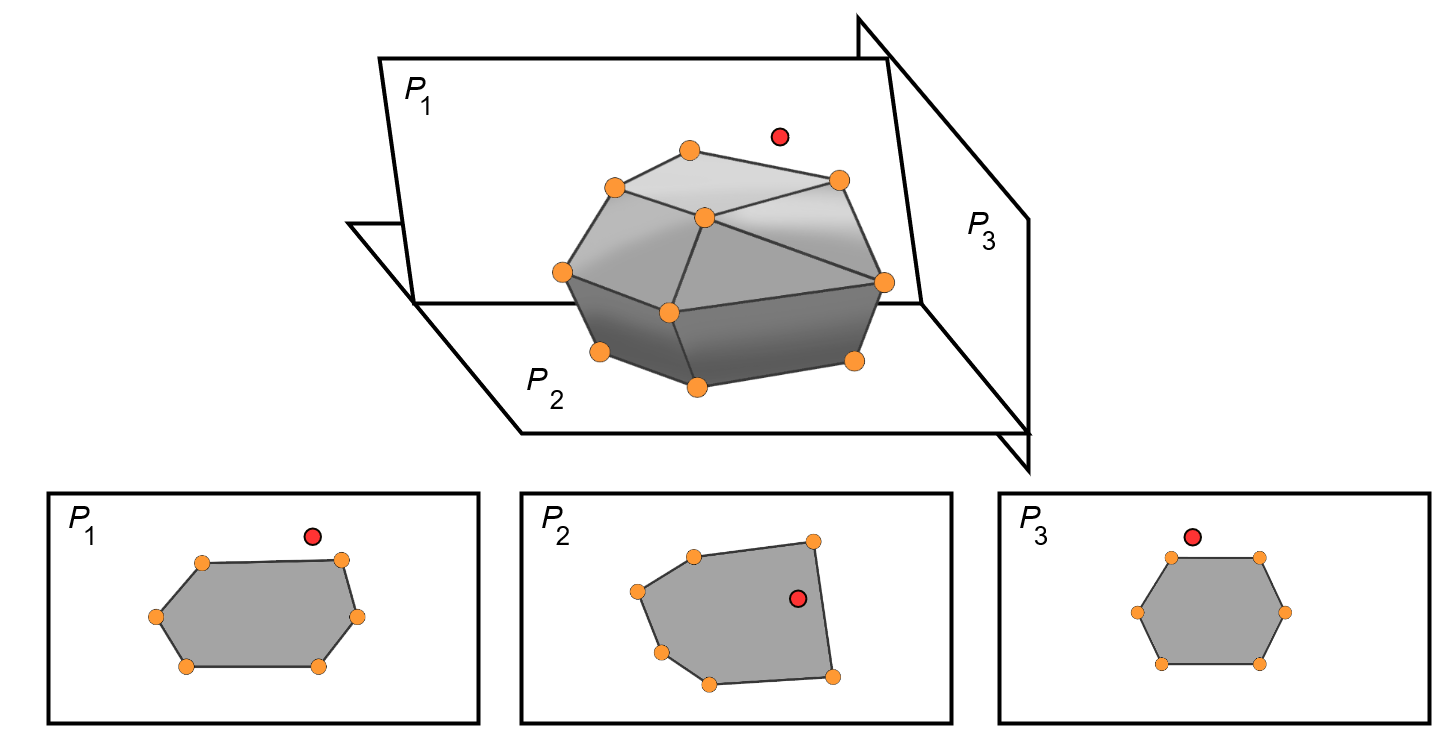
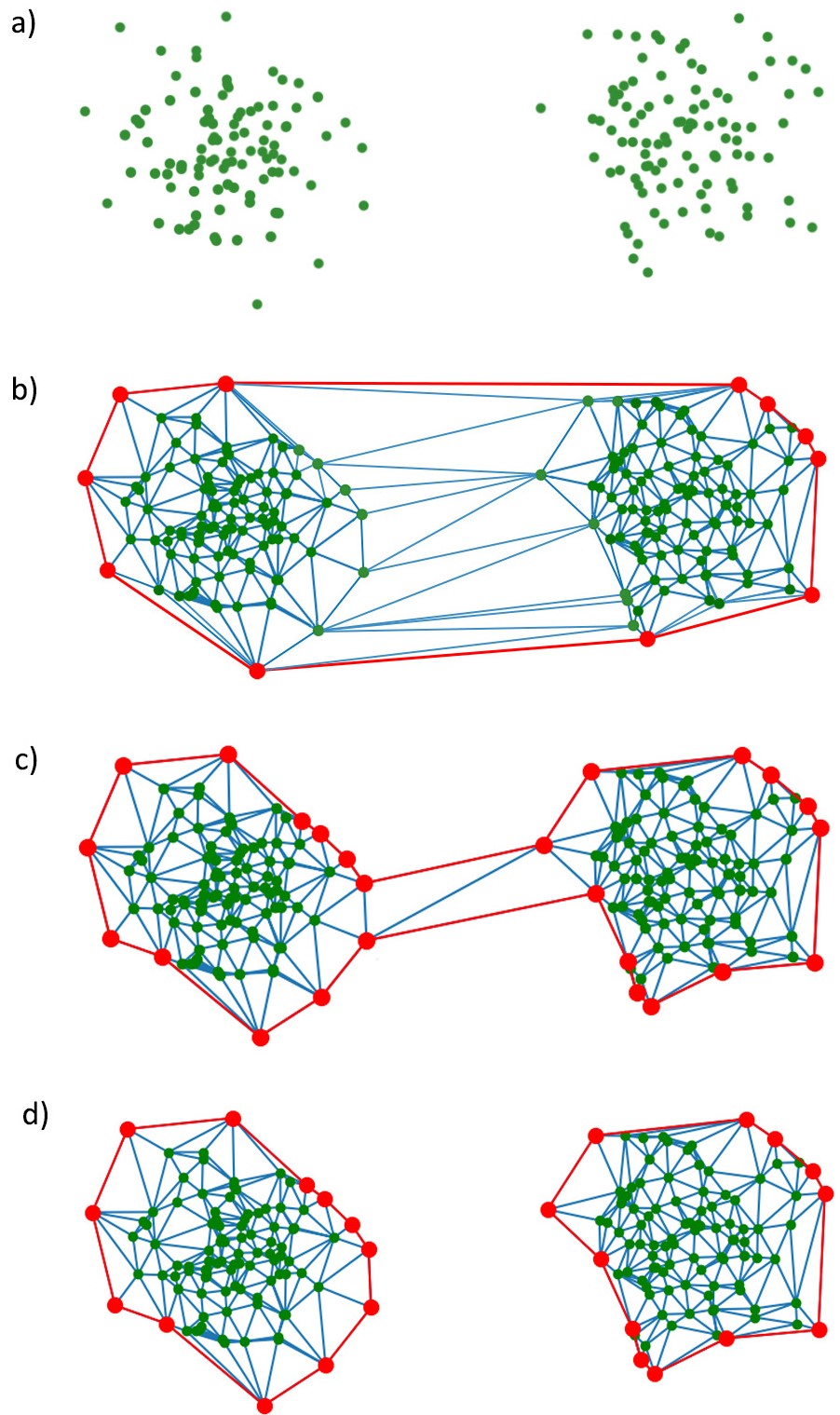
OCENCH is a One-Class Classification and Anomaly Detection method based on the use of random projections of the original data space to reduce their complexity (Figure 1), followed by a process based on Delaunay triangulation to geometrically represent the normal class in these low-dimensional spaces through subdivisible and expandable non-convex hulls (Figure 2).
The limits of the normal class are iteratively adapted during the training phase. This process is carried out based on a normalized parameter (l) that controls the adjustment level and can be easily tuned by the user for each scenario. Furthermore, if in a low-dimensional space the normal class cannot be accurately represented by a single non-convex hull, it will be subdivided as many times as necessary to fit the shape of the data. Finally, to avoid the effect of over-adjustment of the training data, the limits of the NCHs will be expanded based on the expansion factor parameter (extend).
The developed OCENCH algorithm allows working with non-convex data sets in a novel way, offering a robust behavior and remarkable performance, positioning itself as an alternative for both convex and non-convex problems.
Figure 1: Instead of calculating the convex hull of a point cloud in the original space (upper part of Figure 1), the point cloud is projected into two-dimensional spaces in which the calculation of the convex hull is affordable (bottom of Figure 1). Anomalous data (red) will ideally lie outside the normal limits in some of the projections.
