In computer science, the problem of finding a minimum vertex cover is a classical optimization problem. It is NP-hard, so it cannot be solved by a polynomial-time algorithm if P ≠ NP. Moreover, it is hard to approximate – it cannot be approximated up to a factor smaller than 2 if the unique games conjecture is true. On the other hand, it has several simple 2-factor approximations. It is a typical example of an NP-hard optimization problem that has an approximation algorithm. Its decision version, the vertex cover problem, was one of Karp's 21 NP-complete problems and is therefore a classical NP-complete problem in computational complexity theory. Furthermore, the vertex cover problem is fixed-parameter tractable and a central problem in parameterized complexity theory.
Read more about the problem of finding a minimum vertex cover you can here - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vertex_cover and here - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set_cover_problem
In our case, the task looks like this:
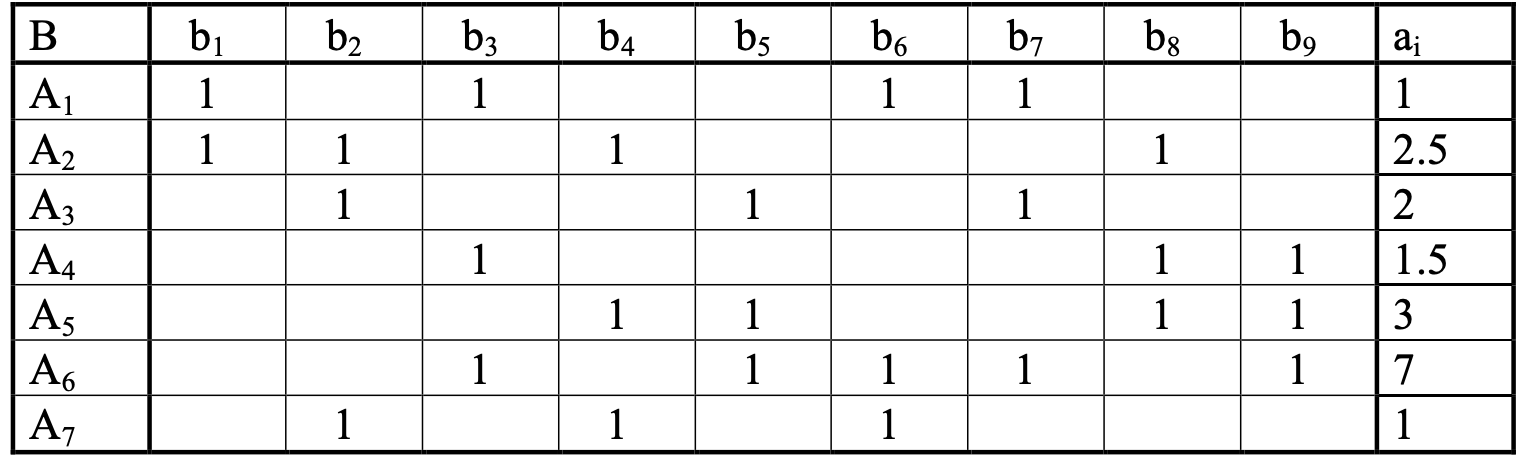
We need to find the coverage for the smallest number of rows of the matrix (table) and for the smallest number by price (the rightmost column of the matrix). The coverage in this case is a combination of rows of a matrix in which there is at least one 1 in each column of the combination.
This repository provides solutions to this problem in several ways: enumeration, boundary enumeration, the minimum column - maximum row method, and the core row method.
I think the meaning of enumeration is clear to everyone. The boundary enumeration method differs in that it tries to skip repetitions of combinations of coverages to the maximum. The meaning of the minimum column - maximum row method is that: In the current table, the column with the smallest number of ones is highlighted. Among the rows containing 1's in this column, one of the largest number of 1's stands out. This row is included in the coverage, this table is reduced by deleting all columns in which the selected row has ones. If the table contains columns that are not crossed out, then item 2 is performed, otherwise the covering is constructed. Note that when counting the number of ones in a row, the ones in the columns that are not crossed out are taken into account.
The most interesting most likely to many will seem the method of core rows. Its algorithm looks like this:
- We take the initial coverage table as the current coverage table, and the set of core lines - empty.
- We find core lines, remember a set of core lines. We shorten the current coverage table: we cross out the core rows and all the columns covered by them.
- Cross out the anticore lines.
- Cross out the absorbing columns.
- Cross out the lines that are absorbed.
- If as a result of execution of pt. 2-5 current coverage table has changed, we perform item 1 again, otherwise we finish the conversion.
The coverage for the cyclic remainder of the table can be built only by methods of enumeration of coverages: marginal enumeration or decomposition by column. When the lines of coverage of the cyclic remainder are added to the core rows, we obtain the coverage for the initial table of coverages.
Files with English captions have the letter E in their names.