(DRAFT)
@mrpackethead, , @taylaand, @nbaillie
502
@TheRealAmazonKendra
( aws-cdk)(vpclattice): L2 for Amazon VPC Lattice #25452
- https://github.com/raindancers/aws-cdk/tree/mrpackethead/aws-vpclattice-alpha/packages/%40aws-cdk/aws-vpclattice-alpha
- https://github.com/raindancers/vpclattice-prealpha-demo
- https://constructs.dev/packages/aws-vpclattice-prealpha
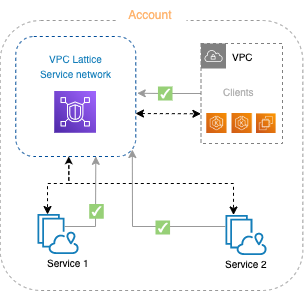
Amazon VPC Lattice is an application networking service that consistently connects, monitors, and secures communications between your services, helping to improve productivity so that your developers can focus on building features that matter to your business. You can define policies for network traffic management, access, and monitoring to connect compute services in a simplified and consistent way across instances, containers, and serverless applications.
The L2 Construct seeks to assist the consumer to create a lattice service easily by abstracting some of the detail. The major part of this is in creating the underlying auth policy and listener rules together, as their is significant intersection in the properties required for both.
- A Service is created
- A Listener is added to the serviceand associated with a ServiceNetwork
- A Rule is assocated with the listener which uses a Lambda function as a target
- A Service Network is created
- The Service is associated with the ServiceNetwork, and two vpcs are attached to it.
- A Lattice Network is created, and associated with two different VPC's, VPC1 and VPC2.
- Two lambdas are created, lambda1 is providing a interface to an api, lambda2 is making requests. Lambda1 will be in VPC1, and Lambda2 in VPC2
import * as core from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { aws_iam as iam } from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
import { SupportResources } from './support';
import { ServiceNetwork, Service, TargetGroup, Target } from '../../lib/index';
export class LatticeTestStack extends core.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: core.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const support = new SupportResources(this, 'supportresources');
// Create a Lattice Service
// this will default to using IAM Authentication
const myLatticeService = new Service(this, 'myLatticeService', {});
// add a listener to the service, using the defaults
// - HTTPS
// - Port 443
// - default action of providing 404 NOT Found,
// - cloudformation name
const myListener = new vpclattice.Listener(this, 'Listener', {
service: myLatticeService,
});
// add a listenerRule that will use the helloworld lambda as a Target
mylistener.addListenerRule({
name: 'helloworld',
priority: 10,
action: [
{
targetGroup: new vpclattice.TargetGroup(this, 'hellolambdatargets', {
name: 'hellowworld',
target: vpclattice.Target.lambda([support.helloWorld]),
}),
},
],
httpMatch: {
pathMatches: { path: '/hello' },
},
// we will only allow access to this service from the ec2 instance
accessMode: vpclattice.RuleAccessMode.UNAUTHENTICATED,
});
//add a listenerRule that will use the goodbyeworld lambda as a Target
mylistener.addListenerRule({
name: 'goodbyeworld',
priority: 20,
action: [
{
targetGroup: new vpclattice.TargetGroup(
this,
'goodbyelambdatargets',
{
name: 'goodbyeworld',
target: vpclattice.Target.lambda([support.goodbyeWorld]),
},
),
},
],
httpMatch: {
pathMatches: { path: '/goodbye' },
},
// we will only allow access to this service from the ec2 instance
allowedPrincipals: [support.ec2instance.role],
accessMode: vpclattice.RuleAccessMode.AUTHENTICATED_ONLY,
});
myLatticeService.applyAuthPolicy();
/**
* Create a ServiceNetwork.
