Reatom is state manager for both simple and complex applications.
Core package of Reatom state manager.
- 🐣 simple abstraction and friendly DX: minimum boilerplate and tiny API
- ⚡ performance: performant updates for partial state changes
- 🧯 reliable: atomicity guaranties
- ❗️ static typed: best type inferences
- 🗜 small size: 2 KB gzipped
- 📦 modular: reusable instances (SSR)
- 🍴 lazy: solution for code splitting out of the box
- 🔌 framework-agnostic: independent and self-sufficient
- 🧪 testing: simple mocking
- 🛠 debugging: immutable data and built-in debugger
- 👴 IE11 support: Can I Use
- synchronous glitch free
- simple integration with other libraries (Observable, redux ecosystem, etc)
- awkward to write bad code
- easy to write good code
Reatom is a mix of all best from MobX and Redux. It processes immutable data by separated atoms and use single global store, which make dataflow predictable, but granular and efficient.
List of companies
import { createAtom } from '@reatom/core'
export const amountAtom = createAtom(
{ clear: () => {}, add: (value: number) => value },
({ onAction, schedule }, state = 0) => {
onAction('clear', () => (state = 0))
onAction('add', (value) => (state = state + value))
schedule(() => console.log(`Amount is ${state}`))
return state
},
)
amountAtom.getState()
// -> 0
amountAtom.add.dispatch(7)
amountAtom.getState()
// -> 7PR welcome for other framework agnostic managers.
| Name | Bundle size | Granularity | API strictness | Lifetime | Atomicity | Effects managements | API | Direction | Glitch free | Immutability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reatom | 2kb gzip | + | + | warm | + | + | selector | pull/push | + | + |
| Redux | 1.6kb gzip | - | - | hot/cold | +/- | - | selector | pull | - | + |
| RTK | 11kb gzip | - | +/- | hot/warm/cold | +/- | +/- | selector | pull | + | + |
| Mobx | 15kb gzip | + | - | warm | - | +/- | proxy | pull/push | + | - |
| Effector | 10kb gzip | + | - | hot | - | + | selector | push | + | + |
| Nanostores | <1kb gzip | + | - | warm | - | +/- | selector | push | - | + |
Explanation
- Bundle size is important because witch it smaller thats more projects you may cover with chosen solution. Reusable tech stack increase your performance and reduce contexts switching.
- Granularity describe the type of dependencies tracking and lack of it may reduce performance.
- TODO...
npm i @reatom/coreor
yarn add @reatom/coreThe features list is reflect our vision of perfectly balanced tool for any kind of application data management. But most important goals probably are performance, atomicity guaranties and tiny basic API with immutable principles for predictable debugging .
State is a term from FSA thats mean a consistent data with predicted shape (and literals) in some time slice of application lifetime. Most libraries for data manipulation which calls itself state manager don't give you atomicity guaranties. But if we take a look at the innovator of this approach React.js we found that without componentDidCatch your application may be destroyed by any error in a render phase. Reatom follow same principles, but instead of throwing a whole state at an error it cancel accumulated state and leave only previous valid state.
Also, state manager provides an API for describe and transform application state in a right way, you may solve a most class of problems with it, management domain data (user profile, entities editing...) or environment data (routing, network cache...). Also it has a reactive interface witch helps to decouple application modules / components.
Those problem you may solve by other ways too: streams / services / classes, but if you want more reliability guaranties and better debugging experience state manager do it best.
