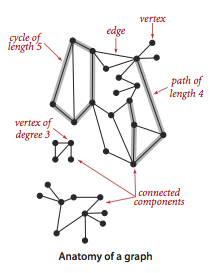
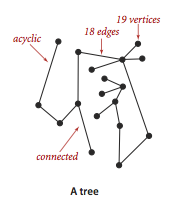
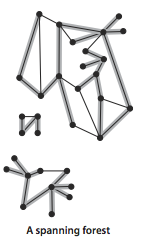
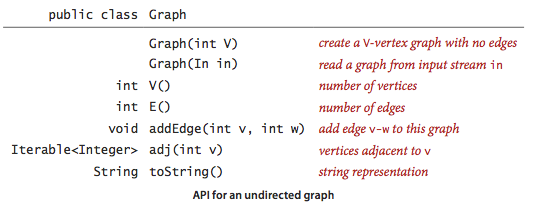
无向图API:
方法 adj() 返回与给定顶点相邻的所有顶点。
下面代码为常用的图处理代码:
public class GraphClient {
// 最大度
public static int maxDegree(Graph G) {
int max = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
if (G.degree(v) > max)
max = G.degree(v);
return max;
}
// 平均度
public static int avgDegree(Graph G) {
// each edge incident on two vertices
return 2 * G.E() / G.V();
}
// 循环数
public static int numberOfSelfLoops(Graph G) {
int count = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
for (int w : G.adj(v))
if (v == w) count++;
return count/2; // self loop appears in adjacency list twice
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
Graph G = new Graph(in);
StdOut.println(G);
StdOut.println("vertex of maximum degree = " + maxDegree(G));
StdOut.println("average degree = " + avgDegree(G));
StdOut.println("number of self loops = " + numberOfSelfLoops(G));
}
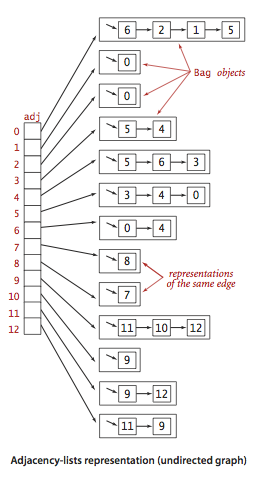
}图常用表示法:邻接矩阵、边的数组、邻接表数组
将每个点的所有相邻顶点都保存在该顶点对应的元素所指向的一张链表中,如上图展示。
public class Graph {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
private final int V;
private int E;
private Bag<Integer>[] adj;
public Graph(int V) {
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
}
public Graph(In in) {
try {
this.V = in.readInt();
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of vertices in a Graph must be nonnegative");
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
int E = in.readInt();
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of edges in a Graph must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
addEdge(v, w);
}
}
catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in Graph constructor", e);
}
}
public Graph(Graph G) {
this(G.V());
this.E = G.E();
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
// reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original
Stack<Integer> reverse = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int w : G.adj[v]) {
reverse.push(w);
}
for (int w : reverse) {
adj[v].add(w);
}
}
}
public int V() {
return V;
}
public int E() {
return E;
}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
E++;
adj[v].add(w);
adj[w].add(v);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
}完整代码:Graph.java
Bag 类:Bag.java
深度优先搜索是一种经典的递归方法,用于系统地检查图中的每个顶点和边。 访问一个顶点:
- 将其标记为已访问过。
- 访问(递归地)与其相邻且尚未标记的所有顶点。
public class DepthFirstSearch {
private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = is there an s-v path?
private int count; // number of vertices connected to s
public DepthFirstSearch(Graph G, int s) {
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
validateVertex(s);
dfs(G, s);
}
// depth first search from v
private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
count++;
marked[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
public boolean marked(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return marked[v];
}
}修改深度优先搜索,不仅要确定两个给定顶点之间是否存在路径,还要找到这样的路径(如果存在)。
以下API:
我们通过将 edgeTo[w] 设置为 v 来记住第一次将我们带到每个顶点 w 的边 v-w 。换句话说,v-w 是从 s 到 w 的已知路径上的最后一条边。 搜索结果是一棵植根于源头的树; edgeTo[] 是该树的父链接表示。
public class DepthFirstPaths {
private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = is there an s-v path?
private int[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on s-v path
private final int s; // source vertex
public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) {
this.s = s;
edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
validateVertex(s);
dfs(G, s);
}
// depth first search from v
private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
edgeTo[w] = v;
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return marked[v];
}
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x])
path.push(x);
path.push(s);
return path;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
int V = marked.length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
}完整代码: DepthFirstPaths.java
广度优先搜索。 深度优先搜索找到从源顶点到目标顶点 v 的一些路径。我们通常需要的是找到最短的路径(具有最小边数的路径)。 广度优先搜索是基于此目标的经典方法。 为了找到从 s 到 v 的最短路径,我们从 s 开始并找我们可以通过一条边就能到达的所有顶点中的 v,然后我们再通过两条边来检查我们可以从 s 到达的所有顶点中的v ..... 以此下去。
为了实现这个策略,我们建立一个已标记但尚未检查其邻接列表的所有顶点的队列。 我们将源顶点放在队列中,然后执行以下步骤直到队列为空:
- 从队列中删除下一个顶点 v。
- 将与 v 相邻的所有未标记顶点放入队列并标记它们。
public class BreadthFirstPaths {
private static final int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = is there an s-v path
private int[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = previous edge on shortest s-v path
private int[] distTo; // distTo[v] = number of edges shortest s-v path
public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) {
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
distTo = new int[G.V()];
edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
validateVertex(s);
bfs(G, s);
assert check(G, s);
}
// breadth-first search from a single source
private void bfs(Graph G, int s) {
Queue<Integer> q = new Queue<Integer>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = INFINITY;
distTo[s] = 0;
marked[s] = true;
q.enqueue(s);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int v = q.dequeue();
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
edgeTo[w] = v;
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + 1;
marked[w] = true;
q.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return marked[v];
}
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>();
int x;
for (x = v; distTo[x] != 0; x = edgeTo[x])
path.push(x);
path.push(x);
return path;
}
}深度优先搜索的下一个直接应用是查找图的连通分量。定义以下API:
public class CC {
private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = has vertex v been marked?
private int[] id; // id[v] = id of connected component containing v
private int[] size; // size[id] = number of vertices in given component
private int count; // number of connected components
/**
* Computes the connected components of the undirected graph {@code G}.
*
* @param G the undirected graph
*/
public CC(Graph G) {
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
id = new int[G.V()];
size = new int[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (!marked[v]) {
dfs(G, v);
count++;
}
}
}
// depth-first search for a Graph
private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
id[v] = count;
size[count]++;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
public int id(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return id[v];
}
public int size(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return size[id[v]];
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
public boolean connected(int v, int w) {
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return id(v) == id(w);
}
}完整代码:CC.java