* OPINIONATED DEFAULT: The default behavior is to create a
* service network that requries an IAM policy, and authenticated access
* ( requestors must send signed requests )
*/
const serviceNetwork = new ServiceNetwork(this, 'LatticeServiceNetwork', {
services: [myLatticeService],
vpcs: [support.vpc1],
});
serviceNetwork.applyAuthPolicyToServiceNetwork();
}
}(The Api is additionally documented on Constructs.dev here)
- ✓ ServiceNetwork
- ✓ [ServiceNetworkAssociation] (#servicenetworkassociation)
- ✓ Service
- ✓ [ServiceAssociation]
- ✓ Listener
- ✓ TargetGroup
- [HealthCheck]
- [LoggingDestination]
- [Target]
- [AuthType]
- [FixedResponse]
- [HTTPMethods]
- [IpAddressType]
- [MatchOperator]
- [PathMatchType]
- [Protocol]
- [ProtocolVersion]
- [RuleAccessMode]
- [ServiceNetworkAccessMode]
- [TargetType]
Creates a cloudformation AWS::VpcLattice::ServiceNetwork
A service network is a logical boundary for a collection of services. Services associated with the network can be authorized for discovery, connectivity, accessibility, and observability. To make requests to services in the network, your service or client must be in a VPC that is associated with the service network.
The construct will extend ServiceNetworkBase and implement IServiceNetwork.
/**
* Create a vpc lattice service network.
* Implemented by `ServiceNetwork`.
*/
export interface IServiceNetwork extends core.IResource {
/**
* The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the service network.
*/
readonly serviceNetworkArn: string;
/**
* The Id of the Service Network
*/
readonly serviceNetworkId: string;
/**
* Is this an imported serviceNetwork
*/
readonly imported: boolean;
/**
* Add Lattice Service
*/
addService(props: AddServiceProps): void;
/**
* Associate a VPC with the Service Network
*/
associateVPC(props: AssociateVPCProps): void;
}The Construct will consume ServiceNetworkProps.
export interface ServiceNetworkProps {
/** The name of the Service Network. If not provided Cloudformation will provide
* a name
* @default cloudformation generated name
*/
readonly name?: string;
/**
* The type of authentication to use with the Service Network. The only method avaialble is
* AWS_IAM, however in anticipation, it is expected that other types will be added.
* @default 'AWS_IAM'
*/
readonly authorizer?: Authorizer | undefined;
/**
* Logging destinations
* @default: no logging
*/
readonly loggingDestinations?: LoggingDestination[];
/**
* Lattice Services that are assocaited with this Service Network
* @default no services are associated with the service network
*/
readonly services?: IService[] | undefined;
/**
* Vpcs that are associated with this Service Network
* @default no vpcs are associated
*/
readonly vpcs?: ec2.IVpc[] | undefined;
/**
* An access mode provides 'pre-canned' conditions for the policy
* @default no conditions
*/
readonly accessmode?: ServiceNetworkAccessMode | undefined;
}ServiceNetwork will implement statics in addition to those in IServiceNetwork, to allow the import of the servicenetwork in other stacks
( potentially cross account ). fromName provides a lookup to obtain the Id, using a custom resource. This provides a way to pass a concrete
value between cross account stacks.
public static fromId(scope: constructs.Construct, id: string, props: ImportedServiceNetworkProps ): IServiceNetwork {
return new ImportedServiceNetwork(scope, id, props);
}
public static fromName(scope: constructs.Construct, id: string, serviceNetworkName: string ): IServiceNetwork {
return new ImportedServiceNetwork(scope, id, { serviceNetworkName: serviceNetworkName });
}ServiceNetwork will implement methods for a variety of tasks;
// adds an iam statement to the the authpolicy. Use this to create policy that is bespoke to this application
addStatementToAuthPolicy(statement: iam.PolicyStatement)// applies the AuthPolicy that has been created, to the serviceNetwork.
applyAuthPolicyToServiceNetwork();// creates and associates a logging subscription to provide visisiblity for the lattice service
addloggingDestination(props: AddloggingDestinationProps)// share the service network using RAM
public share(props: ShareServiceNetworkProps)Creates a Cloudformation AWS::VpcLattice::ServiceNetworkServiceAssociation Associates a service with a service network.
ServiceNetworkAssociation extends core.Resource and consumes ServiceNetworkAssociationProps Consider using .associateWithServiceNetwork method on
Service in preference.
export interface ServiceNetworkAssociationProps {
/**
* lattice Service
*/
readonly serviceNetwork: IServiceNetwork;
/**
* Lattice ServiceId
*/
readonly serviceId: string;
}Creates a cloudformation AWS::VpcLattice::Service
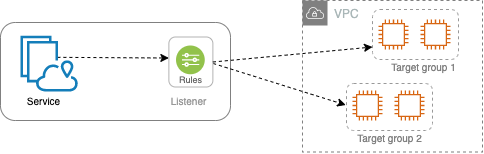
A service within VPC Lattice is an independently deployable unit of software that delivers a specific task or function. A service has listeners that use rules, that you configure to route traffic to your targets. Targets can be EC2 instances, IP addresses, serverless Lambda functions, Application Load Balancers, or Kubernetes Pods. The following diagram shows the key components of a typical service within VPC Lattice.
