This tutorial teaches developers how to deploy multiple apps to the same AWS EC2 instance using Nginx as a reverse proxy and how to configure subdomains. (Node and Pylot apps)
1. First, configure at least one application for deployment. Follow the instructions below for the corresponding type of app.
var server = app.listen(8001);manager.add_command('runserver', Server(host='127.0.0.1',port='5001'))
# NOTE: port must be a string.application.run(host='127.0.0.1',port=5001)
# NOTE: port must be an integer.Rails: You don't need to specify ports because of Phusion Passenger.
Django: Replace your manage.py file (do not forget to replace PROJECTNAME and PORT with your project name and port number)
#!/usr/bin/env python
import os
import sys
if __name__ == "__main__":
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "PROJECTNAME.settings")
# Different port manage.py file
import django
django.setup()
# Override default port for `runserver` command
from django.core.management.commands.runserver import Command as runserver
runserver.default_port = "PORT"
from django.core.management import execute_from_command_line
execute_from_command_line(sys.argv)Consolidate any existing Nginx files into a SINGLE file. Use a similar format as the example file below. There are two server configs for Node, one for Pylot, one for Rails, and one for Django.
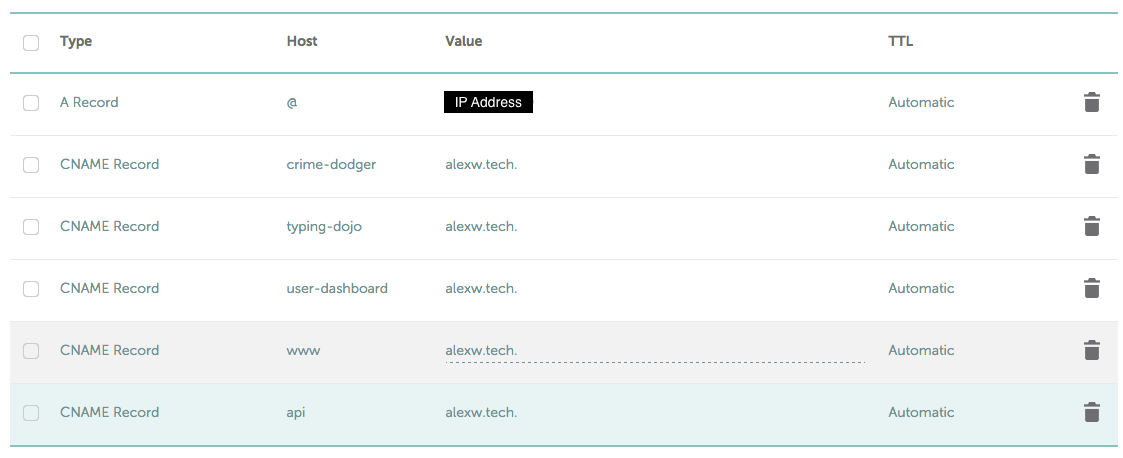
- DOMAIN.com must be replaced by the domain name
- PROJECT#.DOMAIN.com must be replaced by the desired subdomain name
- PORT* must be replaced by the project's port
- PROJECT#.sock must match the configuration of the project.ini file
# Node example (replace PORT1)
server {
server_name DOMAIN.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:PORT1;
}
}
# Node example 2 (replace PROJECT1 and PORT2)
server {
server_name PROJECT1.DOMAIN.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:PORT2;
}
}
# Pylot example (replace PROJECT2 and PORT3)
server {
server_name PROJECT2.DOMAIN.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:PORT3;
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass unix:/home/ubuntu/PROJECT2/PROJECT2.sock;
}
}
# Rails example (replace PROJECT3 and FOLDER)
server {
listen 80;
server_name PROJECT3.DOMAIN.com;
passenger_enabled on;
passenger_app_env development;
root /var/www/FOLDER/public;
}
# Django example (replace REPONAME and PROJECT4)
server {
listen 80;
server_name PROJECT4.DOMAIN.com;
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location /static/ {
root /home/ubuntu/REPONAME;
}
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://unix:/home/ubuntu/REPONAME/PROJECT4.sock;
}
}
cd /var/www
sudo git clone {{project file path on github}}
cd /var/www/{{project_name}}
sudo npm install
pm2 start server.js
sudo service nginx reload && sudo service nginx restartfollow instructions in highlighted blue lines via Pylot Deployment (except for Nginx section)
sudo service nginx reload && sudo service nginx restartfollow instructions via Rails Deployment (except for Nginx section)
sudo service nginx restartfollow instructions via Django Deployment (except for Nginx section) Ubuntu 14.04:
sudo service gunicorn restart
sudo service nginx reload && sudo service nginx restartUbuntu 16.04:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start gunicorn
sudo systemctl enable gunicorn
sudo service nginx restartpm2 statussudo start PROJECTsudo service nginx restartsudo service gunicorn restart
sudo service nginx restartsudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start gunicorn
sudo systemctl enable gunicorn
sudo service nginx restartNote: It may take some time for subdomains to propagate (up to 24 hours). Be sure to test out the domain and subdomains.