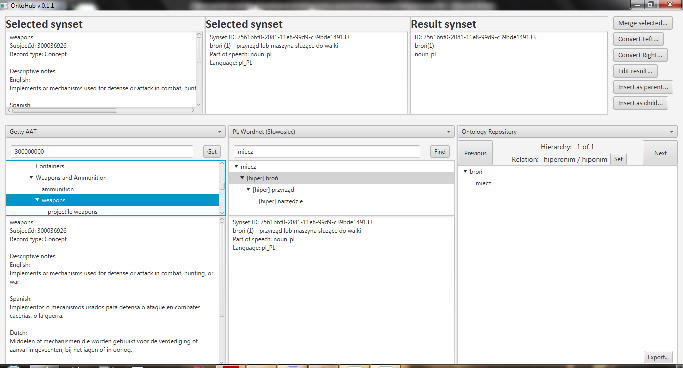
Ontohub (Ontology Hub) is an application that allows to use different knowledge representations (ontologies, thesauri, wordnets) in various formats and operate on them to create new representations of domain or expert knowledge. Starting from choosing various input ontologies, operating on synsets and relations between them, leading to create a brand new knowledge representation.
OntoHub is easily-extensible. Simple implementation of few interfaces allows to add a new Input or Output knowledge representation format. Intuitive and simple interface along with a view that can show two ontologies and result ontology at the same time makes work with the application more enjoyable.
- 3-column view to easily navigate between input and output ontologies
- Merging two synsets into one
- Dynamic synset conversion (application chooses the converter based on input / output formats chosen)
- Editing converted synsets to match user's needs
- Extensibility - adding new ontology formats is fairly simple and generic
Ontohub is currently in an early phase and doesn't support many formats yet. Form the sake of example, Ontohub currently supports following formats:
- Getty Art and Architecture Thesaurus (http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabularies/aat/)
- PL Wordnet (Słowosieć) (http://plwordnet.pwr.wroc.pl/wordnet/)
- Ontology Repository Editor
Extending OntoHub can be achieved by adding new Input or Output formats. To add a new format, the following steps should be performed:
-
Create new Application module (based on gradle).
-
Add module to existing build (Module
onto-hubis the main one) insettings.gradle. -
Create a format main
.fxmlfile that will be loaded to matching column views and corresponding views if applicable in resources folder. -
Implement Controller file. It is important for it to implement
OntologyViewControllerinterface so it can be recognised by application main view. Implement necessary methods. You can follow existing examples or implement it on according to your needs. -
In
commonmodule there are enums that represent formats that are available for application to use. Add the values for your format in desired enum. Add a name for knowledge representation and relative path to.fxml file. That is why you should place view file in resources folder - it can be found easily by the app that way. Path should start from slash and point to valid file - for example/fxml/ontologies/getty_view.fxml. -
Implement your model layer that will represent an ontology - there are no limitations here, so it can be achieved either by generating classes from schemas or implementing it on your own. It is important to have at least one term representation class and one that will reflect relations in that ontology.
-
Wrap your term-representing class by creating a class that implements
KnowledgeRepresentationinterface. If you wonder what class to include in its generic type, just follow the further instructions. -
Create a wrapper that will extend
Relationshipabstract class. Pass theKnowledgeRepresentationclass created in previous step and the Relation-reflecting class from your model. Then add this class implementation as a generic type toKnowledgeRepresentation.
This structure can be a little confusing at the beginnig, but it is the only way to describe proper view of ontology - imagine it by example: A term in the ontology has its own properties, and the list of relationships with other terms in which it can be either a parent or a child. The relation is described by its characteristic and defines its parent and child which are the terms. This created a need to implement a cyclic-generic structure.
-
Add your
KnowledgeRepresentationclass to aSynsetFactoryinconvertermodule. -
All available converters used by application are placed in
convertermodule. Implement your own converters according to desired logic. Converter has to implementFormatConverterinterface with generic types of source and targetKnowledgeRepresentationimplementations. -
Add your
FormatConverterimplementation to aConverterFactoryin aAVAILABLE_CONVERTERSconstant.
- If you are implementing an output format, it is good to use a
TreeRepresentationclass along withResultTreeHandlerclass in your controller implementation. It will cover most cases of inserting new synsets in a result tree. Pass yourKnowledgeRepresentationimplementation along with raw relation model class. - If you want your view to handle polyhierarchical structures, you can use a
MultiTreeControllerclass in your view controller. Pass yourKnowledgeRepresentationimplementation and raw Relation object.
It is important to pass a raw relation object here, because it represents the relation in general, not a particular relationship between terms.