Package avialalbe at NuGet
Install-Package PortaCapena.Authentication.NetCore -Version 2.2.0
As the authorization is based on roles first we have to define roles, requirement and handler i.e:
- Role
public class AdminRole : Role
{
public override object Value => 1;
public override string ToString() => Value.ToString();
}Once we have defined the example role its time to register authentication in Startup.cs class.
First step is to set IdentityRequirements to ConfigureServices method as below. Keep it mind this has to be set before AddMvc() extensions method:
//single roles
services.AddPcIdentityPolicy<AdminRole>("AdminPolicy")
.AddPcIdentityPolicy<UserRole>("UserRole")
//or multiple roles for one policy availalbe since 2.1.0
.AddPcMultiRoleIdentityPolicy<AdminRole, UserRole>("AdminOrUserPolicy")
.AddDefaultPcIdentityPolicy();Second step is to configure the TokenOptions and regiester identity middleware in Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) method as below:
var tokenOptions = TokenOptionsBuilder.Create("access_token")
.SetSecretKey("this is my custom Secret key for authnetication")
.SetExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(15))
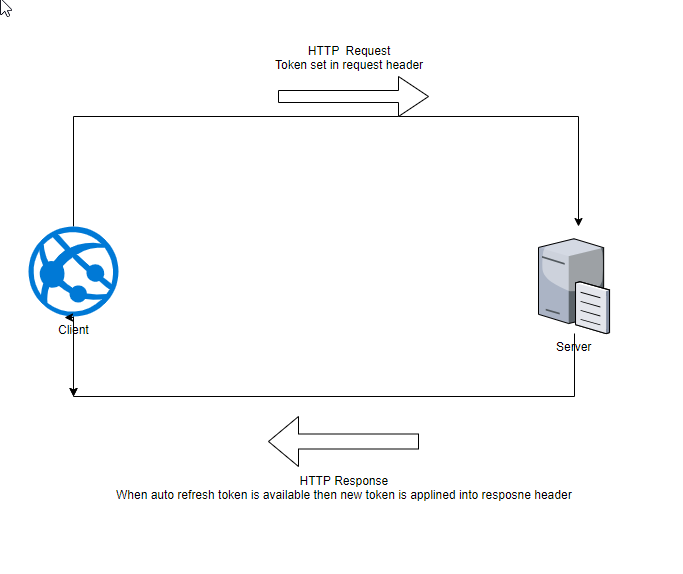
.SetAutoRefresh(false)
.Build();
app.UsePcIdentityMiddleware<PcIdentityMiddleware>(tokenOptions);The last step is handling unauthorize exception. This can be omitted if you have created your own exception middleware or so:
app.HandleAuthException(async (ctx, exc) =>
{
ctx.Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized;
await ctx.Response.WriteAsync(exc.Message);
});In order to generate token simply use TokenManager class:
string token = TokenManager.Create(126, new AdminRole());The usage is based on AuthorizeAttribute. The attribute get the policy name as a parameter. The policy is set in Startup.cs for provided role. There is an option to use the attribute without any policy. This means that if request contain valid token then he is automatically authorized execute the method. In order to use attribute without policy remember to use AddDefaultPcIdentityPolicy() while registering policies in Startup.cs
There is an example controller which uses 3 different policies: -Default -Administrator -User
[Authorize]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class ValuesController : Controller
{
[HttpGet]
///The method is automatically Authorized because controller itslef containg Authroize attribute
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
var uid = HttpContext.Items["UserId"];
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
[HttpGet, Route("adminreq")]
[Authorize(Policy = "AdminPolicy")]
public string TestAdminRequirement()
{
return "Succeed"
}
[HttpGet, Route("userreq")]
[Authorize(Policy = "UserPolicy")]
public string TestUserRequirement()
{
return $"Is in Role1: {isInRole1} {Environment.NewLine} Is in Role2: {isInRole2}";
}
[HttpGet, Route("defaultpolicy")]
[Authorize]
public string TestDefaultPolicy()
{
return "Succeed";
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet, Route("create/admin")]
public string GenerateAdminToken()
{
var token = TokenManager.Create(1, new AdminRole(), new KeyValuePair<string, string>("Dzwig", "Tak"));
var claimsPrincipal = TokenManager.Read(token);
return token;
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet, Route("create/user")]
///The method is authorizartion free bcause of [AllowAnnymous] attribute.
public string GenerateUserToken()
{
var token = TokenManager.Create(2, new UserRole(), new KeyValuePair<string, string>("Dzwig", "Tak"));
var claimsPrincipal = TokenManager.Read(token);
return token;
}
}The resolving user can be made in various options:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class ResolveController : Controller
{
[HttpGet, Route("userreq")]
[Authorize(Policy = "UserPolicy")]
public string TestUserRequirement()
{
var isInRole1 = User.IsInRole(new AdminRole());
var isInRole2 = User.IsInRole(1);
var userId1 = User.GetUserId();
var userId2 = HttpContext.Items[Constants.UserId];
return $"Is in Role1: {isInRole1} {Environment.NewLine} Is in Role2: {isInRole2} {Environment.NewLine} UserId1: {userId1} {Environment.NewLine} UserId2: {userId2}";
}
}
Example request using HttpClient:
httpClient = new HttpClient
{
BaseAddress = new Uri(uri)
};
httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Clear();
httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("access_token", generatedtoken);
//any usage
await httpClient.GetAsync(url);