-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
World
What is the isometry ?
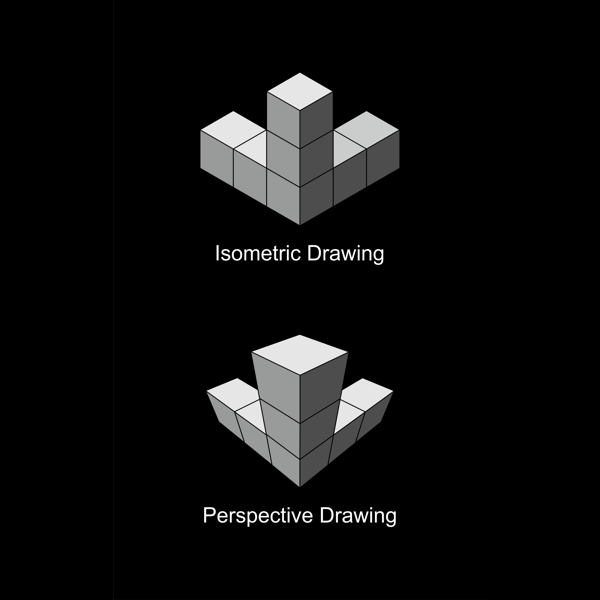
Isometric projection is a method for visually representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions in technical and engineering drawings. It is an axonometric projection in which the three coordinate axes appear equally foreshortened and the angle between any two of them is 120 degrees.
The term 'isometric' comes from the Greek for 'equal measure', reflecting the fact that the scale along each axis of the projection is the same (unlike some other forms of graphical projection).
An isometric view of an object can be obtained by choosing the viewing direction so that the angles between the projections of the x, y and z axes are all equal, i.e. 120°. For a cube, for example, this is done by first looking straight at one face. Then the cube is rotated ±45° about the vertical axis, followed by a rotation of about 35.264° (exactly arcsin 1⁄√3 or arctan 1⁄√2, which is related to the magic angle) about the horizontal axis. Note that in the case of the cube (see figure), the perimeter of the resulting 2D drawing is a perfectly regular hexagon: all the black lines are of equal length and all the faces of the cube have the same area. Isometric graph paper can be placed under a normal piece of drawing paper to achieve this effect without the need for calculation.
Isometry in video games

Isometric design is a design technique that has stood the test of time, having been in use for several decades. First used in video games in 1981 with the debut of Sega's Zaxxon, it quickly gained popularity for its ability to create three-dimensional environments without the need for complex 3D modelling software. The technique's name, 'isometric', comes from the fact that all lines in the drawing are drawn at a 30-degree angle, creating an illusion of depth and perspective.
This technique has proven to be incredibly versatile and is still widely used today in various fields of design, including video game design and graphic design. The ability to create complex and visually appealing environments with ease has made isometric design a favourite among designers worldwide. Furthermore, the technique has been adapted and refined over time, leading to the creation of numerous variants, each with its own unique features and benefits.
In addition to its practical benefits, isometric design can also create a unique visual style that sets games apart from other titles on the market. Games such as Diablo and SimCity have become iconic in part because of their distinctive isometric design.
2:1 pixel ratio is the most common. The terms "3/4 perspective", "3/4 view", "2.5D" and "pseudo 3D" are also sometimes used, although these terms may have slightly different meanings in other contexts.
Once common, isometric projection has become less so with the advent of more powerful 3D graphics systems. However, video games using isometric projection - especially computer role-playing games - have seen a resurgence in the indie gaming scene in recent years.
The formula for the coordinates of an isometric space is: