Find a detailed description of the plan and the curriculum for the semester here:
- Dates: https://datsoftlyngby.github.io/soft2018spring
- Plan: https://datsoftlyngby.github.io/soft2018spring/DB_plan.html
Best fork this repository on GitHub.
And fetch the latest changes before/after each lecture, see https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/.
In the following is a step by step guide to get you up and running with Vagrant and VirtualBox to run an Ubuntu Linux to run the code examples presented in class.
This guide is written for Windows Users.
- VirtualBox
- Vagrant
- GitBash
-
Download URL: https://git-scm.com/download
- During installation choose the following:
- Use Git from the Windows Command Prompt with this option you will be able to use Git from both Git Bash and the Windows Command Prompt.
- Checkout as-is, commit Unix-style line endings
- During installation choose the following:
-
Download and install VirtualBox (https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads)
- The current version is 5.2.6
- Get it from here: http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/5.2.6/VirtualBox-5.2.6-120293-Win.exe
- Download the extension pack too: http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/5.2.6/Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-5.2.6.vbox-extpack
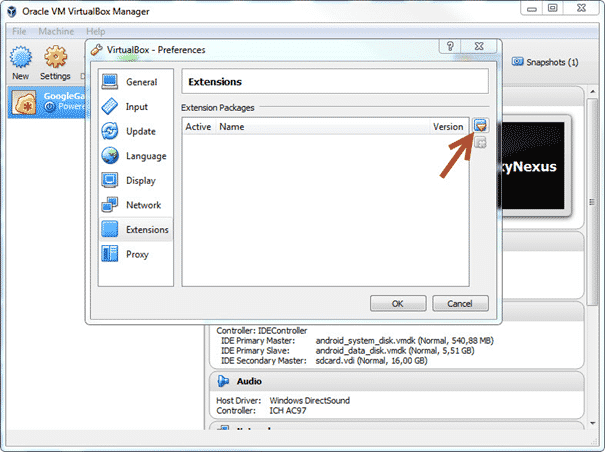
- After installing VirtualBox, open it and click
File->Preferences->Extensionsand click the marked icon - Select the downloaded extension pack and then click
Install->I Agree->Yes
- The current version is 5.2.6
-
Download and install Vagrant (https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html)
-
Adapt the computer's settings:
- Enable VT-X (Intel Virtualization Technology) in your computer BIOS/UEFI. (OBS You enter your BIOS after restarting the computer and hit a key like
F1,F2, up toF12orDELETE. Which button to press depends on the vendor and the model of you computer. Find that in your computer's manual.) - Disable Hyper-V on program and features page in the control panel.
- Enable VT-X (Intel Virtualization Technology) in your computer BIOS/UEFI. (OBS You enter your BIOS after restarting the computer and hit a key like
-
If you did not already generate an SSH keypair, generate one (e.g., via
ssh-keygen -t rsain GitBash) -
Now everything is installed. See if you can run
vagrant --versionin GitBash.
A virtual machine (VM) is created from a Vagrantfile. Get the one for the course from the root of the course's repository https://github.com/datsoftlyngby/soft2018spring-databases-teaching-material.
Likely it is best to fork this repository on GitHub (Fork button on the top right of the page). This will create a fork of the repository for your GitHub user. In the following your GitHub user is designated as <yourghuser>. You have to replace it with your ID before pasting the corresponding commands. All of the following commands have to be run in GitBash.
- Clone the repository:
$ git clone git@github.com:<yourghuser>/soft2018spring-databases-teaching-material.git- Hint In case you want to modify the configuration of the virtual machine, which will be created, you can do this now. Edit it with an editor of your choice. For example, to give the VM more RAM adapt the line
vb.memory = "3072"to a value of RAM in megabyte, which fits your host machine. That is, if you have 8GB of RAM and you want to give your VM 7GB of RAM change3072into7168. - Start-up the VM:
$ cd soft2018spring-databases-teaching-material
$ vagrant up- The first time you run the
vagrant upcommand it will take a bit as it has to download the corresponding Ubuntu Linux image and intall the required software on it. OBS to run this step, you have to be connected to the internet. Do not interrupt the process and keep track that no errors - To log onto the virtual machine after completion of
vagrant upexecute:
vagrant ssh- Now, you should be logged onto the VM and you should see a Bash prompt similar to:
vagrant@vagrant:~$- Docker is installed and configured on the VM. Test it via:
vagrant@vagrant:~$ $ docker run hello-world
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://cloud.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/engine/userguide/- When you are done working on your VM, you can leave it by issuing the exit command.
vagrant@vagrant:~$ exit- Subsequently, you can put the VM to "sleep" (just like closing the lid of your notebook) by running vagrant suspend on your host machine.
$ vagrant suspend- In case you want to discard this VM just run
vagrant destroyfrom within the directory containing theVagrantfile.
This guide is adapted from earlier versions and from https://www.swtestacademy.com/quick-start-vagrant-windows-10/
The easiest way to work with the notebooks in this repository is to run it in a container on MyBinder.
Click here: to start an interactive environment.