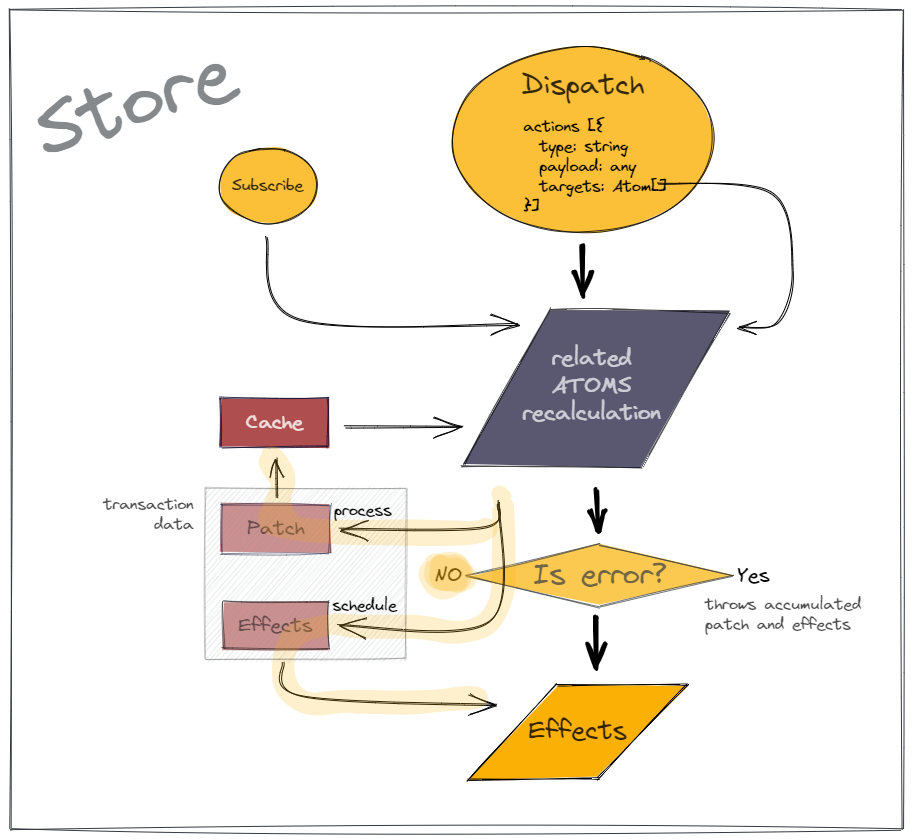
The main item of Reatom core is createAtom. It is a pack of most needed features which help you to solve most tasks. Generally, architecture of Reatom build around a store, which an event emitter with two queues: pure computations and side effect. Atoms allow you to describe reactive computations with fine granted optimizations and schedule effects.
If you need \ interesting in detailed architecture design you should check architecture chapter and next chapter about building your own atom creators.
As any computations, it results and effects processed by a store, it easy for debugging and testing. But not every application need it and for that case we have a defaultStore which bind to createAtom and allow to subscribe to it and dispatch it actions inline without manual store management.
createAtom accept two required arguments: a collection of dependencies and reducer function. Third argument is optional and allow you to set atom indeteficator or reducer decorators.
import { createAtom } from '@reatom/core'
const inputAtom = createAtom(
// Plain function in dependencies are used as mappers
// (calls to convert action creator (AC) arguments to action payload)
// for AC with same names,
// which you may handle in the reducer
{ change: (text: string) => text },
// Reducer is a function which recall on every related dispatch.
// The `track` parameter includes handlers
// to subscribe and react to dependencies actions and atoms
(track, state = '') => {
track.onAction('change', (text) => (state = text))
return state
},
)
const greetingAtom = createAtom(
// Atoms in dependencies available in the reducer
// to receiving it state and subscribe to they changes
{ input: inputAtom },
(track) => `Hello, ${track.get(`input`)}!`,
)
// calculate actual state
greetingAtom.getState()
// -> `Hello, !`
// Get described (in the first argument) action creator
// from static property by the same name
inputAtom.change(`Tom`)
// { type: `atom [1] - change`, payload: `Tom` }
// Instead of action creation, dispatch it to the `defaultStore`
// Similar as `defaultStore.dispatch(inputAtom.change(`Tom`))`
inputAtom.change.dispatch(`Tom`)
// Action creators from `createAtom` includes it owner atom
// and always processed by it
greetingAtom.getState()
// -> `Hello, Tom!`
// Equal to `defaultStore.subscribe(greetingAtom, () => ...)`
greetingAtom.subscribe((greeting) => console.log(greeting))
// -> `Hello, Tom!`
inputAtom.change.dispatch(`Tom`)
// Nothing happen coz the state is not changed
inputAtom.change.dispatch(`Bob`)
// -> `Hello, Bob!`As you may see, Reatom flow looks like Redux flow, but reducers and selectors is unified to atoms, which allows you to describe data receiving naturally, as in MobX. Also, atoms have an API for handling side-effects declarative, but flexible, see below.
Example above is a basic and don't show all cool features of Reatom. See API section or Guides to learn more about how to solve your tasks fast and efficient.
import { createAtom } from '@reatom/core'
type TimerCtx = { intervalId?: number | NodeJS.Timer | any }
/** Timer update interval */
export const intervalAtom = createAtom(
{ setSeconds: (seconds: number) => seconds },
({ onAction }, state = 1000) => {
onAction(`setSeconds`, (seconds) => (state = seconds * 1000))
return state
},
)
export const timerAtom = createAtom(
{
interval: intervalAtom,
start: (delayInSeconds: number) => delayInSeconds,
stop: () => {},
// Action mappers which name starts with underscore
// is not allowed as action creators by atom static properties
// and may be used only as part of internal logic
_update: (remains: number) => remains,
},
({ create, get, onAction, onChange, schedule }, state = 0) => {
const interval = get(`interval`)
function start(delay: number) {
const start = Date.now()
schedule((dispatch, ctx: TimerCtx) => {
clearInterval(ctx.intervalId)
ctx.intervalId = setInterval(() => {
const passed = Date.now() - start
const remains = delay - passed
if (remains <= interval) {
clearInterval(ctx.intervalId)
ctx.intervalId = setTimeout(
() => dispatch(create(`_update`, 0)),
remains,
)
}
dispatch(create(`_update`, remains))
}, interval)
})
}
onAction(`stop`, () => {
state = 0
schedule((dispatch, ctx: TimerCtx) => clearInterval(ctx.intervalId))
})
onAction(`start`, (delaysInSeconds) => start(delaysInSeconds * 1000))
onChange(`interval`, () => {
if (state !== 0) start(state)
})
onAction(`_update`, (remains) => (state = remains))
return state
},
)Primitives is a pack of helpers around primitive data structures, which helps you reduce boilerplate. It not included in 2kb main bundle, but tiny by it selfs and do not includes into your application bundle if you not importing it.
Available primitives:
createBooleanAtom,createEnumAtom,createMapAtom,createNumberAtom,createStringAtom,createSetAtom(crateArrayAtomwill added soon).
import { createBooleanAtom } from '@reatom/core/primitives'
export const isModelOpenAtom = createBooleanAtom(false, 'isModelOpen')
// Available action creators:
isModelOpenAtom.toggle()
// -> { payload: null, type: 'isModelOpen - toggle' }
isModelOpenAtom.setTrue()
// -> { payload: null, type: 'isModelOpen - setTrue' }
isModelOpenAtom.setFalse()
// -> { payload: null, type: 'isModelOpen - setFalse' }
isModelOpenAtom.change((state) => !state)
// -> { payload: Function, type: 'isModelOpen - change' }A string atom is useful to describe an enum.
import { createStringAtom } from '@reatom/core/primitives'
export type Statuses = 'init' | 'loading' | 'loaded' | 'error'
export const statusAtom = createStringAtom<Statuses>('init')But a better way is use the createEnumAtom.
import { createEnumAtom } from '@reatom/core/primitives'
const githubRepoSortFilterAtom = createEnumAtom(
['full_name', 'created', 'updated', 'pushed'],
{ format: 'snake_case' },
)
console.log(sortFilterAtom.getState())
// -> 'full_name'
sortFilterAtom.set_updated.dispatch()
console.log(sortFilterAtom.getState())
// -> 'updated'
/* OR use default `camelCase` format */
const statusesAtom = createEnumAtom(['init', 'loading', 'loaded', 'error'])
console.log(statusesAtom.getState())
// -> 'init'
statusesAtom.setLoading.dispatch()
console.log(statusesAtom.getState())
// -> 'loading'Every enum atom includes enum property with object of the variants.
export const STATUSES = statusesAtom.enum
// ...
statusesAtom.subscribe((status) => {
if (status === STATUSES.error) {
log('Error happen')
}
})createAtom is a main public API you need to describe simple and complex logic of your application, it already includes a few features and optimizations which enough for most programming tasks. Anyway in a rare cases of regular development or if you a library / package author you may need a low level API to build something more flexible or complex. Fortunately we spend a lot of time for improvements of Reatom basic API and made it simple, but powerful.
An atom it a simple reducer like function which accept a transaction context and optional cache object with state data and a few meta fields and return new immutable version of the cache.
export type Atom<State = any> = {
(transaction: Transaction, cache?: CacheTemplate<State>): Cache<State>
id: string
types: Array<Action['type']>
}Atom should have unique field id for it identification (helps with debug and tooling). Also atom should have field types with a list of all dependency types which need to optimize dispatch behavior and archive granular updates in a single global store.
Transaction is a context witch includes list of actions and two functions: process (call and memoize dependency atom) and schedule (schedule effect to the en of success atom computations).
Cache is a immutable data of an atom which includes state, actual dependencies and other meta (check typings).
createAtom accept three argument: dependencies, reducer function and optional options
In the first argument of createAtom you may describe three kind of entities: other atoms, payload mappers for bind action creators and other action creators.
import { createAtom } from '@reatom/core'
import { createStringAtom } from '@reatom/core/primitives'
const emailAtom = createStringAtom()
const passwordAtom = createStringAtom()
const formAtom = createAtom(
{
emailAtom,
passwordAtom,
onEmailChange: emailAtom.change,
submit: () => {},
_fetch: (email, password) => ({ email, password }),
},
reducer,
options,
)If payload mapper name starts with underscore it is not available as atom property, only in reducer.
formAtom.submitis action creator function.formAtom._fetchis undefined.
