This repository contains the code to reproduce the results in our paper Revisiting Simple Neural Probabilistic Language Models, read full paper here.
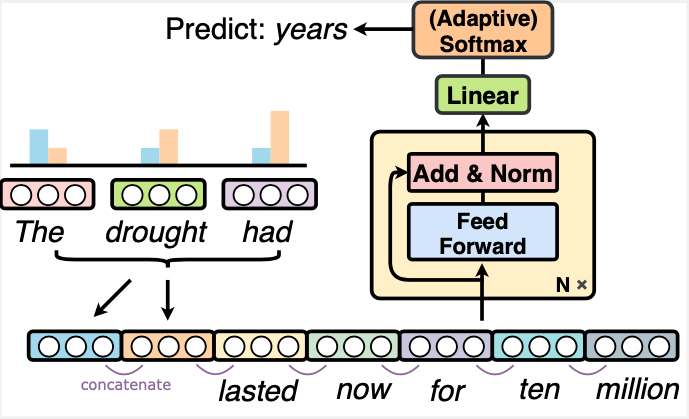
The NPLM in this repository is a modern upgrade to the NPLM proposed by Bengio et al. in this paper. Besides concatenating token embeddings within a fixed local window in the first layer, we additionally include representations of the distant context, which are computed by applying a weighted average to token representations outside the local window.
Part of the code is adapted from SynST and Transformer-xl.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Download raw data of wikitext-103 to data folder $DATA_PATH. We also use wikitext2, enwik8, and lambada. This should work for new datasets, rename different folds of raw .txt files in $DATA_PATH to train.txt, test.txt, and valid.txt if you are using other new datasets.
Run
python main.py --action preprocess -d $DATA_PATH
to preprocess and binarize data. After running this step, there should be three .bin files for each of the train/test/valid fold, and one vocab.pkl in $DATA_PATH.
Example training scripts for training ~148M sized model on wikitext-103:
| Model | Description | Scripts |
|---|---|---|
| NPLM | Modernized NPLM | nplm.sh |
| Transformer | A standard Transformer baseline | transformer.sh |
| Transformer-N | Transformer model with the first layer replaced with token concatenation layer in NPLM | transformer-n.sh |
| Transformer-C | Transformer model with local attention in the first layer | transformer-c.sh |
The scripts assume training with 4 GPUs. You will need to reduce the batch size and increase accumulate-steps to train on fewer GPUs. The training of NPLM should be finished in ~27h on 2080Ti GPUs. Check the appendix of our paper to get information about all hparams for other datasets.
To evaluate perplexity, change the --action arg to evaluate. Relevant model arguments should be the same as what used for training.
Run the following script to evaluate NPLM on wikitext-103 to reproduce ~31.7 perplexity in the paper. $EXPERIMENT_PATH is the path containing the checkpoints, $DATA_PATH is the path containing binarized .bin data files.
python main.py \
--action evaluate --restore $EXPERIMENT_PATH/checkpoint.pt \
--model nplm -v --adaptive \
--tie-projs --tie-weights \
--num-layers 16 --embedding-size 410 --model-size 410 \
--hidden-dim 2100 --mid-dim 1500 --context-config 15 496 \
--num-global-agg 5 --global-aggregate kernel \
-b 4 --batch-length 512 --bsz-gpu0 4 \
-d $DATA_PATH --split valid
Run the following script to evaluate Transformer on wikitext-103 to reproduce ~25.0 perplexity reported in the paper.
python main.py \
--action evaluate \
--model transformer --restore $EXPERIMENT_PATH/checkpoint.pt \
--adaptive --tie-weights --tie-projs --num-layers 16 --num-heads 10 \
--embedding-size 410 --model-size 410 --hidden-dim 2100 \
--attn-type learned --attn-impl full \
--target-length 128 -b 4 \
--batch-length 512 --bsz-gpu0 4 -d $DATA_PATH \
--split valid
To evaluate the target token prediction accuracy of LAMBADA, change the action to acc, and change batch size to 1. Example script for evaluating the Transformer model is shown below:
python main.py \
--action acc --restore $EXPERIMENT_PATH/checkpoint.pt \
--model transformer -v --tie-projs --tie-weights \
--num-layers 16 --embedding-size 512 --model-size 512 \
--num-heads 16 --hidden-dim 4096 --div-val 1\
--attn-type learned --attn-impl full \
--cutoffs 2e4,1e5,2e5 --dropout-p 0.1 --emb-std 0.03 \
--return-rank \
--checkpoint-directory $EXPERIMENT_PATH \
-b 1 --bsz-gpu0 1 --batch-length 512 -d $DATA_PATH \
--split valid
This codebase also supports generate from existing models. To generate from a trained transformer, use the command below:
python main.py\
--action generate --restore $EXPERIMENT_PATH/checkpoint.pt \
--model transformer -v --adaptive \
--tie-weights --tie-projs \
--num-layers 16 --num-heads 10 --embedding-size 410 \
--model-size 410 --hidden-dim 2100 \
--attn-type learned --attn-impl full \
-d $DATA_PATH --split test \
--max-length 30 \
--decoding-algorithm greedy \
--prompt-file generation_prompt.txt \
--output-directory ./ \
--output-filename generation_output.txt
--prompt-file contains line-by-line prompts. --output-filename contains the output from the model, each proceeded by the corresponding prompt.
Current --decoding-algorithm only supports greedy decoding, other sampling-based algorithms will be added in the future.
If you have a comet.ml account, on you can track experiments, by prefixing the script call with:
env $(cat ~/.comet.ml | xargs) python main.py --track ...Where ~/.comet.ml is the file which contains your API key for logging
experiments on the service. By default, this will track experiments in a
workspace named umass-nlp with project name transformer-attn. You can change the project name by specifying --project-name. See args.py in order to
configure the experiment tracking to suit your needs.
If you use this code base or related results in our paper, please cite:
@inproceedings{sun-iyyer-2021-revisiting,
title = "Revisiting Simple Neural Probabilistic Language Models",
author = "Sun, Simeng and
Iyyer, Mohit",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies",
month = jun,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2021.naacl-main.407",
pages = "5181--5188",
abstract = "Recent progress in language modeling has been driven not only by advances in neural architectures, but also through hardware and optimization improvements. In this paper, we revisit the neural probabilistic language model (NPLM) of Bengio et al. (2003), which simply concatenates word embeddings within a fixed window and passes the result through a feed-forward network to predict the next word. When scaled up to modern hardware, this model (despite its many limitations) performs much better than expected on word-level language model benchmarks. Our analysis reveals that the NPLM achieves lower perplexity than a baseline Transformer with short input contexts but struggles to handle long-term dependencies. Inspired by this result, we modify the Transformer by replacing its first self-attention layer with the NPLM{'}s local concatenation layer, which results in small but consistent perplexity decreases across three word-level language modeling datasets.",
}