Service extends core.Resource and implments IService
export interface IService extends core.IResource {
/**
* The Id of the Service
*/
readonly serviceId: string;
/**
* The Arn of the Service
*/
readonly serviceArn: string;
/**
* the discovered OrgId
*/
readonly orgId: string | undefined;
/**
* Imported
*/
readonly imported: boolean;
/**
* The authType of the service.
*/
authType: AuthType | undefined;
/**
* A certificate that may be used by the service
*/
certificate: certificatemanager.Certificate | undefined;
/**
* A custom Domain used by the service
*/
customDomain: string | undefined;
/**
* A DNS Entry for the service
*/
dnsEntry: aws_vpclattice.CfnService.DnsEntryProperty | undefined;
/**
* A name for the service
*/
name: string | undefined;
/**
* The auth Policy for the service.
*/
authPolicy: iam.PolicyDocument;
/**
* associate the service with a servicenetwork.
*/
associateWithServiceNetwork(serviceNetwork: IServiceNetwork): void;
}Service will take ServiceProps as props
/**
* Properties for a Lattice Service
*/
/**
* Properties for a Lattice Service
*/
export interface ServiceProps {
/**
* Name for the service
* @default cloudformation will provide a name
*/
readonly name?: string | undefined;
/**
* The authType of the Service
* @default 'AWS_IAM'
*/
readonly authorizer: IAuthorizer;
/**
* Listeners that will be attached to the service
* @default no listeners
*/
readonly listeners?: IListener[] | undefined;
/**
* A certificate that may be used by the service
* @default no custom certificate is used
*/
readonly certificate?: certificatemanager.Certificate | undefined;
/**
* A customDomain used by the service
* @default no customdomain is used
*/
readonly customDomain?: string | undefined;
/**
* A custom hosname
* @default no hostname is used
*/
readonly dnsEntry?: aws_vpclattice.CfnService.DnsEntryProperty | undefined;
/**
* Share Service
*@default no sharing of the service
*/
readonly shares?: ShareServiceProps[] | undefined;
/**
* ServiceNetwork to associate with.
* @default will not assocaite with any serviceNetwork.
*/
readonly serviceNetwork?: IServiceNetwork | undefined;
}Service will implement a static for importing the service.
public static fromId(scope: constructs.Construct, id: string, serviceId: string): IService {
return new ImportedService(scope, id, serviceId);
}Note: unlike ServiceNetwork there are minimal reason to implmenet a import by name, (so a concrete reference can be used cross accounts), as a services 'boundarys' are within a single account. THe fromId allows an import of the service from within an account, if required to implement multiple stacks.. (this however is probably an edge case as well). The use case here is dependant on the security stance of how lattice will be configured and who has control of the service/servicenetworks. Its unclear if a crossAccount method should be implemeneted.
Service will implement methods for the following
/**
* .grantAccess on a lattice service, will permit the principals to
* access all resoruces of the service. Consider using finer permissions
* at the rule level.
*
* @param principals
*/
public grantAccess(principals: iam.IPrincipal[]) { } /**
* apply an authpolicy to the service
*/
public applyAuthPolicy(): iam.PolicyDocument { } /**
* Add a PolicyStatement to the auth policy
*/
public addPolicyStatement(statement: iam.PolicyStatement): void { } /**
* Share the service to other accounts via RAM
*/
public shareToAccounts(props: ShareServiceProps): void { }/**
* Associate with a Service Network
*/
public associateWithServiceNetwork(serviceNetwork: IServiceNetwork): void { }Associates a ServiceNetwork to a Service
ServiceNetworkAssociation extends core.Resource and consumes
ServiceNetworkAssocationProps.
