Reservoir Operation Optimization using the Charged System Search (CSS) Metaheuristic Optimization algorithm
Main publication: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5338/6/1/5
- This algorithm is used by me for the first time in the field of water resources management
Optimization of Water-Supply and Hydropower Reservoir Operation Using the CSS Algorithm The CSS algorithm is a metaheuristic optimization method inspired by the governing laws of electrostatics in physics and motion from the Newtonian mechanics. The CSS algorithm is used to optimally solve the water-supply and hydropower operation of “Dez” reservoir in southern Iran over three different operation periods of 60, 240, and 480 months. Here the codes are presented for the 480-month operations.
In a water-supply reservoir operation, the objective is to obtain a set of releases from the reservoir (or a set of reservoir storage volumes) for the operation period with given inflow such that a predefined pattern of demands is met. In the other words, the objective is to set the released flow as close as possible to the demand and decrease the unnecessary overflows from the reservoirs, and hence, minimize the water deficit.
Minimize F = ∑_t=1_to_NT [ (D(t)−R(t)) / Dmax)^2 ]
Subject to continuity equations at each time step:
S(t+1) = S(t)+I(t)−R(t)−Loss(t)
Smin ≤ S(t) ≤ Smax
Rmin ≤ R(t) ≤ Rmax
Loss(t) = Ev(t) × A(t)/1000
A(t) = x0+x1×S(t)+x2×S(t)^2+x3×S(t)^3
where NT is the number of time steps, D(t) is water demand in time step t in million cubic meters (MCM), R(t) is release from the reservoir in time step t (MCM), Dmax is maximum demand (MCM), S(t) is storage at the start of time step t (MCM), I (t) is inflow in time step t (MCM), Smin and Smax are minimum and maximum storage of reservoir (MCM), respectively and Rmin and Rmax are minimum and maximum allowed release from reservoir (MCM), respectively. Loss (t) is net amount of gain and loss of the reservoir resulting from precipitation and evaporation in time step t. Ev(t) is the evaporation height during the time step t, and x0, x1, x2 and x3 are constants that can be obtained by fitting the A(t) Equation to the existing data.
In a hydropower reservoir operation, the objective is to obtain a set of releases from the reservoir (or a set of reservoir storage volumes) such that the power generation from the reservoir is maximum, or as close as possible to the installed capacity of the hydro-electric plant.
Minimize F = ∑_t=1_to_NT [ 1 - (p(t) / power) ]
Subject to continuity equations at each time step as described in the water supply operation. Here p (t) is power generated in megawatts (MW) in time step t, power is the installed capacity of hydro-electric plant (MW), and other parameters are defined as before. The power generated in time step t can be stated as follow:
p(t) = min[ (g×η×r(t)/PF) × (h(t)/1000) , power ]
in which h(t) is the effective head of the hydroelectric plant as defined by Equation below:
h(t) = ( (H(t)+H(t+1)) / 2) − TWL
H(t) is the elevation of water in reservoir at time step t which may be defined as a function of storage in the reservoir as:
H(t) = a+b×S(t)+c×S(t)^2+d×S(t)^3
where g is the Earth’s gravity acceleration, η is the efficiency of the hydroelectric plant, r (t) is release from reservoir (m3/s), PF is the plant factor, TWL (tail water level) is the downstream elevation of the hydroelectric plant (m), a, b, c and d are constants that can be obtained by fitting the H(t) Equation to the reservoir’s data.
Total storage capacity of “Dez” reservoir in pre-defined normal water level is 2510 MCM and the average inflow of the reservoir over 40 years period from 1970–2010 is 5900 MCM. The initial storage of the reservoir is taken equal to 1430 MCM. The maximum and minimum allowable storage volumes are set equal to 3340 and 830 MCM, respectively. The maximum and minimum monthly water release set equal to 1000 MCM and zero, respectively. The total installed capacity of hydroelectric power plant of the Dez reservoir is 650 MW, being operated with plant factor of 0.417 and 90% efficiency. The tail water level in downstream is assumed constant at 172 m above sea level.
