This work was published in the 16th ACM Conference on Security and Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks 2023 (WiSec23), Guildford, Surrey (UK), May 29 - June 01. You can read "E-Spoofer: Attacking and Defending Xiaomi Electric Scooter Ecosystem" at the following link.
E-Spoofer is a toolkit that reverse-engineers the Xiaomi proprietary application-layer protocols spoken over BLE, and attacks Xiaomi electric scooters (M365, Pro 1, Pro 2, 1S, Essential, Mi 3) and the Mi Home app. It also offers countermeasures that fix the design and implementation flaws of Xiaomi protocols exploited by our attacks. You can find the E-Spoofer open-source repository at https://github.com/Skiti/ESpoofer.
The toolkit works with minimal resources: a computer that supports BLE, Python (+ libraries), NodeJS (+ libraries), an Android phone (no root required), and a Xiaomi e-scooter (among the models previously mentioned).
E-Spoofer implements the Malicious Pairing and the Session Downgrade attacks. Both of them can be perfomed either in proximity (over-the-air from a nearby BLE central), or from remote (by exploiting an already compromised Android smartphone), resulting in a total of four attack.
E-Spoofer fixes the four proposed attacks with two usable, backward-compliant, and low-cost countermeasures.
- The first countermeasure stops the Malicious Pairing attacks by providing a stronger pairing mechanism that is appropriately authorized and authenticated.
- The second countermeasure fixes the Session Downgrade attacks by patching away a hidden downgrade command from the vulnerable e-scooter BLE firmware.
E-Spoofer includes a reverse-engineering module to facilitate future work on the Xiaomi proprietary application-layer protocols, the Xiaomi e-scooter's BLE firmware, and the Mi Home app.
To learn more about our work, please refer to the paper E-Spoofer: Attacking and Defending Xiaomi Electric Scooter Ecosystem. It was published on the 16th ACM Conference on Security and Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks (WiSec23), Guildford, Surrey, United Kingdom, May 29 - June 01, 2023.
Our setup includes a laptop, three smartphones, and three Xiaomi electric scooters.
- The laptop is a Dell Inspiron 15 3000 (11th Gen Intel Core i3-1115G4, 6 MB cache, 2 cores, 4 threads, up to 4.10 GHz Turbo).
- The three smartphones are a rooted Pixel 2 (Android 11), a rooted Oneplus 3 (Android 9), and a Realme GT (Android 12).
- The three Xiaomi e-scooters are an M365, an Essential, and a Mi 3.
More details about our exact setup can be found in the specific README.md file included in each subfolder of the E-Spoofer repository.
The Attacks folder contains the implementation of the Malicious Pairing and Session Downgrade attacks.
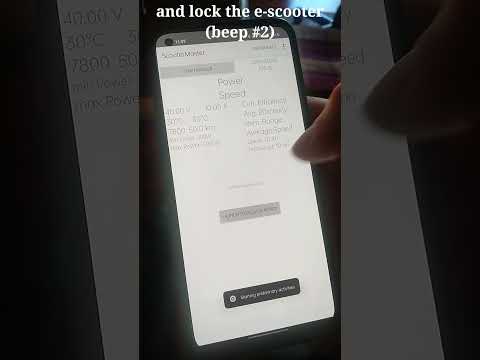
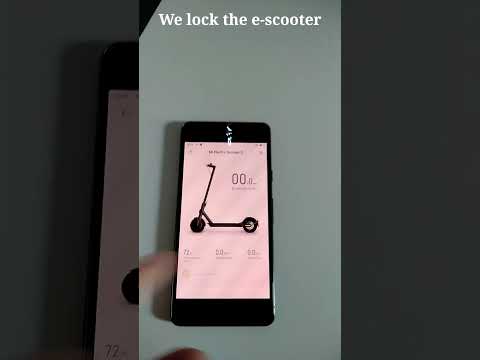
We release the proximity Malicious Pairing attack as a NodeJS script, and the remote Session Downgrade as an Android app. Our attacks are automated, fast (they only need a few seconds) and require a low-cost setup. They can unlock/lock an e-scooter (and prevent access to the device from Mi Home) with no prior knowledge.
Video demonstration of the Malicious Pairing attack on a Xiaomi Mi3 e-scooter:
Video demonstration of the Session Downgrade attack on a Xiaomi M365 e-scooter:
The Countermeasures folder contains one (out of two) proposed countermeasures to the Malicious Pairing and Session Downgrade attacks.
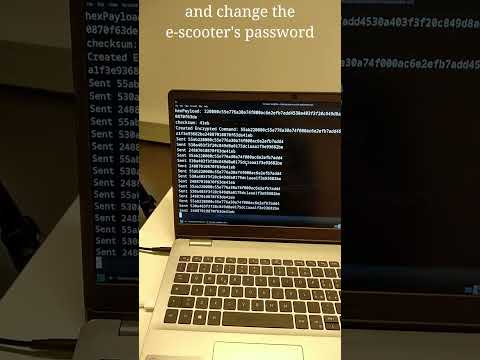
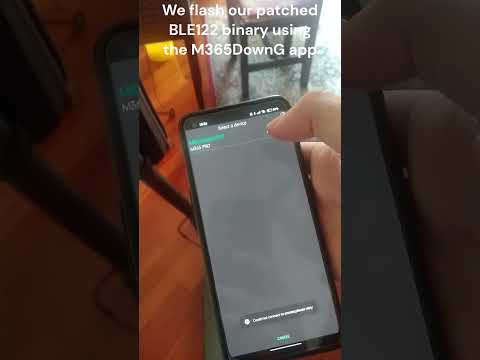
We release a Python script that automatically patches vulnerable BLE firmware vulnerable, protecting it from the Session Downgrade attack.
Video demonstration of the Anti-Downgrade BLE Firmware Patching:
The Reverse-Engineering folder contains tools useful for reverse-engineering Xiaomi e-scooters and the Mi Home app.
We release Frida hooks for Mi Home, that track the cryptograpy used during Xiaomi proprietary Pairing and Session protocols. We implement dissectors, scripts, tests and utilities for the analysis of Xiaomi protocols and BLE captures. We share our Ghidra project that reverse-engineers a huge part of the Xiaomi BLE152 firmware.
During our reverse-engineering experiments, we identified and disclosed a severe UI authentication bug in Mi Home (both Android and iOS versions). From Mi Home v7.6.704 onwards, the user can lock or unlock a password-protected e-scooter without actually entering the password. The cause is an UI delay of password prompt.
Video demonstration of the Mi Home security issue: