-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Initial Setup
There are two main ways to set up ESBMC-AI, via PyPi as a package, or through source code.
Make sure PyPi is installed on your system:
pip install esbmc-aiAlternatively, PipX can be used to install in an isolated environment:
pipx install esbmc-aiNow, ESBMC-AI can be invoked with the following command:
esbmc-ai ...ESBMC-AI is now installed on your system, however, it requires additional components to be setup. Follow the instructions in Additional Setup to complete the setup process.
The following steps detail how to set up ESBMC-AI from the source code. After going into the project root folder, the following steps should be followed:
- Install required Python modules:
pip install -dr requirements.txtAlternatively, use pipenv to install into an environment.
pipenv shell
pipenv lock -d
pipenv sync -dThe following script can be used to launch ESBMC-AI:
./esbmc-aiNow that the project has been set up. You can install using the build script to generate the files:
./build.shThen run pip install ./dist/<wheel-file-name>. Alternatively, you can directly run ESBMC-AI from the project instead of installing it, by calling the script ./esbmc-ai, however, this may yield unexpected behavior if called from a different directory. For non-development usage, it is recommended to install.
ESBMC-AI is now on your system, however, it requires additional components to be setup. Follow the instructions in Additional Setup to complete the setup process.
-
ESBMC: ESBMC-AI does not come with the original ESBMC software. In order to use ESBMC-AI you must download ESBMC. Download the ESBMC executable or build from source. The location of ESBMC can be customized through the config JSON, however, the default location will be
~/.local/binon Linux and macOS, on Windows it needs to be set explicitly. -
Configure ESBMC-AI: The environment variables need to now be setup that ESBMC-AI uses, along with the JSON config. The details can be accessed in the Configuration Wiki Page.
ESBMC-AI can be invoked from the command-line, it only requires providing a filename to a source code file. Arguments provided are position dependent to the filename argument. Arguments before the filename will be handled by ESBMC-AI, while arguments after will be used by the backend ESBMC. The diagram below visualizes the layout:
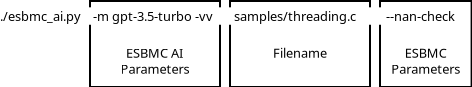
ESBMC-AI can be used to scan a file with default parameters like this:
esbmc-ai /path/to/source_code.cThe execution of the program can be configured from the config.json.
As mentioned above, any parameters before the filename will be processed and consumed by ESBMC-AI. So in this case -v will be consumed by ESBMC-AI, and ESBMC will not get any
arguments.
esbmc-ai -v /path/to/source_code.cAny parameters after the filename will be invoked by the backend ESBMC, they will have no effect on ESBMC-AI.
esbmc-ai /path/to/source_code.c --nan-checkBasic help menu can be accessed with the -h or --help parameter.
./esbmc-ai -hType the following command when inside the chat to view the in-chat commands:
/help
Alternatively, they can be viewed by executing the following command from the command-line:
esbmc-ai -c helpBelow are some very useful arguments that can be passed to ESBMC, they have been taken from ESBMC's help command:
Property checking:
--compact-trace add trace information to output
--no-assertions ignore assertions
--no-bounds-check do not do array bounds check
--no-div-by-zero-check do not do division by zero check
--no-pointer-check do not do pointer check
--no-align-check do not check pointer alignment
--no-pointer-relation-check do not check pointer relations
--no-unlimited-scanf-check do not do overflow check for scanf/fscanf
with unlimited character width.
--nan-check check floating-point for NaN
--memory-leak-check enable memory leak check
--overflow-check enable arithmetic over- and underflow check
--ub-shift-check enable undefined behaviour check on shift
operations
--struct-fields-check enable over-sized read checks for struct
fields
--deadlock-check enable global and local deadlock check with
mutex
--data-races-check enable data races check
--lock-order-check enable for lock acquisition ordering check
--atomicity-check enable atomicity check at visible
assignments
--stack-limit bits (=-1) check if stack limit is respected
--error-label label check if label is unreachable
--force-malloc-success do not check for malloc/new failure
ESBMC-AI made by Yiannis Charalambous
• https://yiannis-charalambous.com • https://github.com/Yiannis128 •