Данный репозиторий содержит реализации различных алгоритмов на графах и транспортных сетях. Здесь вы найдете генератор ориентированных и неориентированных графов, реализации поиска в глубину и ширину, алгоритм Краскала для построения минимального остовного дерева, алгоритм Косараджу для выделения максимальной связной компоненты, алгоритм Диница для поиска максимального потока в транспортной сети и алгоритм Венгерского для поиска максимального паросочетания в двудольном графе.
Генерирует граф разной связности. На входе программы данные из config.ini, а именно максимальное количество вершин и максимальное количество связей у каждой вершины. Результат выводится в CSV файле, представленном в виде списка смежности.
На вход программы подается CSV файл с графом, записанным в виде списка смежности. На выходе в консоль выводится конечная связь для BFS и DFS.
На вход программы поступает CSV файл со списками смежности графа. Результатом работы являются связи для минимального остовного дерева.
На вход программы поступает CSV файл со списками смежности. Результатом работы являются списки смежностей максимальной связной компоненты.
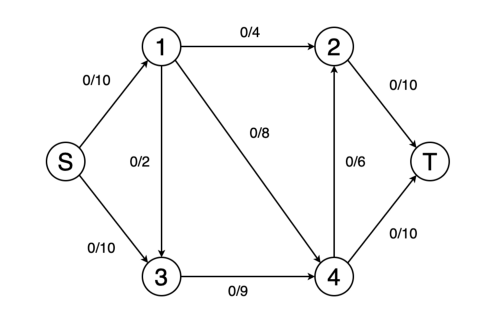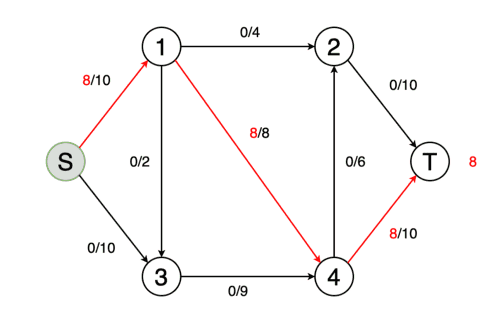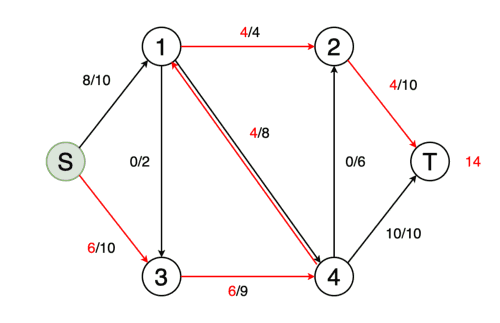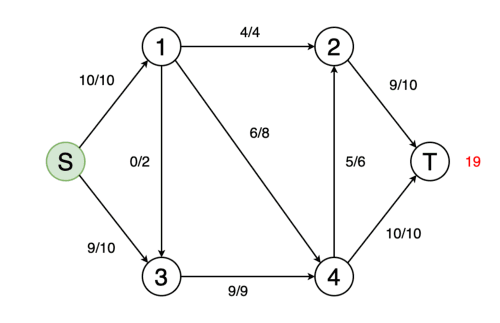
На вход программы поступает CSV файл со списками смежности транспортной сети. Результатом является значение максимального потока в сети.
Реализация Венгерского алгоритма для поиска максимального паросочетания в двудольном графе. В программу на вход поступает матрица транспортной сети, на выходе программа выдает значение максимального паросочетания
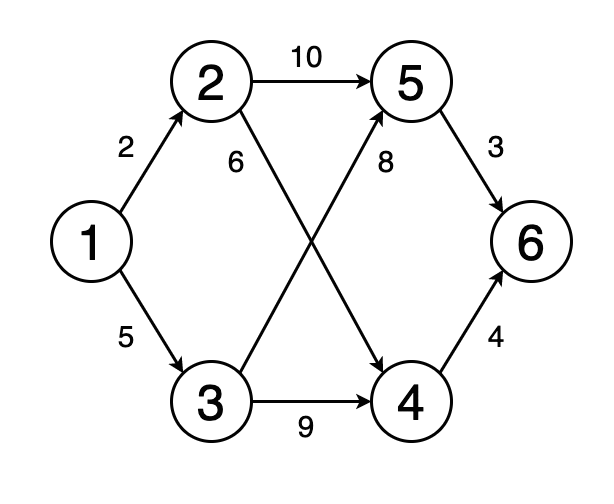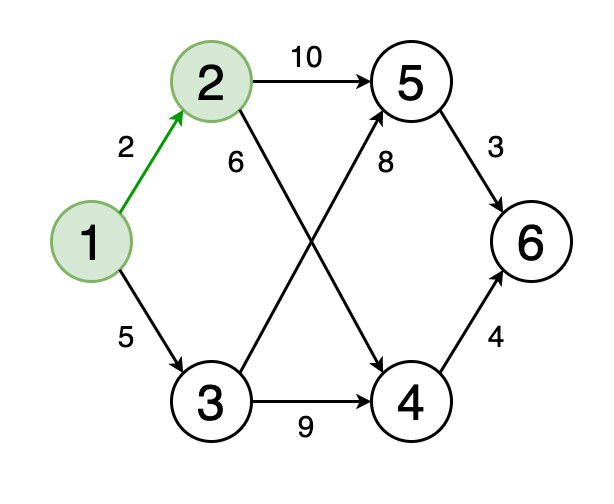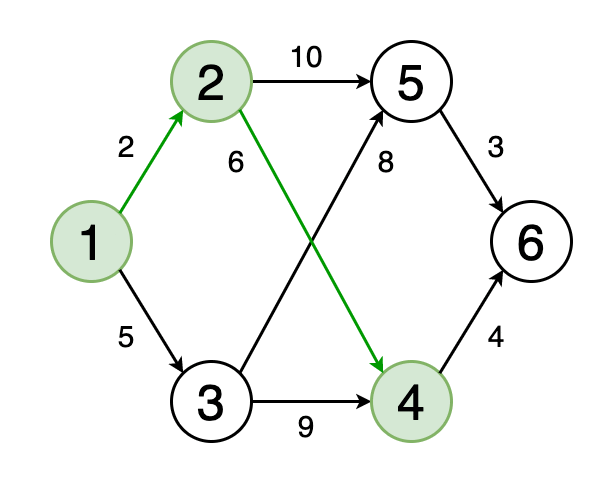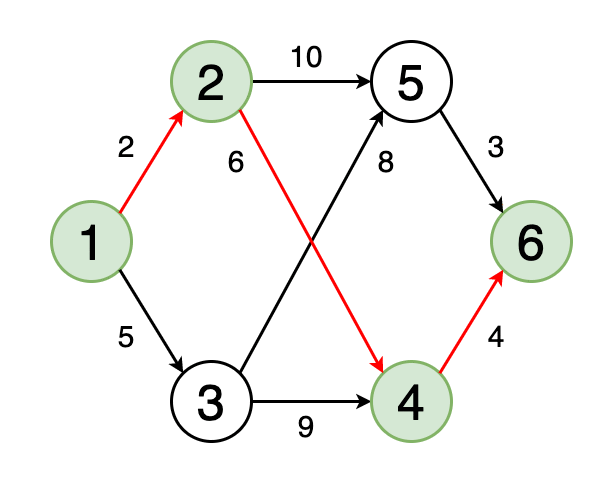
Алгоритм Дейкстры - это алгоритм поиска кратчайшего пути во взвешенном графе с неотрицательными весами ребер. Он был предложен голландским ученым Эдсгером Дейкстрой в 1959 году.
Алгоритм начинает работу с выбора стартовой вершины и установки для нее нулевого расстояния. Затем он переходит к соседним вершинам и обновляет их расстояния, если находит более короткий путь. Этот процесс повторяется, пока все вершины не будут посещены.
Алгоритм Дейкстры использует очередь с приоритетом для хранения вершин, которые нужно обработать. В начале алгоритма в очередь добавляется стартовая вершина с приоритетом 0. Затем на каждой итерации из очереди извлекается вершина с наименьшим приоритетом и обрабатывается.
Для каждой соседней вершины, которая еще не была обработана, алгоритм вычисляет новое расстояние, равное сумме расстояния до текущей вершины и веса ребра, соединяющего текущую вершину с соседней. Если это новое расстояние короче, чем текущее расстояние до соседней вершины, то оно обновляется.
Алгоритм продолжает работу, пока все вершины не будут обработаны, либо пока не будет найден кратчайший путь до конечной вершины. В результате выполнения алгоритма для каждой вершины графа будет найден кратчайший путь до стартовой вершины, а также его длина.