The second argument of createAtom is reducer function which accepts the track collection and optional state, which should change immutably and returns from the reducer.
track collections is a set of helpers to process and subscribe to dependencies, it includes:
get- read and subscribe dependency atom value. It doesn't subscribe insideonAction\onChange, just read it. If you describe an atom in dependencies, but didn't use it bygetthe reducer function will not rerun to it changesonAction- react to dependency action.onChange- react to change of state of dependency atom.schedule- schedule side effect. The only way to receivedispatchfor set effect result.create- call payload mapper from dependencies and create action object.onInit- react only to first reducer call.getUnlistedState- read state of atom outside dependencies without subscribing to it.
const formAtom = createAtom(
{
emailAtom,
passwordAtom,
onEmailChange: emailAtom.change,
submit: () => {},
_fetch: (email, password) => ({ email, password }),
},
(track, state = { isLoading: false, error: null as null | string }) => {
track.onAction('onEmailChange', (email) => {
// Here `email === track.get('emailAtom')`
})
track.onChange('passwordAtom', (password, prevPassword) => {
// TODO: validate password
})
track.onAction('submit', () => {
const email = track.get('emailAtom')
const password = track.get('passwordAtom')
schedule((dispatch) =>
dispatch(
// ERROR here: `Outdated track call`
// you should't call `track.get` async
// (scheduled callback calls async after all atoms)
// (use `email` and `password` variables instead)
track.create(
'_fetch',
track.get('emailAtom'),
track.get('passwordAtom'),
),
),
)
})
return state
},
options,
)
Outdated track callis throwed when you try to use reactive handlers outside synchronous reducer call. For example,scheduleis called only after all atoms recalculation.
The third argument options allows you to override the default atom settings:
id- setup id for this atomdecorators- array of (atom decorators)[#atom-decorators]store- redefine store bindings fordispatch,getStateandsubscribeof this atom (by defaultdefaultStoreusing)
TODO: Add example
When state managers come to web development it improves an application architecture and debugging, one-directional dataflow is more obvious and predictable. But race conditions, cyclic dependencies and glitches were shoots a legs still sometimes. Redux was fix it by immutable data (with DAG limitations) and single global store, but comes with performance limitations. Reatom try to improve redux and make a little step forward in state management generally. Basically, Reatom is two queues event emitter with actions instead of events.
One of the biggest feature and goal of the Reatom is atomicity guarantees for processed state (from atoms). It is achieved by separating calculations for two consecutive stages: pure computations and side-effects. If first stage (pure computations) throws an error, accumulated patch from touched atoms will be ignored, state will be not changed and the second stage (side-effects calls) will be not processed. It is the difference between events and actions: event is statement of happened fact, but action is intentions to do something (change state) so we may react to it only after it (state changing) happen.
Each atom have a list of all dependencies action types which used to match a dispatch and related atoms. As we focus only on types which is leafs of atoms graph we do not need for bidirectional atoms links what give to us unidirectional graph of atoms relationship which totally immutable and friendly to some processing and debug.
In createAtom you may use native language mechanic for branching you data flow: if/else statement or ternary operator right in place of your reactive data receiving (a get function), Reatom do smart dynamical tracking of all dependencies and subscribe / unsubscribe only for needed.
We want to grow a huge ecosystem around Reatom and make it qualitative. We are welcome for PRs with new utilities, not meter how huge or small it is, but the good way to test the API and stability of the new package is trying it in a demo mode first. For thats purposes and for prevent holding an name of subpackage by unfinished utilities we recommends to add an new utilities in experiments folder of the domain package. Feel free to make breaking changes in this code, but try to finish your experiment faster and publish it as a subpackage.
This approach increase domain package size in node_modules whe you install it, but 100% treeshakable so it looks a good way.
There is no sense to write all code with immutable principles, Clojure docs describe it better. If you still woried about this you may use aditional mutable variable.
const counterAtom = createAtom({ inc: () => {} }, ({ onAction }, state = 0) => {
let newState = state
onAction('inc', () => {
newState++
})
return newState
})Important note. Feel free to mutate variable, not a value. Reducer functions should not mutate any input values.
const counterAtom = createAtom(
{ inc: () => {} },
({ onAction }, state = { count: 0 }) => {
// WRONG
onAction('inc', () => {
state.count++
})
// Right
onAction('inc', () => {
state = { count: state.count + 1 }
})
return state
},
)Probably you should not to do this, try to use (batch)[#Batch] instead.
const handleSubmit = () => {
return [formAtom.clear(), routerAtom.go('/')]
}
// ...
dispatch(handleSubmit())Each Store have own WeakMap to store atoms cache. WeakMap have no API to iterate over stored data and we just can not read it. We can iterate and read data from atoms with active listeners, but it may be not enough and result may be unpredictable in a different time of application runtime. Also, in practice, we do not need all state snapshot, only critical parts. So, the better way is wrap each needed atom to something like persist helper.