Type: Master's Thesis
Author: Lukas Vöge
1st Examiner: Prof. Dr. Lessmann
2nd Examiner: Prof. Dr. Akbik
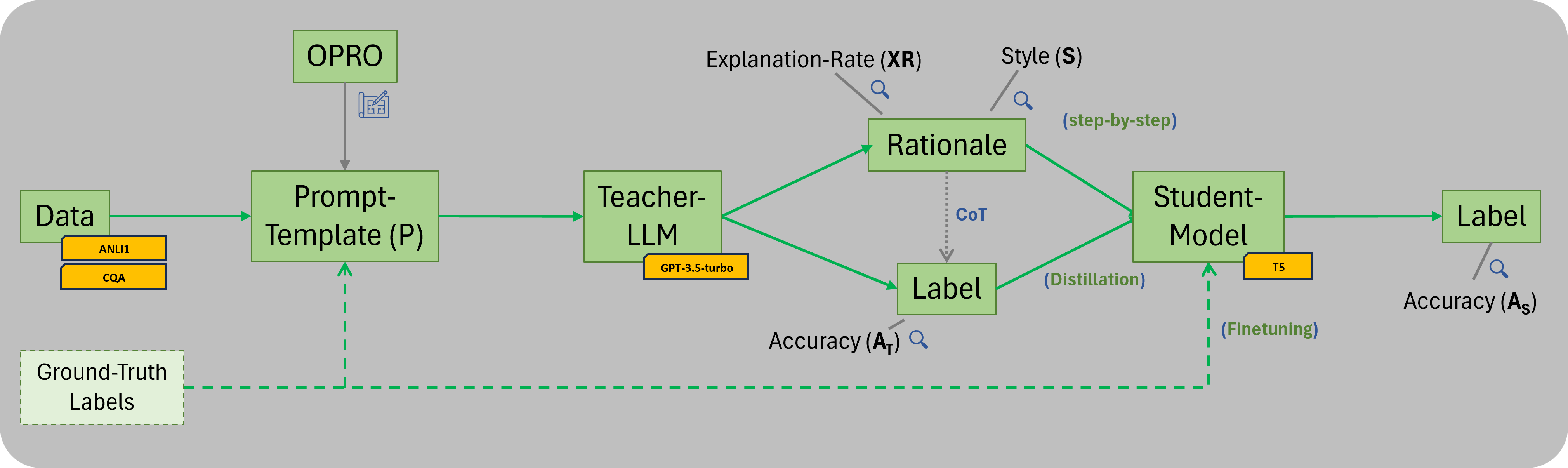
The rise of powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) poses challenges in deploying their capabilities efficiently due to high resource requirements. To address this, finetuning and distillation methods have been explored, but both demand substantial amounts of labeled data. Hsieh et al. (2023) propose an innovative distillation technique, leveraging LLMs as teachers to reason and generate labels along with explanations to justify each label (rationale). These rationales augment the training data for ask-specific student models in an additional training task. This multi-task training framework substantially improves the finetuning efficiency. Resulting models outperform LLMs while being much smaller and using less data.
We propose Zero-Shot step-by-step Distillation, an improvement upon Hsieh et al.'s original step-by-step distillation, significantly reducing costs of the technique without losing any performance. This is achieved by utilizing optimal Zero-Shot prompts against an instruction-tuned teacher LLM, to obtain the labels and rationales. Cost reductions of over 85% are achieved. Further, we do research on the effects isolated properties of the rationales have on the student models. Compelling evidence for further opportunities to cut costs are presented, since we find that not all labels need to be supported by an explanation to capitalize on the mechanism.
Keywords: NLP, LLMs, Distillation, Finetuning, Chain of Thought Prompting, step-by-step Distillation
This repository contains the code to perform Zero-Shot step-by-step Distillation on top of distilling-step-by-step by Hsieh et al. (2023).
This repository only concerns the Zero-Shot adaptation, the actual finetuning of student models on the annotated datasets is done with the original code by Hsieh et al. (2023) in the submodule ./distilling-step-by-step.
- Prompt Template: Used to query the Teacher LLM. Template that defines the structure of a prompt, including the appropriate placeholders for the input to the model. Also, defines regex parsing instructions for the expected responses from the model into definite label and rationale parts. Prompt templates are defined in
./prompt_templates, by dataset name and are identified by a unique ID. - Prompt Mix: Used to annotate complete datasets with labels and rationales from the teacher LLM. A prompt mix defines a relative mix of prompt templates for the annotation of a dataset with labels and rationales. This means, a dataset can be annotated with multiple prompt templates and different prompt templates for labels and rationales (e.g. 75% of labels are queried with prompt template 1 and 25% with prompt template 2 and 100% of rationales are from prompt template 3). A Teacher-Writer object will query the teacher LLM accordingly, to build a dataset adhering to the defined prompt-mix. The most basic prompt-mix just states one prompt template with 100% for label and rationale. Prompt mixes are defined in
./prompt_mixes, by a unique ID. - Prompt Metadata: Performance metadata for prompt templates. Prompt metadata is stored in
./prompt_metadataby dataset name and prompt template ID. Prompt metadata is updated by prompt experiments and stores information about occurring costs, the parsing behaviour of resulting responses, and characteristics of labels and rationales.