Я не являюсь профессиональным разработчиком, данные программы сделаны в целях обучения, я никого не призываю использовать данный код как профессиональный.
This repository contains implementations of various algorithms on graphs and transport networks. Here you will find a generator of oriented and undirected graphs, implementations of depth and width search, Kraskal's algorithm for constructing a minimum spanning tree, Kosaraju's algorithm for allocating the maximum connected component, Dinitz's algorithm for finding the maximum flow in the transport network and Hungarian's algorithm for finding the maximum matching in a bipartite graph.
Generates a graph of different connectivity. At the input of the program, the data from config.ini, namely the maximum number of vertices and the maximum number of connections for each vertex. The result is output in a CSV file, presented as an adjacency list.
A CSV file with a graph written as an adjacency list is submitted to the program input. The final link for BFS and DFS is output to the console.
The program receives a CSV file with the adjacency lists of the graph. The result of the work are connections for a minimal spanning tree.
A CSV file with adjacency lists is received at the input of the program. The result of the work are lists of adjacencies of the maximum connected component.
A CSV file with lists of transport network adjacency is received at the input of the program. The result is the value of the maximum flow in the network.
Implementation of the Hungarian algorithm for finding the maximum match in a bipartite graph. The program receives a matrix of the transport network at the input, at the output the program outputs the value of the maximum match
Dijkstra's algorithm is an algorithm for finding the shortest path in a weighted graph with non-negative edge weights. It was proposed by the Dutch scientist Edsger Dijkstra in 1959.
The algorithm starts by selecting a starting vertex and setting a zero distance for it. Then it goes to neighboring vertices and updates their distances if it finds a shorter path. This process is repeated until all vertices are visited.
Dijkstra's algorithm uses a priority queue to store the vertices that need to be processed. At the beginning of the algorithm, a starting vertex with priority 0 is added to the queue. Then, at each iteration, the vertex with the lowest priority is extracted from the queue and processed.
For each neighboring vertex that has not yet been processed, the algorithm calculates a new distance equal to the sum of the distance to the current vertex and the weight of the edge connecting the current vertex to the neighboring one. If this new distance is shorter than the current distance to the neighboring vertex, then it is updated.
The algorithm continues to work until all vertices are processed, or until the shortest path to the final vertex is found. As a result of the algorithm, for each vertex of the graph, the shortest path to the starting vertex will be found, as well as its length.
I am not a professional developer, these programs are made for training purposes, I do not encourage anyone to use this code as professional.