/**
* Props for Service Assocaition
*/
export interface ServiceNetworkAssociationProps {
/**
* lattice Service
*/
readonly serviceNetwork: IServiceNetwork;
/**
* Lattice ServiceId
*/
readonly serviceId: string;
}Creates a cloudformation AWS::VpcLattice::Listener
A listener is a process that checks for connection requests, using the protocol and port that you configure. The rules that you define for a listener determine how the service routes requests to its registered targets.
It is not expected that a direct call to Listener will be made, instead the .addListener() should be used on a service
Listener extends core.resource implements IListener
/**
* Create a vpcLattice Listener.
* Implemented by `Listener`.
*/
export interface IListener extends core.IResource {
/**
* The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the service.
*/
readonly listenerArn: string;
/**
* The Id of the Service Network
*/
readonly listenerId: string;
/**
* Add A Listener Rule to the Listener
*/
addListenerRule(props: AddRuleProps): void;
}Listener will consome ListenerProps
/**
* Propertys to Create a Lattice Listener
*/
export interface ListenerProps {
/**
* * A default action that will be taken if no rules match.
* @default 404 NOT Found
*/
readonly defaultAction?:
| aws_vpclattice.CfnListener.DefaultActionProperty
| undefined;
/**
* protocol that the listener will listen on
* @default HTTPS
*/
readonly protocol?: Protocol | undefined;
/**
* Optional port number for the listener. If not supplied, will default to 80 or 443, depending on the Protocol
* @default 80 or 443 depending on the Protocol
*/
readonly port?: number | undefined;
/**
* The Name of the service.
* @default CloudFormation provided name.
*/
readonly name?: string;
/**
* The Id of the service that this listener is associated with.
*/
readonly service: IService;
}Listener will implement methods
/**
* add a rule to the listener, which will implement AWS::VpcLattice::Rule
* @param props AddRuleProps
*/
public addListenerRule(props: AddRuleProps): void { }Creates a cloudformation AWS::VpcLattice::TargetGroup
A VPC Lattice target group is a collection of targets, or compute resources, that run your application or service. Targets can be EC2 instances, IP addresses, Lambda functions, Application Load Balancers
TargetGroup extends core.Resource and implements ITargetGroup
/** Create a vpc lattice TargetGroup.
* Implemented by `TargetGroup`.
*/
export interface ITargetGroup extends core.IResource {
/**
* The id of the target group
*/
readonly targetGroupId: string;
/**
* The Arn of the target group
*/
readonly targetGroupArn: string;
}TargetGroup will take TargetGroupProps
/**
* Properties for a Target Group, Only supply one of instancetargets, lambdaTargets, albTargets, ipTargets
*/
export interface TargetGroupProps {
/**
* The name of the target group
*/
readonly name: string;
/**
* Targets
*/
readonly target: Target;
}Authorizer is an enum like class with static functions to return propertys for an Authorizer Type. At present the only type of
Authorizers are NONE or AWS_IAM. In order to provide non breaking upgrades for the possiblity of other authorizers in the future
this class is used rather than an enum.
/**
* Authorization Types for VPC Lattice. The class type Enum is used to allow
* for the creation of other authentication methods easily in the future.
*/
export enum AuthorizerMode {
/**
* No Authorization is used for Lattice Requests
*/
NONE = 'NONE',
/**
* IAM Policys are used for Lattice Requests.
*/
AWS_IAM = 'AWS_IAM'
}
/**
* Authorizer Interface.
*/
export interface IAuthorizer {
/**
* Authorizer Mode
*/
readonly type: AuthorizerMode;
}
/**
* Authorization Type for Lattice.
*/
export abstract class Authorizer implements IAuthorizer {
/**
* Use IAM Policy for Authorization
*/
public static iam(): IAuthorizer {
return {
type: AuthorizerMode.AWS_IAM,
};
}
/**
* Use no Authorization for Lattice Requests
*/
public static none(): IAuthorizer {
return {
type: AuthorizerMode.NONE,
};
}
/**
* THe AuthMode TYpe
*/
public abstract readonly type: AuthorizerMode;
protected constructor() {};
}Target is an abstract class with static function to return propertys for use in a TargetGroup Targets can be lambda, ipAddress, ec2instances, or
applicaiton loadbalancers.
/**
* Targets for target Groups
*/
export abstract class Target {
/**
* Lambda Target
* @param lambda
*/
public static lambda(lambda: aws_lambda.Function[]): Target { };
/**
* IpAddress as Targets
* @param ipAddress
* @param config
*/
public static ipAddress(ipAddress: string[], config: aws_vpclattice.CfnTargetGroup.TargetGroupConfigProperty ): Target { };
/**
* EC2 Instances as Targets
* @param ec2instance
* @param config
*/
public static ec2instance(ec2instance: ec2.Instance[], config: aws_vpclattice.CfnTargetGroup.TargetGroupConfigProperty): Target { };
/**
* Application Load Balancer as Targets
* @param alb
* @param config
*/
public static applicationLoadBalancer(alb: elbv2.ApplicationListener[], config: aws_vpclattice.CfnTargetGroup.TargetGroupConfigProperty): Target { }LoggingDestination is a abstract class to return properties for a LoggingSubscription
/**
* Logging options
*/
export abstract class LoggingDestination {
/**
* Construct a logging destination for a S3 Bucket
* @param bucket an s3 bucket
*/
public static s3(bucket: s3.IBucket): LoggingDestination {}
/**
* Send to CLoudwatch
* @param logGroup
*/
public static cloudwatch(logGroup: logs.ILogGroup): LoggingDestination {}
/**
* Stream to Kinesis
* @param stream
*/
public static kinesis(stream: kinesis.IStream): LoggingDestination {}
}HealthChecks is an abstract class that is used to build a Health Check which can be optionally used as part of a listener rule.
/**
* A Configuration of the TargetGroup Health Check.
*/
export interface TargetGroupHealthCheckProps {
/**
* Enable this Health Check
* @default true
*/
readonly enabled?: boolean | undefined;
/**
* Health Check Interval
* @default 30 seconds
*/
readonly healthCheckInterval?: core.Duration | undefined;
/**
* TimeOut Period
* @default 5 seconds
*/
readonly healthCheckTimeout?: core.Duration | undefined;
/**
* Number of Healthy Responses before Target is considered healthy
* @default 2
*/
readonly healthyThresholdCount?: number | undefined;
/**
* Check based on Response from target
* @default 200 OK
*/
readonly matcher?: FixedResponse | undefined;
/**
* Path to use for Health Check
* @default '/'
*/
readonly path?: string | undefined;
/**
* Port to use for Health Check
* @default 443
*/
readonly port?: number | undefined;
/**
* Protocol to use for Health Check
* @default HTTPS
*/
readonly protocol?: Protocol | undefined;
/**
* Protocol to use for Health Check
* @default HTTP2
*/
readonly protocolVersion?: ProtocolVersion | undefined;
/**
* Number of unhealty events before Target is considered unhealthy
* @default 1
*/
readonly unhealthyThresholdCount?: number | undefined;
}
/**
* Create a Health Check for a target
*/
export abstract class HealthCheck {
/**
* A Health Check configuration object for a target
* @param props
* @returns HealthCheck
*/
public static check(props: TargetGroupHealthCheckProps): HealthCheck {
// validate the ranges for the health check
if (props.healthCheckInterval) {
if (
props.healthCheckInterval.toSeconds() < 5 ||
props.healthCheckInterval.toSeconds() > 300
) {
throw new Error(
'HealthCheckInterval must be between 5 and 300 seconds',
);
}
}
if (props.healthCheckTimeout) {
if (
props.healthCheckTimeout.toSeconds() < 1 ||
props.healthCheckTimeout.toSeconds() > 120
) {
throw new Error('HealthCheckTimeout must be between 1 and 120seconds');
}
}
if (props.healthyThresholdCount) {
if (props.healthyThresholdCount < 1 || props.healthyThresholdCount > 10) {
throw new Error('HealthyThresholdCount must be between 1 and 10');
}
}
if (props.protocolVersion) {
if (props.protocolVersion === ProtocolVersion.GRPC) {
throw new Error('GRPC is not supported');
}
}
if (props.unhealthyThresholdCount) {
if (
props.unhealthyThresholdCount < 2 ||
props.unhealthyThresholdCount > 10
) {
throw new Error('UnhealthyThresholdCount must be between 2 and 10');
}
}
var port: number;
if (props.port) {
port = props.port;
} else if (props.protocol === Protocol.HTTP) {
port = 80;
} else {
port = 443;
}
let matcher: aws_vpclattice.CfnTargetGroup.MatcherProperty | undefined =
undefined;
if (props.matcher) {
const codeAsString = props.matcher.toString();
matcher = { httpCode: codeAsString };
}
return {
enabled: props.enabled ?? true,
healthCheckInterval:
props.healthCheckInterval ?? core.Duration.seconds(30),
healthCheckTimeout: props.healthCheckTimeout ?? core.Duration.seconds(5),
path: props.path ?? '/',
protocol: props.protocol ?? 'HTTPS',
port: port,
protocolVersion: props.protocolVersion ?? 'HTTP1',
unhealthyThresholdCount: props.unhealthyThresholdCount ?? 2,
healthyThresholdCount: props.healthyThresholdCount ?? 5,
matcher: matcher,
};
}
/**
* health check is enabled.
*/
public abstract readonly enabled: boolean;
/**
* healthCheck Interval
*/
public abstract readonly healthCheckInterval: core.Duration;
/**
* HealthCheck Timeout
*/
public abstract readonly healthCheckTimeout: core.Duration;
/**
* Target Match reponse
*/
public abstract readonly matcher:
| aws_vpclattice.CfnTargetGroup.MatcherProperty
| undefined;
/**
* Path to check
*/
public abstract readonly path: string;
/**
* Port to check
*/
public abstract readonly port: number;
/** Protocol
*
*/
public abstract readonly protocol: string;
/**
* HTTP Protocol Version
*/
public abstract readonly protocolVersion: string;
/**
* Unhealthy Threshold Count
*/
public abstract readonly unhealthyThresholdCount: number;
/**
* Healthy Threshold Count
*/
public abstract readonly healthyThresholdCount: number;
protected constructor() {}
}The enums in this construct are intended to provide a way to reduce deployment time errors. Many of the L1 constructs will accept string however
there are only certain valid options.
Provides valid HTTP Responses such as NOT_FOUND and OK. This is intended for using primarly with configuring default rules. This list may well need expanding
Valid HTTP Methods, these are used for constructing Rules.
IPv4 and IPv6, used for creating rules
Contains, Exact and Prefix used for creating rules
Exact Prefix, used for creating path matches in rules.
HTTP or HTTPS - used for creating rules.
HTTP1, HTTP2 or GRPC - used for creating rules.
Used for creating Authenticaiton Policy Access Modes.
Used for creating Authenticaiton Policy Access Modes. (Note a different set of options from RuleAccessMode)
LAMBDA, IP, INSTANCE, ALB. Used for creating targets.
What are we launching today?
Amazon VPC Lattice AWS CDK L2 Construct
Why should I use this construct?
This CDK L2 Construct can be used to deploy resources from Amazon VPC Lattice. VPC Lattice is a fully managed application networking service that you
use to connect, secure, and monitor all your services across multiple accounts and virtual private clouds (VPCs).
This construct handles all the different resources you can use with VPC Lattice: Service Network, Service, Listeners, Listener Rules, Target Groups (and targets), and Associations (Service or VPC). You have the freedom to create the combination of resources you need, so in multi-AWS Account environments you can make use of the module as many times as needed (different providers) to create your application network architecture.
You can check common Amazon VPC Lattice Reference Architectures to understand the different use cases you can build with the AWS service.
- It simplifies the deployment of common patterns for AWS VPC Lattice
- It has been tested and implemented as part of a number of wider architectures
- It is extensible to support other patterns as they emerge
- It simplifies AWS VPC Lattice adoption and administration
- Allows you to integrate infrastructure deployment with your application code
- Reduces time to deploy and test AWS VPC Lattice
- Provides separation of concerns with a common interface for user personas
Why are we doing this?
- To provide a CDK native interface for AWS VPC Lattice
- Provide a way to deploy AWS VPC Lattice deterministically
Is this a breaking change
No.
What are the drawbacks of this solution?
- It is an opinionated pattern, however there are escapes to help customisation where needed.
- It is a new AWS Service and its common usecases and features may change and evolve
Ticking the box below indicates that the public API of this RFC has been signed-off by the API bar raiser (the api-approved label was applied to the RFC pull request):
[ ] Signed-off by API Bar Raiser @TheRealAmazonKendra