Many AMP components and extensions take advantage of remote endpoints by using Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) requests. This document explains the key aspects of using CORS in AMP. To learn about CORS itself, see the W3 CORS Spec.
You might be confused as to why you'd need CORS for requests to your own origin, let's dig into that.
AMP components that fetch dynamic data (e.g., amp-form, amp-list, etc.) make CORS requests to remote endpoints to retrieve the data. If your AMP page includes such components, you'll need to handle CORS so that those requests do not fail.
Let's illustrate this with an example:
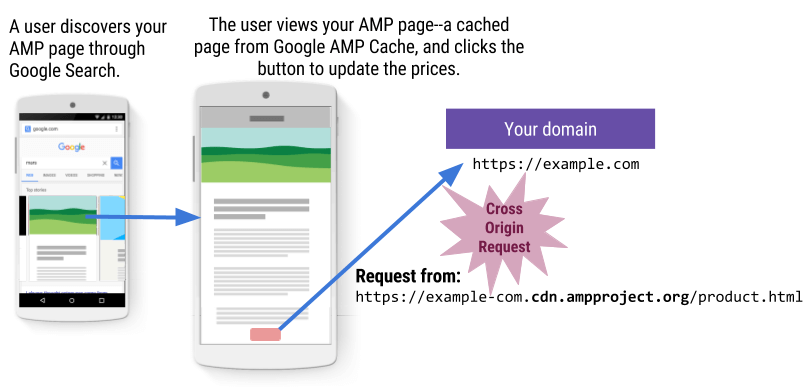
Let's say you have an AMP page that lists products with prices. To update the prices on the page, the user clicks a button, which retrieves the latest prices from a JSON endpoint (done via the amp-list component). The JSON is on your domain.
Okay, so the page is on my domain and the JSON is on my domain. I see no problem!
Ah, but how did your user get to your AMP page? Is it a cached page they access? It's quite likely that your user did not access your AMP page directly, but instead they discovered your page through another platform. For example, Google Search uses the Google AMP Cache to render AMP pages quickly; these are cached pages that are served from the Google AMP Cache, which is a different domain. When your user clicks the button to update the prices on your page, the cached AMP page sends a request to your origin domain to get the prices, which is a mismatch between origins (cache -> origin domain). To allow for such cross-origin requests, you need to handle CORS, otherwise, the request fails.
Okay, what should I do?
- For AMP pages that fetch dynamic data, make sure you test the cached version of those pages; don't just test on your own domain.
- Follow the instructions in this document for handling CORS requests and responses.
Most AMP components that use CORS requests either automatically set the
credentials mode
or allow the author to optionally enable it. For example, the
amp-list
component fetches dynamic content from a CORS JSON endpoint, and allows the
author to set the credential mode through the credentials attribute.
Example: Including personalized content in an amp-list via cookies
<amp-list credentials="include"
src="<%host%>/json/product.json?clientId=CLIENT_ID(myCookieId)">
<template type="amp-mustache">
Your personal offer: ${{price}}
</template>
</amp-list>By specifying the credentials mode, the origin can include cookies in the CORS request and also set cookies in the response (subject to third-party cookie restrictions).
The same third-party cookie restrictions specified in the browser also apply to the credentialed CORS requests in AMP. These restrictions depend on the browser and the platform, but for some browsers, the origin can only set cookies if the user has previously visited the origin in a 1st-party (top) window. Or, in other words, only after the user has directly visited the origin website itself. Given this, a service accessed via CORS cannot assume that it will be able to set cookies by default.
The AMP CORS security protocol consists of three components:
- The CORS
Originheader - The
AMP-Same-Origincustom header - Source origin restrictions via
__amp_source_origin
CORS endpoints receive the requesting origin via the Origin HTTP header.
Endpoints should restrict requests to allow only the following origins:
- Google AMP Cache subdomain:
https://<publisher's subdomain>.cdn.ampproject.org(for example,https://nytimes-com.cdn.ampproject.org) - Google AMP Cache (legacy):
https://cdn.ampproject.org - Cloudflare AMP Cache:
https://<publisher's domain>.amp.cloudflare.com - The Publisher’s own origins
For information on AMP Cache URL formats, see these resources:
For same-origin requests where the Origin header is missing, AMP sets the
following custom header:
AMP-Same-Origin: true
This custom header is sent by the AMP Runtime when an XHR request is made on
the same origin (i.e., document served from a non-cache URL). Allow requests
that contain the AMP-Same-Origin:true header.
In all fetch requests, the AMP Runtime passes the "__amp_source_origin" query
parameter, which contains the value of the source origin (for example,
"https://publisher1.com").
To restrict requests to only source origins, check that the value of the
"__amp_source_origin" parameter is within a set of the Publisher's own
origins.
Important: Perform these validation checks before you process the request. This validation helps to provide protection against CSRF attacks, and avoids processing untrusted sources requests.
Before processing requests that could change the state of your system (for example, a user subscribes to or unsubscribes from a mailing list), check the following:
If the Origin header is set:
-
If the origin does not match one of the following values, stop and return an error response:
*.ampproject.org*.amp.cloudflare.com- the publisher's origin (aka yours)
where
*represents a wildcard match, and not an actual asterisk ( * ). -
If the value of the
__amp_source_originquery parameter is not the publisher's origin, stop and return an error response. -
If the two checks above pass, process the request.
If the Origin header is NOT set:
- Verify that the request contains the
AMP-Same-Origin: trueheader. If the request does not contain this header, stop and return an error response. - Otherwise, process the request.
The resulting HTTP response to a CORS request must contain the following headers:
-
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: <origin>- This header is a W3 CORS Spec requirement,
where
originrefers to the requesting origin that was allowed via the CORSOriginrequest header (for example,"https://cdn.ampproject.org"). Although the W3 CORS spec allows the value of*to be returned in the response, for improved security, you should validate and echo the value of the"Origin"header.
- This header is a W3 CORS Spec requirement,
where
-
AMP-Access-Control-Allow-Source-Origin: <source-origin>- This header allows the specified
source-originto read the authorization response. Thesource-originis the value specified and verified in the"__amp_source_origin"URL parameter (for example,"https://publisher1.com").
- This header allows the specified
-
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: AMP-Access-Control-Allow-Source-Origin- This header simply allows the CORS response to contain the
AMP-Access-Control-Allow-Source-Originheader.
- This header simply allows the CORS response to contain the