Figure 2: Characterization of two separate point regions using OCENCH: (a) Projected data set; (b) Initial convex hull; (c) Pruned non-convex hull; (d) Subdivided non-convex hulls.
OCENCH can be installed from PyPI using the command:
pip install ocench
To run OCENCH it is necessary to have installed the libraries listed in the requirements.txt file.
After this, we can now execute the two available methods. We recommend you read the original article to understand the operation and impact of the parameters in detail.
- NCH_train (X, n_projections, l, extend): Trains the model with only normal data.
- Parameters:
- X: training dataset as a numpy array where each row corresponds with a sample and each column with a feature.
- n_projections: Number of random 2D-projections.
- l : Maximum edge length allowed in the NCH (Non-Convex Hull). Typical values: 0.3, 0.5, 1, 2.
- extend: Expansion parameter of the NCH. Extend = 0 implies no expansion, while extend > 0 will expand the edges if it's possible). Typical values: 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3.
- Returns:
- model: entire model containing the information about the projection matrices and the ENCHs (Expanded Non-Convex Hulls).
- Parameters:
- NCH_classify (X, model): Predicts the class of new (normal and anomalous) data.
- Parameters:
- X: test dataset as a numpy array where each row corresponds with a sample and each column with a feature.
- model: Model returned during training.
- Returns:
- labels: 1-D numpy array containing the predicted labels for the input dataset, where 0 = Normal and 1 = Anomaly.
- Parameters:
from ocench import *
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
# Create a toy dataset using two isotropic Gaussian blobs (one for each class)
num_normal_samples = 1000 # Training dataset size (only normal data)
num_abnormal_samples = 10 # Number of anomalies to classify in test
X_train, _ = make_blobs(n_samples=num_normal_samples, centers= [(1,1)], n_features=10, cluster_std=1, random_state=0)
X_test_abnormal, _ = make_blobs(n_samples=num_abnormal_samples, centers=[(20,20)], n_features=10, cluster_std=1, random_state=0)
X_test_normal, _ = make_blobs(n_samples=num_abnormal_samples, centers=[(1,1)], n_features=10, cluster_std=1, random_state=0)
Y_train = [0] * num_normal_samples
Y_test_abnormal = [1] * num_abnormal_samples
Y_test_normal = [0] * num_abnormal_samples
X_test = np.concatenate((X_test_normal, X_test_abnormal), axis=0)
Y_test = np.concatenate((Y_test_normal, Y_test_abnormal), axis=0)
# Train the model with only normal data
model = OCENCH_train(X=X_train, n_projections=20, l=2, extend=0.3)
# Predict new (normal and abnormal) data
prediction = OCENCH_classify(X=X_test, model=model)
# [0 = Normal | 1 = Anomaly]
print("Real classes: ", Y_test)
print("Predictions: ", prediction)If you plan to use this code, please cite the following paper where the method was originally proposed:
@article{NOVOAPARADELA20231,
title = {A One-Class Classification method based on Expanded Non-Convex Hulls},
journal = {Information Fusion},
volume = {89},
pages = {1-15},
year = {2023},
issn = {1566-2535},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.07.023},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253522000896},
author = {David Novoa-Paradela and Oscar Fontenla-Romero and Bertha Guijarro-Berdiñas},
keywords = {Machine learning, One-Class Classification, Convex Hull, Delaunay triangulation, Random projections, Ensemble learning},
abstract = {This paper presents an intuitive, robust and efficient One-Class Classification algorithm. The method developed is called OCENCH (One-class Classification via Expanded Non-Convex Hulls) and bases its operation on the construction of subdivisible and expandable non-convex hulls to represent the target class. The method begins by reducing the dimensionality of the data to two-dimensional spaces using random projections. After that, an iterative process based on Delaunay triangulations is applied to these spaces to obtain simple polygons that characterizes the non-convex shape of the normal class data. In addition, the method subdivides the non-convex hulls to represent separate regions in space if necessary. The method has been evaluated and compared to several main algorithms of the field using real data sets. In contrast to other methods, OCENCH can deal with non-convex and disjointed shapes. Finally, its execution can be carried out in a parallel way, which is interesting to reduce the execution time.}
}