server:
port: 9002 # 服务端口
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: user-service-impl # 路由ID
uri: lb://user-service-impl # 匹配的服务名称
predicates:
- Path=/user/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由 -> http://user-service-impl/user/...
- id: order-service-impl # 路由ID
uri: lb://order-service-impl # 匹配的服务名称
predicates:
- Path=/order/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由 -> http://order-service-impl/order/...<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>Starters可以理解为启动器,它包含了一系列可以集成到应用里面的依赖包。所以它大概率会和SpringBoot自动装配有联系,找一下spring.factories文件。
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayResilience4JCircuitBreakerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayNoLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayMetricsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayRedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.discovery.GatewayDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.SimpleUrlHandlerMappingGlobalCorsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayReactiveLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayReactiveOAuth2AutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Failure Analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.MvcFoundOnClasspathFailureAnalyzer
package org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
// 自动装配生效
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.cloud.gateway.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
// 自动配置前置条件
@AutoConfigureBefore({ HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class })
// 自动配置后置组件
@AutoConfigureAfter({ GatewayReactiveLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration.class,
GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguration.class })
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherHandler.class)
public class GatewayAutoConfiguration {
// ...会注入很多 Bean
}从配置类上定义的注解可以了解到:
-
spring.cloud.gateway.enabled配置项为true时,自动配置才会生效,默认true。 -
在注入Gateway之前,容器中必须存在
WebFlux和HttpHandler组件。 -
在注入Gateway之后,需要对请求负载均衡,所以后置组件为负载均衡组件。
GatewayAutoConfiguration在内部会初始化很多bean,这里列举几个重要的:
-
PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator:用于从配置文件(yaml/properties)中读取路由配置信息。
-
RouteDefinitionLocator:把 RouteDefinition 转化为 Route。
-
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping:类似于 MVC 的HandlerMapping,不过这里是 Gateway 实现的。用于匹配对应的请求route。
-
GatewayProperties:yaml配置信息被封装在 GatewayProperties 对象中。
-
AfterRoutePredicateFactory:路由断言工厂。
-
RetryGatewayFilterFactory:重试 Gateway 过滤器工厂。
-
GlobalFilter:全局过滤器。
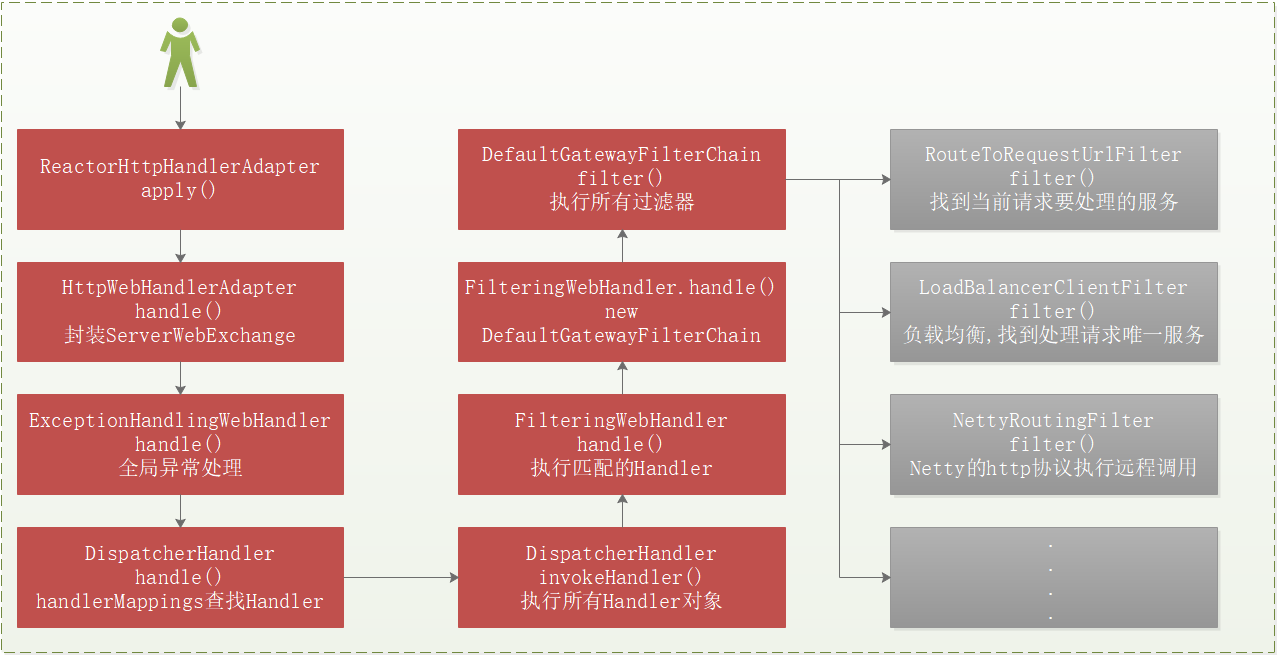
Gateway 的执行流程大致如下图所示:
其中GatewayAutoConfiguration是Gateway的自动配置类。
Gateway采用的是 webFlux 响应式编程,其请求处理流程与Spring MVC类似。
| Gateway | Spring MVC | |
|---|---|---|
| 请求分发 | DispatcherHandler | DispatcherServlet |
| 请求映射 | HandlerMapping | HandlerMapping |
| 请求适配 | HandlerAdapter | HandlerAdapter |
| 请求处理 | WebHandler | Handler |
所有的请求都会经过 Gateway 的DispatcherHandler#handler()方法。
public class DispatcherHandler implements WebHandler, ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
return createNotFoundError();
}
return Flux
// 遍历所有的 handlerMapping
.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings)
// 获取到请求映射的 handler,最终获取到的是 FilteringWebHandler
.concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange))
.next()
.switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError())
// 获取对应的适配器处理器,执行目标处理器方法
.flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler))
// 返回处理结果
.flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result));
}
}AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandler()
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends ApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Override
public Mono<Object> getHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// 获取匹配的路由 Route
return getHandlerInternal(exchange).map(handler -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(exchange.getLogPrefix() + "Mapped to " + handler);
}
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(exchange) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, exchange);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
if (!this.corsProcessor.process(config, exchange) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return REQUEST_HANDLED_HANDLER;
}
}
return handler;
});
}
}由于是网关组件,当请求进入时,会先判断路由,所以会进入实现类 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的逻辑中。
public class RoutePredicateHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMapping {
@Override
protected Mono<?> getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// don't handle requests on management port if set and different than server port
if (this.managementPortType == DIFFERENT && this.managementPort != null
&& exchange.getRequest().getURI().getPort() == this.managementPort) {
return Mono.empty();
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_HANDLER_MAPPER_ATTR, getSimpleName());
// 查找路由,包含自定义Filter
return lookupRoute(exchange)
// .log("route-predicate-handler-mapping", Level.FINER) //name this
.flatMap((Function<Route, Mono<?>>) r -> {
// 除上下文中旧的属性
exchange.getAttributes().remove(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "] to " + r);
}
// 将匹配到的路由与上下文绑定,用于后续的负载均衡
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r);
return Mono.just(webHandler);
}).switchIfEmpty(Mono.empty().then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
exchange.getAttributes().remove(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})));
}
}**lookupRoute()**会找到配置的所有路由断言工厂,然后判断是否允许请求通过。
public class RoutePredicateHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMapping {
protected Mono<Route> lookupRoute(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// getRoutes > 获取配置的所有断言工厂
return this.routeLocator.getRoutes()
// individually filter routes so that filterWhen error delaying is not a
// problem
.concatMap(route -> Mono.just(route).filterWhen(r -> {
// add the current route we are testing
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR, r.getId());
// 先获取Route的predicate(断言)属性,然后调用apply()执行断言,判断请求是否允许通过
return r.getPredicate().apply(exchange);
})
// instead of immediately stopping main flux due to error, log and
// swallow it
.doOnError(e -> logger.error("Error applying predicate for route: " + route.getId(), e))
.onErrorResume(e -> Mono.empty()))
// .defaultIfEmpty() put a static Route not found
// or .switchIfEmpty()
// .switchIfEmpty(Mono.<Route>empty().log("noroute"))
.next()
// TODO: error handling
.map(route -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Route matched: " + route.getId());
}
validateRoute(route, exchange);
return route;
});
}
}**getRoutes()**获取配置的所有路由。
public class RouteDefinitionRouteLocator implements RouteLocator {
@Override
public Flux<Route> getRoutes() {
// 从配置文件中获取所有路由,并转换成 Route
Flux<Route> routes = this.routeDefinitionLocator.getRouteDefinitions().map(this::convertToRoute);
if (!gatewayProperties.isFailOnRouteDefinitionError()) {
// instead of letting error bubble up, continue
routes = routes.onErrorContinue((error, obj) -> {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("RouteDefinition id " + ((RouteDefinition) obj).getId()
+ " will be ignored. Definition has invalid configs, " + error.getMessage());
}
});
}
return routes.map(route -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("RouteDefinition matched: " + route.getId());
}
return route;
});
}
}
// Route内部结构
public class Route implements Ordered {
// 路由id
private final String id;
// 请求URI
private final URI uri;
// 排序
private final int order;
// 断言
private final AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate;
// 过滤器
private final List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters;
// 元数据
private final Map<String, Object> metadata;
}在前面已经获取到了 handlerMapping,处理器映射器,并执行断言。假设请求符合断言,第二步就是执行过滤器链了。
public class DispatcherHandler implements WebHandler, ApplicationContextAware {
private Mono<HandlerResult> invokeHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
// 找到所有的 handlerAdapter,匹配 WebFlux,默认会由 SimpleHandlerAdapter 处理
for (HandlerAdapter handlerAdapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (handlerAdapter.supports(handler)) {
return handlerAdapter.handle(exchange, handler);
}
}
}
return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException("No HandlerAdapter: " + handler));
}
}SimpleHandlerAdapter.handle()
public class SimpleHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
@Override
public Mono<HandlerResult> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) {
WebHandler webHandler = (WebHandler) handler;
Mono<Void> mono = webHandler.handle(exchange);
return mono.then(Mono.empty());
}
}**FilteringWebHandler.handle()**执行过滤器链,该过滤器链包括 globalFilters 和 gatewayFilters。
public class FilteringWebHandler implements WebHandler {
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// 根据路由与上下文的绑定关系,获取对应的路由 Route
Route route = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = route.getFilters();
List<GatewayFilter> combined = new ArrayList<>(this.globalFilters);
// 全局过滤器 + gatewayFilters 形成一条过滤器链,先执行的是GlobalFilter,然后是gatewayFilter
combined.addAll(gatewayFilters);
// TODO: needed or cached?
