Pytorch Implementation of paper:
Hand Gesture Authentication by Discovering Fine-grained Spatiotemporal Identity Characteristics
Wenwei Song, Wenxiong Kang*, and Liang Lin.
Dynamic hand gesture is an emerging and promising biometric trait containing both physiological and behavioral characteristics. Possessing the two kinds of characteristics makes dynamic hand gesture have more identity information enabling more accurate and secure authentication theoretically, but also poses a challenge of efficient fine-grained spatiotemporal feature extraction. This challenge involves a seemingly paradoxical problem that high-frame-rate videos are required for behavioral characteristic analysis, but they can also introduce high computational costs. To mitigate this issue, we propose a Frequency Spatiotemporal Attention Network (FSTA-Net) with a focus on satisfying the high-performance and low-computation requirements of authentication systems. The FSTA-Net is established with a two-stage identity characteristic analysis paradigm for short- and long-term modeling. Specifically, considering that models prefer to analyze physiological characteristics which are relatively straightforward to understand, we first design a Behavior Enhanced (BE) module to emphasize hand motions and facilitate local identity feature distillation in the first stage, and then present a Frequency Spatiotemporal Attention (FSTA) module to summarize global identity features with decent FLOPs and GPU memory occupation in the second stage. Incorporating BE and FSTA modules enables them to complement each other's strengths, resulting in a clear-cut improvement in equal error rate and running speed. Extensive experiments on the SCUT-DHGA dataset demonstrate the superiority of the FSTA-Net.
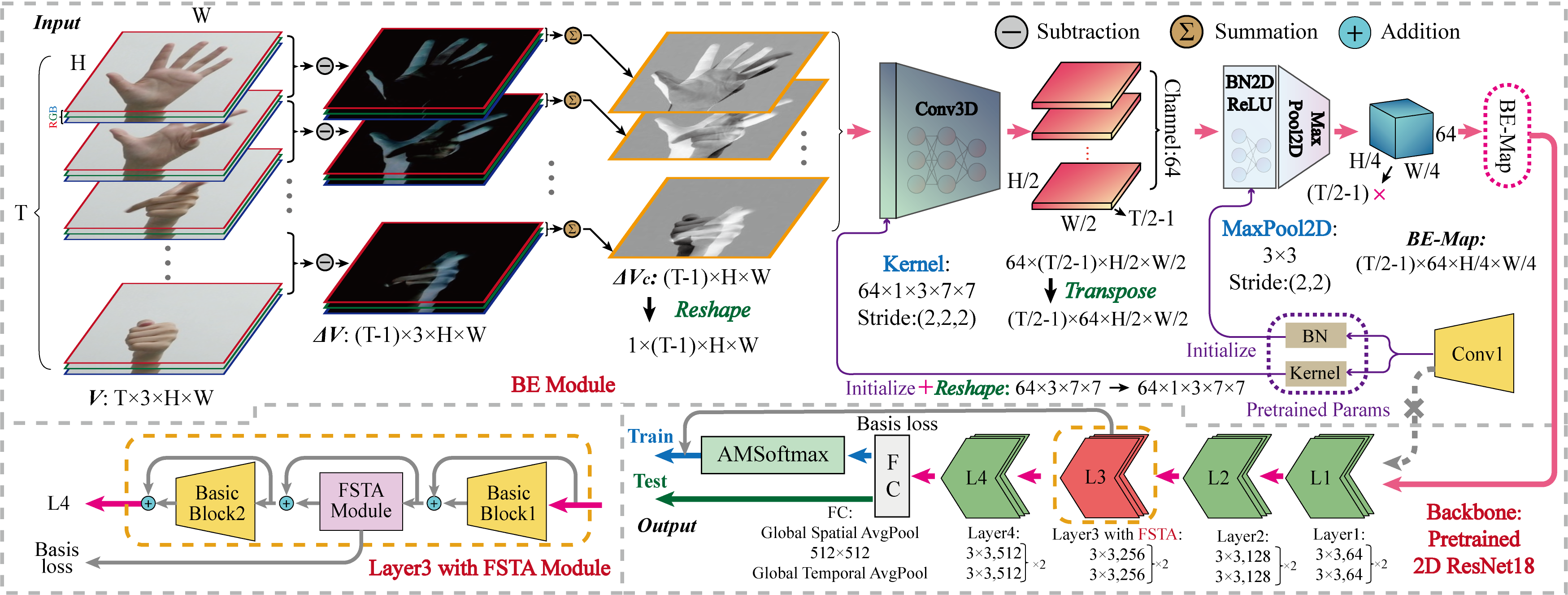
The overall architecture of FSTA-Net. FSTA-Net consists of three components: 2D CNN backbone (bottom right corner), BE Module (top half), and FSTA Module (bottom left corner). For brevity, in the BE module, the 3D kernel shape is in the order of output and input channel, temporal and spatial kernel size; in terms of "Stride" and "Padding", the relevant coefficients are also in the order of temporal and spatial dimension. As for the backbone, we adopt the standard ResNet18; the network configuration values {64, 128, 256, 512} denote the output channel number of each convolutional layer. In the forward propagation of the backbone, the (
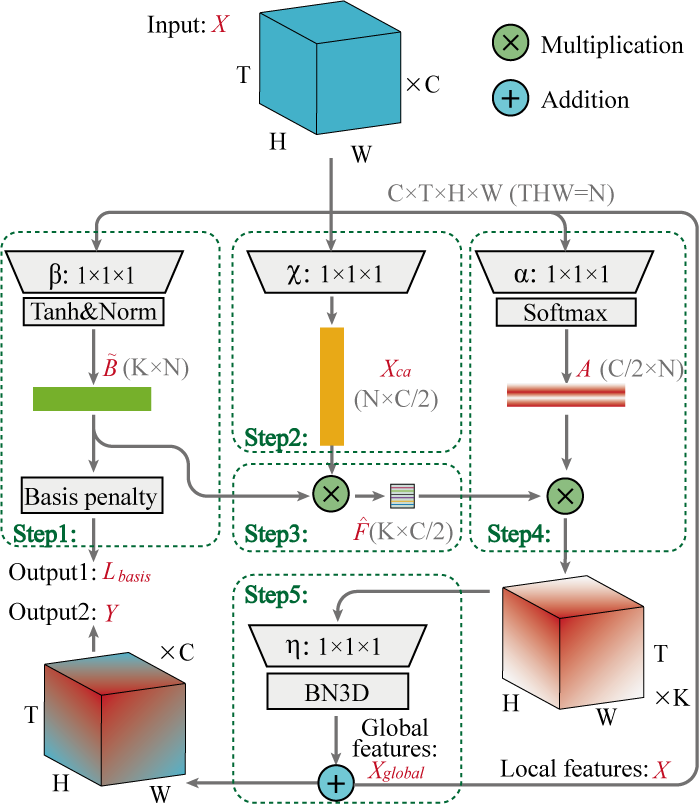
FSTA is mainly formed by four different convolutions (i.e.,
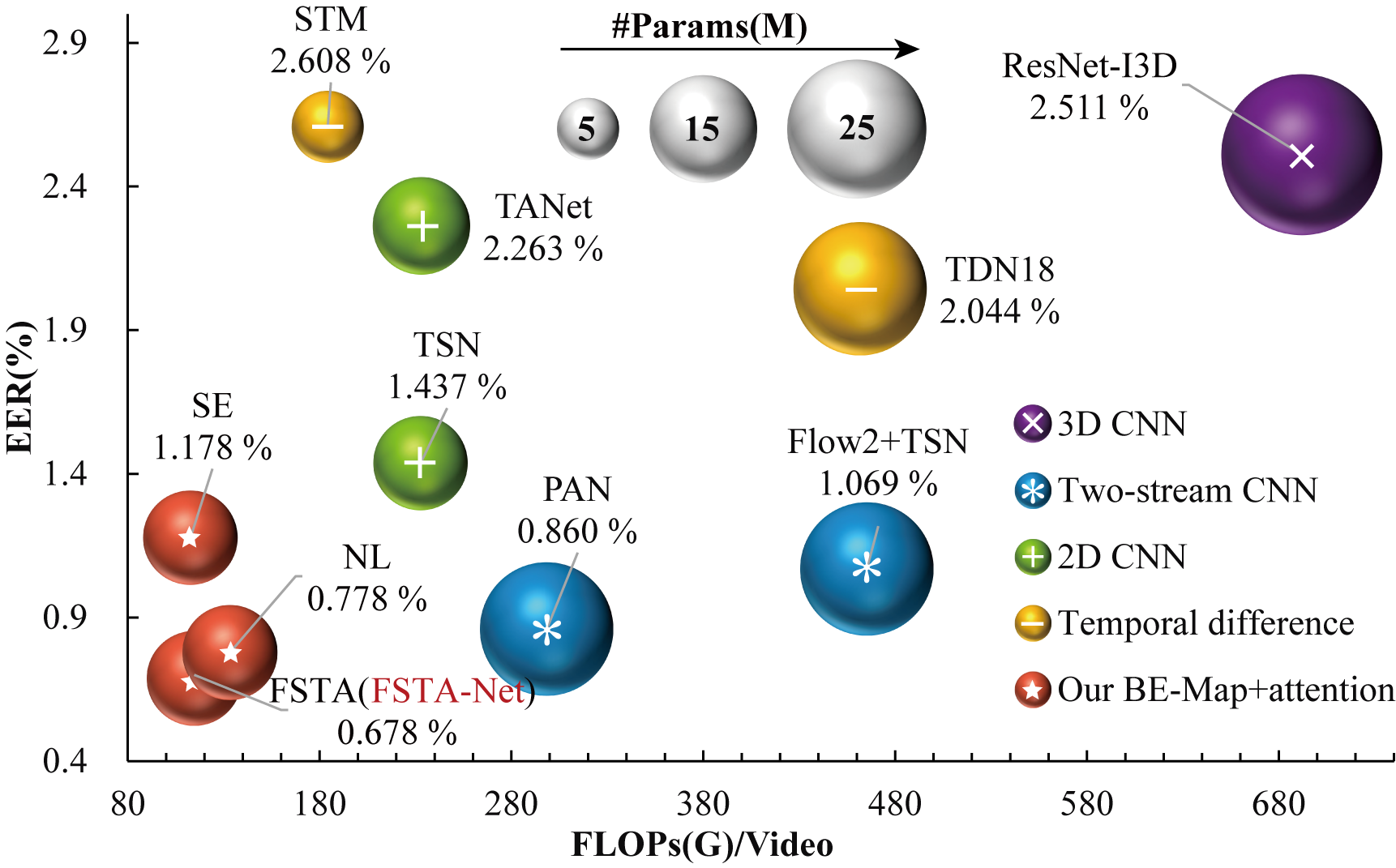
We conduct experiments in three dimensions, including pseudo-modality, attention module, and video understanding network architecture, to justify the superiority of our FSTANet in terms of EER and resource consuming. Extensive experiments evidence that FSTANet achieves SOTA results on the SCUT-DHGA dataset under the MG and UMG setting. The performance of some representative models (selected from the experiment part) under the MG setting are shown below.
Dynamic hand gesture authentication performance comparison on the SCUT-DHGA dataset in terms of equal error rate (EER), computational cost (FLOPs/Video), and model size (#Params). Our proposed FSTA-Net achieves the best trade-off between accuracy and efficiency, compared with the excellent previous methods selected from the experiment part. These models cover 3D CNN, two-stream CNN, 2D CNN, temporal difference, and attention module based on our proposed BE-Map.Please make sure the following libraries are installed successfully:
- PyTorch >= 1.7.0
This repository is a demo of FSTANet. Through debugging (main.py), you can quickly understand the configuration and building method of FSTANet, including BE and FSTA module.
If you want to explore the entire dynamic hand gesture authentication framework, please refer to our pervious work SCUT-DHGA or send an email to Prof. Kang (auwxkang@scut.edu.cn).