Ultrasound 3D Reconstruction of Malignant Masses in Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy Using the PAF Rail System: a Comparison Study
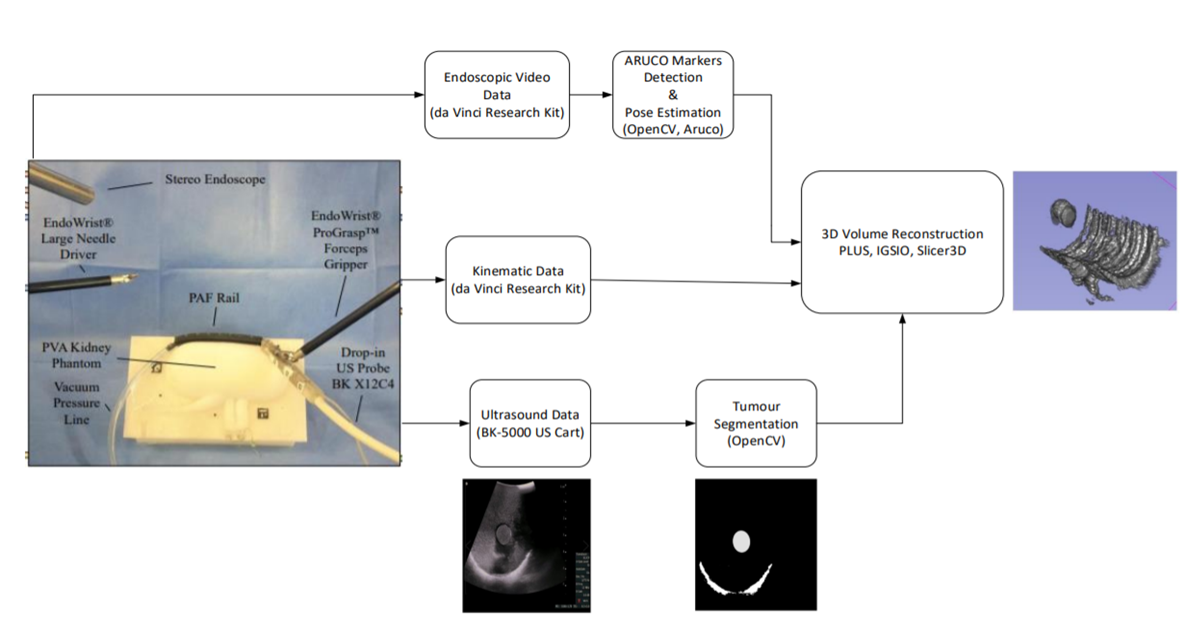
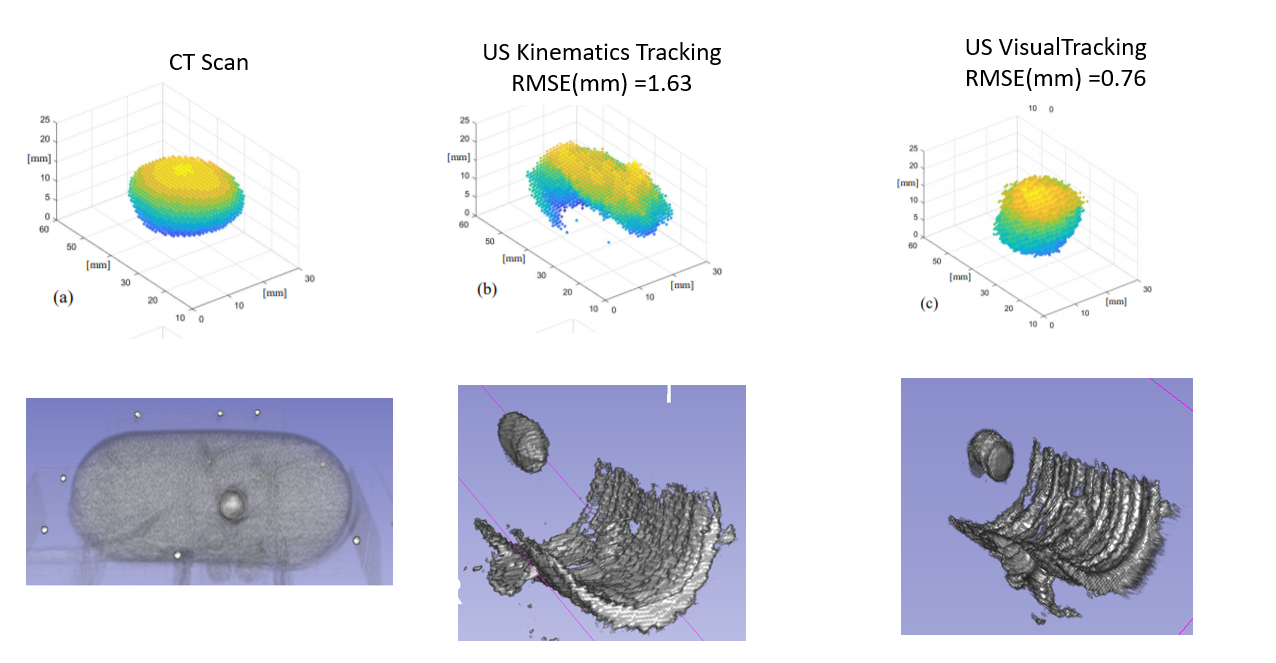
In Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) the use of intraoperative ultrasound (IOUS) helps to localise and outline the tumours as well as the blood vessels within the kidney. The aim of this work is to evaluate the use of the Pneumatically Attachable Flexible (PAF) rail system for US 3D reconstruction of malignant masses in RAPN. The PAF rail system is a novel device developed and previously presented by the authors to enable track-guided US scanning. Methods: We present a comparison study between US 3D reconstruction of masses based on: the da Vinci Surgical System kinematics, single- and stereocamera tracking of visual markers embedded on the probe. An US-realistic kidney phantom embedding a mass is used for testing. A new design for the US probe attachment to enhance the performance of the kinematic approach is presented. A feature extraction algorithm is proposed to detect the margins of the targeted mass in US images. Results: To evaluate the performance of the investigated approaches the resulting 3D reconstructions have been compared to a CT scan of the phantom. The data collected indicates that single camera reconstruction outperformed the other approaches, reconstructing with a sub-millimetre accuracy the targeted mass. Conclusion: This work demonstrates that the PAF rail system provides a reliable platform to enable accurate US 3D reconstruction of masses in RAPN procedures. The proposed system has also the potential to be employed in other surgical procedures such as hepatectomy or laparoscopic liver resection.
Keywords: 3D Ultrasound · Laparoscopy · Surgical Robotics · Soft Robotics
https://www.dropbox.com/sh/56216r3lpz1xqng/AABVkUpLBPB6mJ6YOTE1x03da?dl=0
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11548-020-02149-4
- Kinematics: Data of the PSM recorded via the dVRK, the pose between the camera coordinate system and the current end-effector in the Cartesian space
- Optical Tracking:

Suffering from the speckle noise, it is difficult to segment the mass from the phantom in ultrasound images.
A feature extraction algorithm implemented to detect the region of the mass and outline its boundary:
- Apply a high-pass filter to the image to sharpen it
- Apply image thresholding to the sharpened image
- Find the connected components using blob analysis
- Apply edge detector to targeted components and find their contours
