This repository contains the implementations of various data structures.
I think it will be helpful to implement the data structure by myself for deeply understanding the inner process and the usage of data structure.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/?ref=shm
I usually refer to the link above to study about the data structures.
Let's get started!
A Heap is a special Tree-based Data Structure in which the tree is complete binary tree.
Heap : a complete binary tree based data structure
Complete binary tree : a binary tree that all levels of the tree are fully filled except possibly the last level
- Max Heap : max value in root node. same thing must be done for its left and right sub-tree also.
- Min Heap : min value in root node. same thing must be done for its left and right sub-tree also.
- Complete Binary Tree : fully filled tree -> represented using array
- Heap Property : minimum(or maximum) value always at root
- Parent-Child Relationship : Parent node index = i -> left child node index = 2i+1, right child node index = 2i+2
- Efficient Insertion and Removal
- Insertion(O(logN)) : inserted at the next available position in the bottom-rightmost level -> heapify(restore heap property by comparing the element with its parent and swapping if necessary)
- Removal of root element (O(logN)): replace root with the last element -> heapify
- Efficient Access to Extremal Elements
Heapify is the process to rearrange the elements to maintain the property of heap data structure
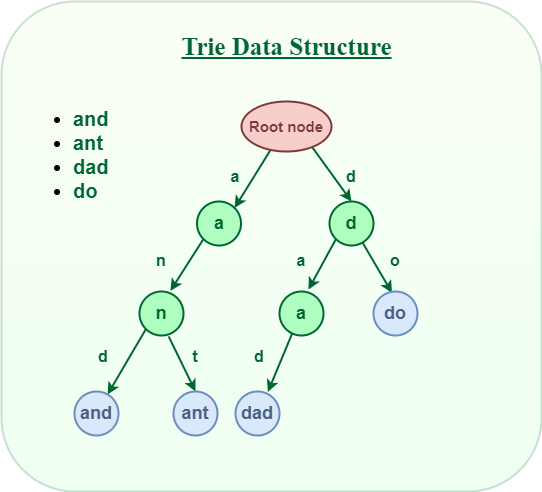
Trie is a type of k-ary search tree used for storing and searching a specific key from a set. Using Trie, search complexities can be brought to optimal limit (key length).
Trie : a search tree to store and search keys.
- all strings sharing common prefix should come from a common node
- Known as digital tree, or prefix tree.
- Used to store a large amount of strings.
- Easy for pattern matching
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-of-b-tree-2/
https://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs3110/2012sp/recitations/rec25-B-trees/rec25.html
B-Tree, Balanced Tree, is a type of self-balancing tree that was designed to solve the limitation of Binary Search Tree.
- can store a lot of keys in a single node -> "large key tree"
- multiple keys -> large branches -> shallow height -> Less Dist I/O -> faster read/write
- well suited for storage with slow and bulky data access
- maintains balance by ensuring that each node has the minimum number of keys
- searching, insertion, deletion : O(logN)
- order : the maximum number of the children of each nonleaf node
- degree : the minimum number of children possible except for the root
- nonleaf nodes contain only keys
- degree : t
- All leaves are at the same level. The actual elements of the collection are stored in the leaves.
- Every node except root must contain at least t-1 keys (degree)
- All nodes(including rrot) may contain at most 2t-1 keys (order)
- number of children of a node = number of keys + 1
- All keys of a node are sorted in increasing order. The child between two keys k1 and k2 contains all keys in the range from k1 and k2
- B-Tree grows and shrinks from the root (unlike BST)
- Insertion of a Node in B-Tree happens only at Leaf Node
- used in large databases to access data stored on the disk
- natural language processing, computer networks, and cryptography
- CAD systems to organize and search geometric data