Image segmentation is an important step in image processing, and it seems everywhere if we want to analyze what’s inside the image. For example, if we seek to find if there is a chair or person inside an indoor image, we may need image segmentation to separate objects and analyze each object individually to check what it is. Image segmentation usually serves as the pre-processing before pattern recognition, feature extraction, and compression of the image.
Image segmentation is the classification of an image into different groups. Many kinds of research have been done in the area of image segmentation using clustering. There are different methods and one of the most popular methods is K-Means clustering algorithm.
Image Segmentation involves converting an image into a collection of regions of pixels that are represented by a mask or a labeled image. By dividing an image into segments, you can process only the important segments of the image instead of processing the entire image.
The goal of Image segmentation is to change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze.
- Jupyter Notebook
- Matplotlib
- SkLearn
- Numpy
- Cv2
K-Means clustering algorithm is an unsupervised algorithm and it is used to segment the interest area from the background. It clusters, or partitions the given data into K-clusters or parts based on the K-centroids.
The algorithm is used when you have unlabeled data(i.e. data without defined categories or groups). The goal is to find certain groups based on some kind of similarity in the data with the number of groups represented by K.
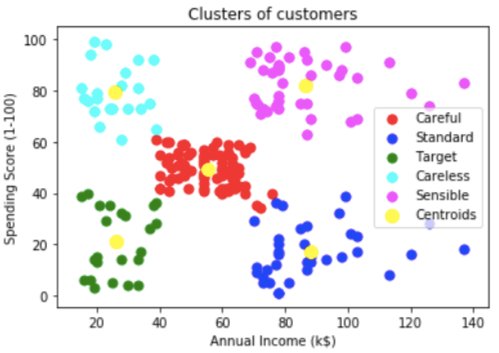
In the above figure, Customers of a shopping mall have been grouped into 5 clusters based on their income and spending score. Yellow dots represent the Centroid of each cluster.
The objective of K-Means clustering is to minimize the sum of squared distances between all points and the cluster center.
==> Steps in K-Means algorithm:-
1. Choose the number of clusters K.
2. Select at random K points, the centroids(not necessarily from your dataset).
3. Assign each data point to the closest centroid → that forms K clusters.
4. Compute and place the new centroid of each cluster.
5. Reassign each data point to the new closest centroid. If any reassignment . took place, go to step 4, otherwise, the model is ready.
==> Steps to choose the optimal number of clusters K:-(Elbow Method)
1. Compute K-Means clustering for different values of K by varying K from 1 to 10 clusters.
2. For each K, calculate the total within-cluster sum of square (WCSS).
3. Plot the curve of WCSS vs the number of clusters K.
4. The location of a bend (knee) in the plot is generally considered as an indicator of the appropriate number of clusters.
Due to advancements in Image processing, Machine learning, AI and related technologies, there will be millions of robots in the world in a few decades' time, transforming the way we live our daily lives. These advancements will involve spoken commands, anticipating the information requirements of governments, translating languages, recognizing and tracking people and things, diagnosing medical conditions, performing surgery, reprogramming defects in human DNA, driverless cars and many more applications, the count of real-life applications is endless.