to the output stream;
conversion specifiers, each of which results in
fetching zero or more subsequent arguments.
Conversion specification is
introduced by the character % and ends with a conversion specifier.
This project does not include the zero or more flags, optional minimum field width, optional precision or optional length modifier.
The conversion specifier (introduced by the character %) is a character that
specifies the type of conversion to be applied. The _printf function
supports the following conversion specifiers: c,s,i,d,%
The int argument is converted to signed decimal notation.
Example main.c:
int main(void)
{
_printf("%d\n", 7);
}
Output:
7
by Crystal Carrillo and Ann Adel Knode