we are provided with two jugs: one having the capacity to hold 3 gallons of water and the other has the capacity to hold 4 gallons of water.
There is no other measuring equipment available and the jugs also do not have any kind of marking on them.
So, the agent’s task here is to fill the 4-gallon jug with 2 gallons
of water by using only these two jugs and no other material. Initially, both our jugs are empty.
S.No. Initial State Condition Final state Description of action taken
-
- (x,y) If x<4 (4,y) Fill the 4 gallon jug completely
-
- (x,y) if y<3 (x,3) Fill the 3 gallon jug completely
-
- (x,y) If x>0 (x-d,y) Pour some part from the 4 gallon jug
-
- (x,y) If y>0 (x,y-d) Pour some part from the 3 gallon jug
-
- (x,y) If x>0 (0,y) Empty the 4 gallon jug
-
- (x,y) If y>0 (x,0) Empty the 3 gallon jug
-
- (x,y) If (x+y)<7 (4, y-[4-x]) Pour some water from the 3 gallon jug to fill the four gallon jug
-
- (x,y) If (x+y)<7 (x-[3-y],y) Pour some water from the 4 gallon jug to fill the 3 gallon jug.
-
- (x,y) If (x+y)<4 (x+y,0) Pour all water from 3 gallon jug to the 4 gallon jug
-
- (x,y) if (x+y)<3 (0, x+y) Pour all water from the 4 gallon jug to the 3 gallon jug
Solution of water jug problem according to the production rules S.No. 4 gallon jug contents 3 gallon jug contents Rule followed
- 0 gallon 0 gallon Initial state
- 0 gallon 3 gallons Rule no.2
- 3 gallons 0 gallon Rule no. 9
- 3 gallons 3 gallons Rule no. 2
- 4 gallons 2 gallons Rule no. 7
- 0 gallon 2 gallons Rule no. 5
- 2 gallons 0 gallon Rule no. 9
This Program is Written in Cpp
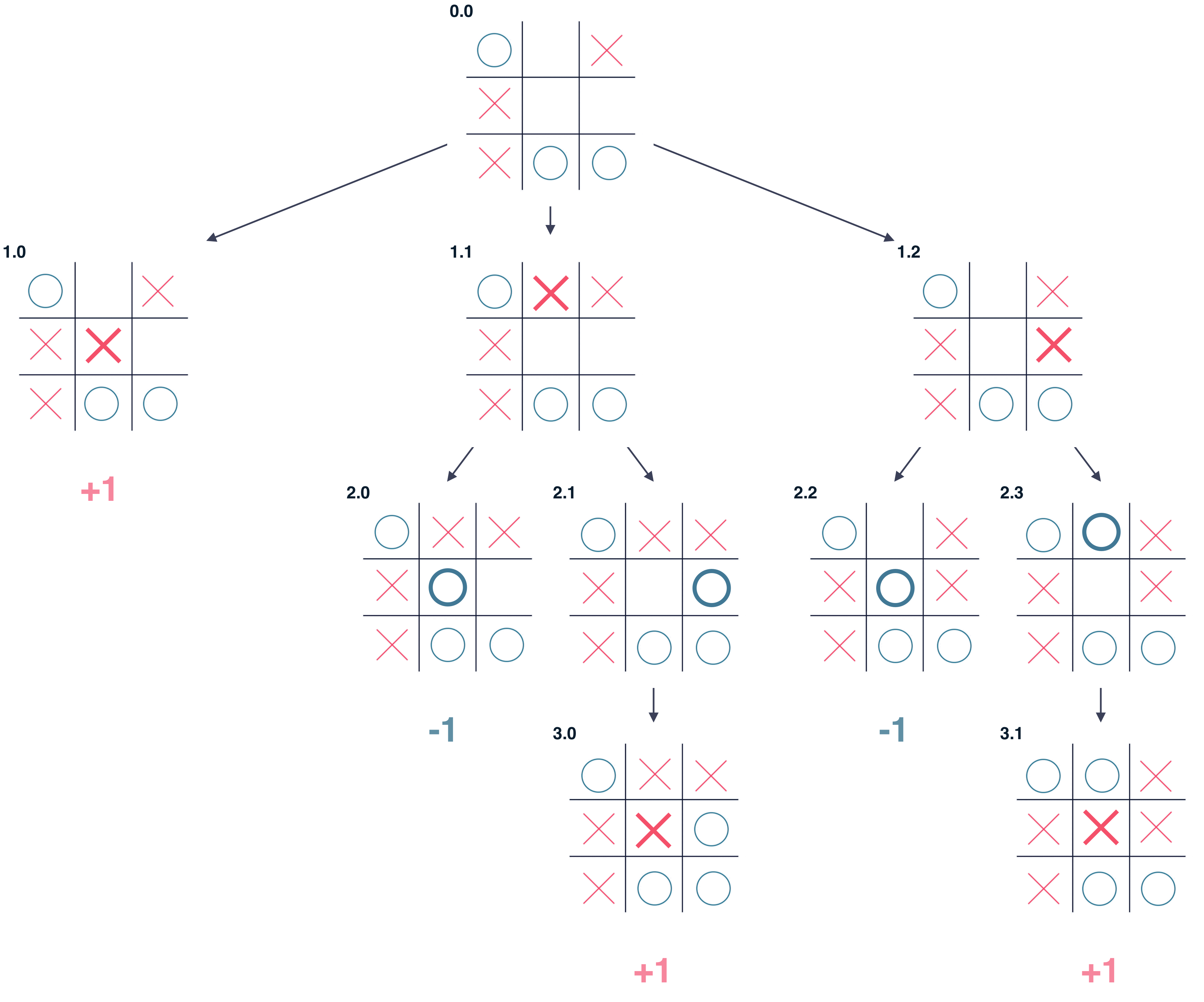
The idea of Best First Search is to use an evaluation function to decide which adjacent is most promising and then explore.