Figure 4: Best solution yielded by the CSS algorithm for 60-month water-supply operation considering evaporation losses: water demand versus release from the reservoir (a), and river inflow versus storage volume at each time step (b). As seen from the figure, the storage is confined between maximum (S_max) and minimum (S_min) allowable storage.
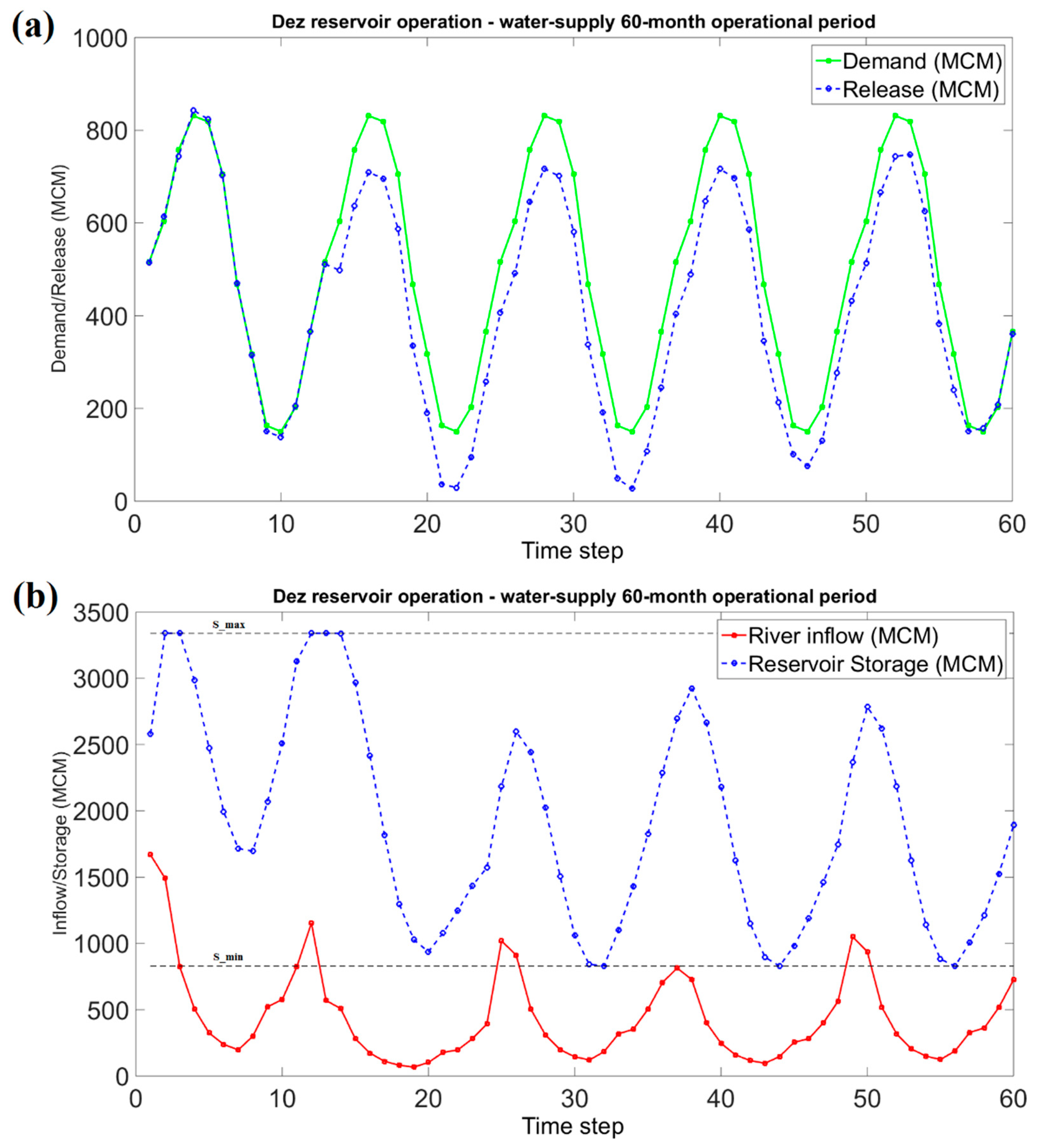
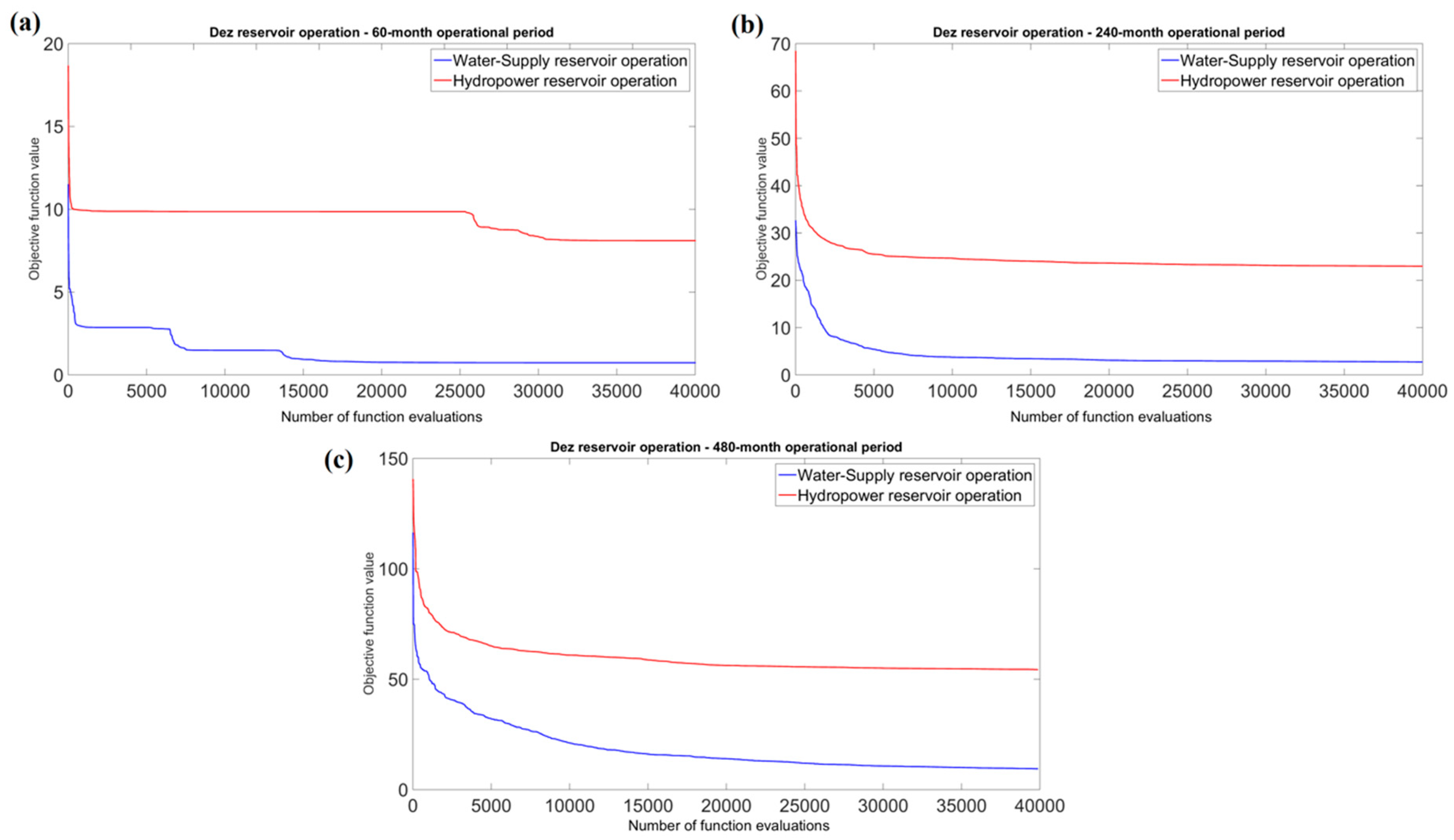
Figure 5: Convergence curve of the optimum solution obtained by the CSS algorithm for “Dez” reservoir water-supply and hydropower operation, considering evaporation losses, over 60 (a), 240 (b) and 480 (c) months periods.