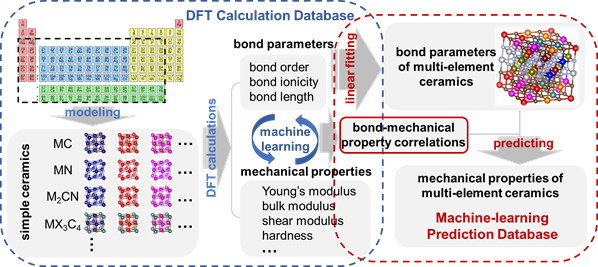
This strategy is hoped to help accelerate the design of high-entropy ceramics with desired mechanical properties.
Step 1: Build a database containing mechanical properties and bond parameters of ceramics with a certain structure, e.g. the rock-salt structure, by a series of DFT calculations. Properties of the simplest ceramics (e.g. mono carbides for rock-salt carbides) must be included.
Step 2: Train prediction models correlating mechanical properties and bond parameters by machine-learning based on the DFT dataset.
Step 3: Prepare the inputs (bond parameters of multi-element ceramics) for prediction, which can be weighted from those of involved constituents from the DFT dataset according to their atomic concentrations.
Step 4: Building the machine-learning prediction database. Bulk, shear and Young’s moduli of multi-element ceramics can be predicted using the trained prediction models in Step 2 and the bond parameters fitted in Step 3. Properties such as hardness, brittleness and densities can also be estimated from the obtained data and be included in the prediction database.
Step 5: Screening ceramics with desired properties from the machine-learning prediction database in Step 4 for further tests of calculations or experiments.
The inputs are three bond parameters (average values in a unit cell): the sum of bond order contributed by atoms in a bond, the bond length and the net charge of a cation. In the uploaded data and code, the three predictors are named as SBO, BL and NETM respectively.
The outputs are mechanical properties of bulk, shear and Young's moduli. In the uploaded data and code, the three mechanical properties are named as B, G and E respectively.
The training code for ML models for bulk, shear and Young's moduli are named as trainModelB.m, trainModelG.m and trainModelE.m respectively. To train a model for the prediction of a mechancial property, e.g. Young's modulus, you can sent the command "[ModelE, validationRMSE] = trainModelE(trainingData)". The output RMSE is a 10-fold cross-validation result, and the output file "ModelE" is the ML prediction model for Young's modulus. The trainingData is the DFT dataset or its subset, which can be found in the "examples" folder.
To use the traned ML model to predict a mechancial property, e.g. Young's modulus, you can use the command "fitE = ModelE.predictFcn(predictioninputs)". The predicted results are stored in the output file "fitE". The prediction inputs for multi-element rock-salt ceramics are provided in the "examples" folder.