Best First Search falls under the category of Heuristic Search or Informed Search.
It uses the combination of Depth First and Breadth First Search.
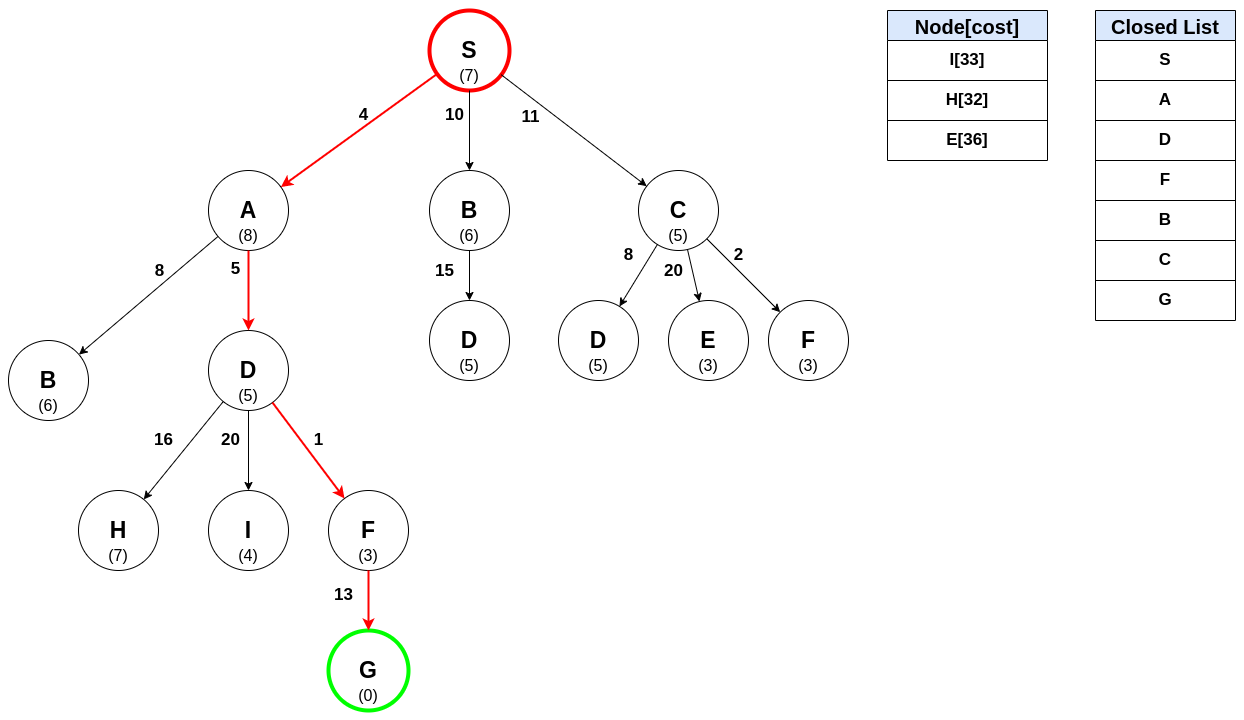
This example is Considered to Find the Desired Solution:
-
The worst-case time complexity for Best First Search is O(n * log n) where n is the number of nodes. In the worst case, we may have to visit all nodes before we reach goal. Note that priority queue is implemented using Min(or Max) Heap, and insert and remove operations take O(log n) time.
-
The performance of the algorithm depends on how well the cost or evaluation function is designed.
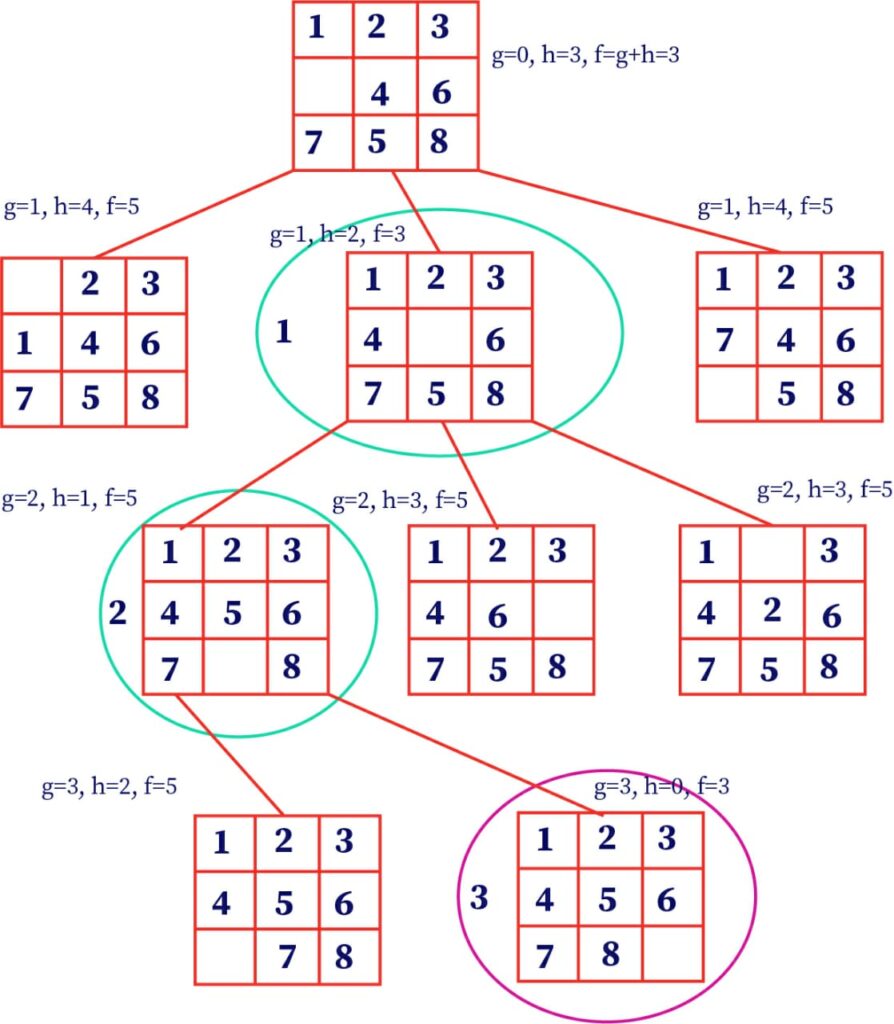
A*Algorithm (pronounced as A-star) is a combination of ‘branch and bound search algorithm’ and ‘best search algorithm’ combined with the dynamic programming principle. The A* Algorithm is well-known because it is used for locating path and graph traversals. This algorithm is used in numerous online maps and games. It uses a heuristic or evaluation function usually denoted by f(X) to determine the order in which the search visits nodes in the tree. The heuristic function for a node N is defined as f(N) = g(N)+h(N) The function g is a measure of the cost of getting from the start node to the current node N, i.e., it is the sum of the costs of the rules that were applied along the best path to the current node. The function h is an estimate of the additional cost of getting from the current node N to the goal node. This is the place where knowledge about the problem domain is exploited. Generally, the A* algorithm is called OR graph/tree search algorithm.
- Hill climbing algorithm is a local search algorithm which continuously moves in the direction of increasing elevation/value to find the peak of the mountain or best solution to the problem. It terminates when it reaches a peak value where no neighbor has a higher value.
- Hill climbing algorithm is a technique which is used for optimizing the mathematical problems. One of the widely discussed examples of Hill climbing algorithm is Traveling-salesman Problem in which we need to minimize the distance traveled by the salesman.
- It is also called greedy local search as it only looks to its good immediate neighbor state and not beyond that.
- A node of hill climbing algorithm has two components which are state and value.
- Hill Climbing is mostly used when a good heuristic is available.
- In this algorithm, we don't need to maintain and handle the search tree or graph as it only keeps a single current state.
Following are some main features of Hill Climbing Algorithm:
-
Generate and Test variant: Hill Climbing is the variant of Generate and Test method. The Generate and Test method produce feedback which helps to decide which direction to move in the search space.
-
Greedy approach: Hill-climbing algorithm search moves in the direction which optimizes the cost.
-
No backtracking: It does not backtrack the search space, as it does not remember the previous states.
In the given problem we are considering a matrix filled with random value and the user is asked to give the starting co-ordinates the code will reach the final solution once no moves are left