// 根据order排序,order值越小越先执行,order相同的则按照文件名排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(combined);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Sorted gatewayFilterFactories: " + combined);
}
// 构造过滤器链,执行过滤器链中的每一个过滤器方法
return new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange);
}
private static class GatewayFilterAdapter implements GatewayFilter {
// 封装了 GlobalFilter
private final GlobalFilter delegate;
GatewayFilterAdapter(GlobalFilter delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
return this.delegate.filter(exchange, chain);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GatewayFilterAdapter{");
sb.append("delegate=").append(delegate);
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
}
}全局过滤器会被封装为 GatewayFilterAdapter,其实现了 GatewayFilter,解决了 globalFilters 想要放入List<GatewayFilter>中的类型不一致问题。
然后在执行过滤器链中的 globalFilters 和 gatewayFilters 的 filter() 方法时,就会为请求加上请求头、请求参数等扩展点。
Gateway的负载均衡只需要在yaml中配置uri: lb://mall-order即可实现负载均衡,底层是由全局过滤器**ReactiveLoadBalancerClientFilter.filter()**方法去做的。
使用负载均衡客户端选取后端服务实例, 构建目标URL并存储在ServerWebExchange中。
public class ReactiveLoadBalancerClientFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
URI url = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
String schemePrefix = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_SCHEME_PREFIX_ATTR);
if (url == null || (!"lb".equals(url.getScheme()) && !"lb".equals(schemePrefix))) {
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
// preserve the original url
addOriginalRequestUrl(exchange, url);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(ReactiveLoadBalancerClientFilter.class.getSimpleName() + " url before: " + url);
}
URI requestUri = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
String serviceId = requestUri.getHost();
Set<LoadBalancerLifecycle> supportedLifecycleProcessors = LoadBalancerLifecycleValidator
.getSupportedLifecycleProcessors(clientFactory.getInstances(serviceId, LoadBalancerLifecycle.class),
RequestDataContext.class, ResponseData.class, ServiceInstance.class);
DefaultRequest<RequestDataContext> lbRequest = new DefaultRequest<>(
new RequestDataContext(new RequestData(exchange.getRequest()), getHint(serviceId)));
LoadBalancerProperties loadBalancerProperties = clientFactory.getProperties(serviceId);
// 使用 doOnNext() 处理 choose 方法返回的 ServiceInstance 实例
// choose() 选择服务的逻辑和 OpenFeign 类似,如果使用的是 Nacos,则调用 Nacos 的组件
return choose(lbRequest, serviceId, supportedLifecycleProcessors).doOnNext(response -> {
if (!response.hasServer()) {
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle
.onComplete(new CompletionContext<>(CompletionContext.Status.DISCARD, lbRequest, response)));
throw NotFoundException.create(properties.isUse404(), "Unable to find instance for " + url.getHost());
}
ServiceInstance retrievedInstance = response.getServer();
URI uri = exchange.getRequest().getURI();
// if the `lb:<scheme>` mechanism was used, use `<scheme>` as the default,
// if the loadbalancer doesn't provide one.
// 协议
String overrideScheme = retrievedInstance.isSecure() ? "https" : "http";
if (schemePrefix != null) {
overrideScheme = url.getScheme();
}
DelegatingServiceInstance serviceInstance = new DelegatingServiceInstance(retrievedInstance,
overrideScheme);
// 构建目标请求 uri 将服务名替换为 ip
URI requestUrl = reconstructURI(serviceInstance, uri);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("LoadBalancerClientFilter url chosen: " + requestUrl);
}
// 将构建的目标请求URI存储到ServerWebExchange的属性中提供给后续的过滤器
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR, requestUrl);
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_LOADBALANCER_RESPONSE_ATTR, response);
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onStartRequest(lbRequest, response));
}).then(chain.filter(exchange))
.doOnError(throwable -> supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle
.onComplete(new CompletionContext<ResponseData, ServiceInstance, RequestDataContext>(
CompletionContext.Status.FAILED, throwable, lbRequest,
exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_LOADBALANCER_RESPONSE_ATTR)))))
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle
.onComplete(new CompletionContext<ResponseData, ServiceInstance, RequestDataContext>(
CompletionContext.Status.SUCCESS, lbRequest,
exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_LOADBALANCER_RESPONSE_ATTR), buildResponseData(exchange,
loadBalancerProperties.isUseRawStatusCodeInResponseData())))));
}
private Mono<Response<ServiceInstance>> choose(Request<RequestDataContext> lbRequest, String serviceId,
Set<LoadBalancerLifecycle> supportedLifecycleProcessors) {
// 获取负载策略
ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> loadBalancer = this.clientFactory.getInstance(serviceId,
ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer.class);
if (loadBalancer == null) {
throw new NotFoundException("No loadbalancer available for " + serviceId);
}
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onStart(lbRequest));
// NacosLoadBalancer
return loadBalancer.choose(lbRequest);
}
}GateWay的源码体量相对较小,但想要用一篇文章来深入也不太现实,都是挑执行链路上的核心点进行剖析。