-
Prompt Experiment: A prompt experiment queries all available prompt-templates for a given dataset n times and evaluates the responses (label accuracy and rationale characteristics). Results will be updating the prompt metadata for each prompt. Run prompt experiments with the
--experimentflag. -
Generate Training Data: A training data generation run will query the teacher LLM for a given dataset and according to a prompt mix. It will annotate a part or the whole dataset with Teacher Labels and Rationales and write the annotations in a file to be used for model finetuning with the distilling-step-by-step submodule. Run training data generation with the
--generate_trainingdataflag.
-
Query Results: All Teacher LLM responses for a given dataset, split and prompt template. Teacher-Querier classes will check the query-results directory for existing query results before each query to avoid querying the same exact query twice.
-
Results: Results from T5 finetuning experiments by hyperparameter configuration. Outputs of the evaluation of the best checkpoint after training.
├── distilling-step-by-step # submodule, contains the original code by Hsieh et al. (2023) to (step-by-step) finetune T5 models
├── experiment-tracking
│ ├── scripts # bash scripts to run T5 finetuning experiments
│ ├── experiment_tracking.csv # file containing all T5 finetuning experiments
│ ├── experiment_tracking.py # script to create T5 finetuning scripts and update the tracking file
├── opro
│ ├── meta-prompts # folder containing meta-prompts
│ ├── opro.py # script to run the OPRO prompt optimization
├── prompt-metadata # prompt metadata files
├── prompt-mixes # prompt mix files
├── prompt-templates # prompt templates files
├── query-results # query results by dataset, split and prompt template
├── results # results from T5 finetuning experiments by hyperparameter configuration
├── src
│ ├── factories.py # class factories
│ ├── metadata.py # handling of prompt metadata
│ ├── teacher_query_tools.py # classes to handle the uniform querying of the teacher model by prompt templates
│ ├── teacher_response_evaluator.py # handling of the evaluation of teacher responses
│ ├── teacher_response_parser.py # handling of the parsing of teacher responses
│ ├── teacher_writer.py # annotating of datasets by teacher LLM based on prompt-mixes
│ ├── utils.py # utility functions
├── analytics.ipynb # plotting of results
├── datasets.zip # datasets
├── .env # environment file containing the OpenAI API key
├── README.md # this file
├── requirements.txt # python requirements
├── run.py # main script, orchestrates the source code
Clone this repository and initialize the submodule
git clone https://github.com/lukasvoege/ZeroShot-step-by-step-distillation.git
cd ZeroShot-step-by-step-distillation
git submodule update --initUnzip the datasets.zip file in the root directory
# on Linux / Mac / WSL on Windows
unzip datasets.zip
# on Windows
Expand-Archive .\datasets.zip .Create a virtual environment and activate it (Python 3.8.10)
python -m venv .venv
# on Linux / Mac / WSL on Windows
source .venv/bin/activate
# on Windows
.\.venv\Scripts\activateInstall requirements
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txtCreate .env file in the root directory and add the following variable
OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-api-key"--experiment: run a Prompt experiment--test_size: float between0and1to specify the test set size based on the train set size, or an integer to specify the test set size in absolute numbers--evaluate: run prompt evaluation of all query results for a given dataset to update the prompt metadata file--generate_trainingdata: generate training data for a given dataset and prompt mix--subsam_expl_rate: downsample the explanation rate to a given value between0and1, must be smaller than the actual explanation rate of the prompt mix--splits:train,valid,test--prompt_mix: Integer that refers to a prompt mix yaml in the./prompt_mixesdirectory--include_prompts: list of integers that refers to a prompt yaml in the./promptsdirectory, to only include specific prompts in an experiment. All if not specified.--samples: Integer, the number of samples to generate--dataset:esnli,anli1,cqa,svamp--seed: random seed to use
The following command runs a Prompt experiment on the CQA dataset with a test set size of 100 samples and a random seed of 42. It will query and evaluate the same 100 random samples for all available prompt templates for the CQA dataset.
python run.py --experiment --dataset cqa --test_size 100 --seed 42The following command runs prompt evaluation on the ANLI1 dataset. This will only evaluate all available query results across all prompt templates for the ANLI1 dataset and update the prompt metadata file ./prompt_metadata/anli1.yaml.
python run.py --evaluate --dataset anli1The following command generates training data for the CQA dataset using the 2.yaml prompt mix. It will query the first 500 samples of the train and test split using prompt templates in a mix defined in ./prompt_mixes/2.yaml. The query results will be parsed and dataset files ready for model finetuning will be saved to ./datasets/cqa/gpt_35_turbo/2/.
python run.py --generate_trainingdata --dataset cqa --splits train test --prompt_mix 2 --samples 500To generate the full training testing and evaluation data for the ANLI1 dataset using the 6.yaml prompt mix and downsample the explanation rate to 0.5, run the following command:
python run.py --generate_trainingdata --dataset anli1 --splits train test valid --prompt_mix 6 --subsam_expl_rate 0.5