Mentoring Organization: Portland State University
Mentor: Bart Massey
Student: Abhishek Sehgal
Digital halftoning refers to the process of converting a continuous-tone image or photograph into a pattern of black and white picture elements for reproduction by a binary display device such as an ink jet printer, which can only choose to print or not print dots. The human visual, acting like a low-pass filter, blurs these printed and not printed dots together to create the illusion of continuous shades of gray. Typical halftoning algorithms produce bitmaps as output. However, there are cases when scalable halftone patterns would be useful.
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector image format for two-dimensional graphics with support for interactivity and animation and thus obvious choice for scalable graphics. The project aims to create SVG equivalents of standard halftone patterns. These would allow a lower resolution grayscale image to be approximated by an infinite resolution monochrome vector image.
This project aims to create scalable halftone patterns.
Following algorithms were used and modified to produce vector halftones.
For each possible value in the image, we create and display a pattern of pixels that approximates that value. Remembering the concept of spatial integration, if we choose the appropriate patterns we can simulate the appearance of various intensity levels -- even though our display can only generate a limited set of intensities.
For example, consider a 3 x 3 pattern. It can have one of 512 different arrangements of pixels: however, in terms of intensity, not all of them are unique. Since the number of black pixels in the pattern determines the darkness of the pattern, we really have only 10 discrete intensity patterns (including the all-white pattern), each one having one more black pixel than the previous one.
Algorithm:
- First, intensity of each pixel is calculated on a scale of 0 to 9. (0 being the lowest intensity)
- Then each pixel according to its intensity is mapped into a block of 3*3 .
Now mapping to a block of 3*3 works in case of raster images i.e. when we are creating raster halftone from raster images, but to create SVG halftone we have to map intensity levels to some mathematical figure. So what we did is, we mapped our intensity level to a. Circle b. Triangle c. Hexagon. 0 mapped to the maximum area Circle/Triangle/Hexagon.
- Then using python library svgwrite we created the SVG halftone.
In ordered dithering each dot in the source image must be mapped to a pixel on the display device on a one-to-one basis. Accordingly, the patterning concept was redefined so that instead of plotting the whole pattern for each image dot, THE IMAGE DOT IS MAPPED ONLY TO ONE PIXEL IN THE PATTERN. Returning to our example of a 3 x 3 pattern, this means that we would be mapping NINE image dots into this pattern.
After considerable research, it was found that a set of techniques known as error diffusion (also termed error dispersion or error distribution) accomplished this quite effectively. In fact, error diffusion generates the best results of any of the digital halftoning methods described here.
Error diffusion is very simple to describe. For each point in our image, we first find the closest intensity (or color) available. We then calculate the difference between the image value at that point and that nearest available intensity/color: this difference is our error value. Now we divide up the error value and distribute it to some of the neighboring image areas which we have not visited (or processed) yet. When we get to these later dots, we add in the portions of error values which were distributed there from the preceding dots, and clip the cumulative value to an allowed range if needed. This new, modified value now becomes the image value that we use for processing this point.
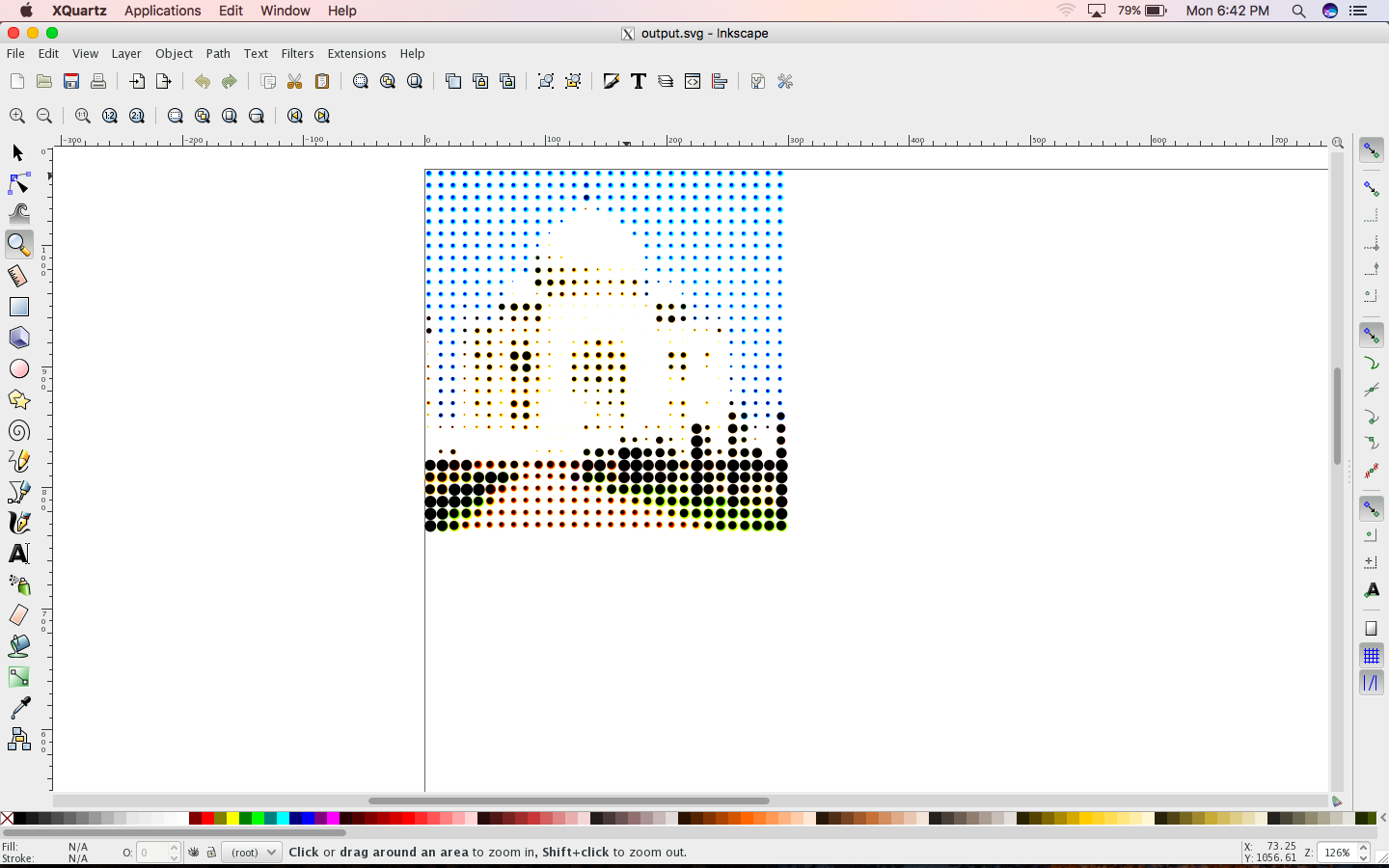
A halftone pattern similar to GIMP's newsprint filter is created using ImageStat. Block by block mean is calculated and each block is mapped to ellipse.