- Fit an ellipse to each contour in the original image
- US volume reconstruction methods construct a 3D Cartesian volume from a set of 2D US frames that are sweeping across a region
- This is implemented by iterating through each pixel of the rectangular region of the slice and inserting the pixel value into the corresponding volume voxel (“nearest-neighbor interpolation” option) or distributing it in the closest 8 volume voxels (“linear interpolation” option).
- The voxel value can be determined by simply using the latest coinciding pixel value or as a weighted average of all coinciding pixels (“compounding” option)
-
Kinematics data, endoscopic and ultrasound images were collected from multiple swipe sequences in this experiment.
-
A swipe sequence is considered successfully completed when the probe moves from one side of the kidney to the other without losing contact with the kidney surface and the embedded mass is correctly displayed in the ultrasound images collected. Please watch the video: https://github.com/HarrisKomn/3D-US-Reconstruction-of-tumor-masses/blob/master/Aruco_Tracking.mp4
C++ compiler
Visual Studio >= 2015
VTK = 8.2
OpenCV
CMake = 3.14
Slicer = 4.10.1
- Clone IGSIO into a directory of your choice
- Configure the project with CMake
- Enter VTK directory (VTK_DIR) pointing to the location of VTKConfig.cmake
- Enable desired components:
- IGSIO_BUILD_SEQUENCEIO: Read/write sequence files to vtkIGSIOTrackedFrameList
- IGSIO_BUILD_SEQUENCEIO: Read/write sequence files to vtkIGSIOTrackedFrameList
- IGSIO_BUILD_VOLUMERECONSTRUCTION: Reconstruct volumes using images and transforms in vtkIGSIOTrackedFrameList
- Open IGSIO.sln file and build the solution
- Copy paste some necessary opencv_@@@.dll and vtk@@@@@.dll
- Ready to work on VolumeReconstructorTest project
- Define Ultrasound Video file in 'vreader_Ultra'
- Define Endoscopic Video file in 'videoR'
- Define Output Volume Filename in 'outputVolumeFileName'
- Define the method for tracking the probe in 'visual' (true = aruco markers detection and pose estimation , false = kinematics)
- Define the how many frames/images will be used in 'used_frames'
If you encounter any issues or have any questions, feel free to contact me to harris.komninos@gmail.com .
- IGSIO: A collection of tools and algorithms for image guided systems (https://github.com/IGSIO/IGSIO)
- Plus: Free, open-source library and applications for data acquisition, pre-processing, calibration, and real-time streaming of imaging, position tracking, and other sensor data (https://plustoolkit.github.io/)