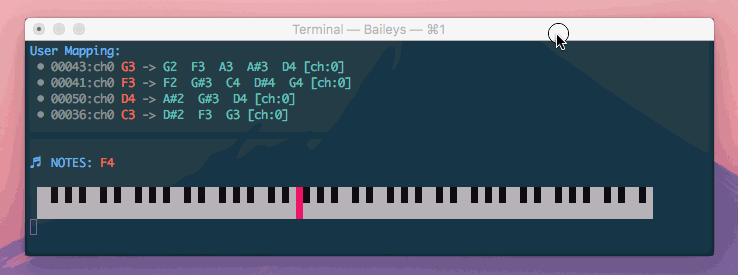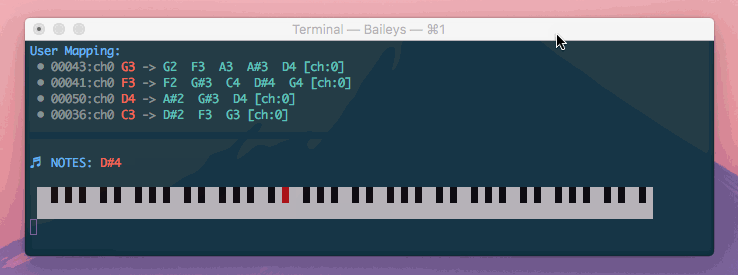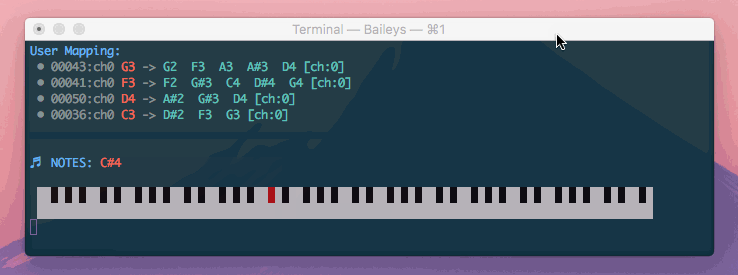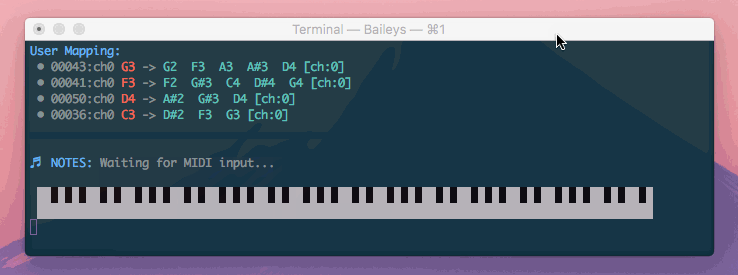
Di'Mappio allows you create a virtual midi interface that intercepts another device, enhancing your notes with additional mappings and chord harmonization.
The magenta keys show the keys that I am actually pressing, where the green keys are additional keys triggered by Di'Mappio.
In the above demonstration, I am able to play a variety of chords spanning 4 octaves - Gm9, Fm9, Bb7, and Ebadd9
However, I am using just one hand an a mini 25-key device (which supports only 2 octaves at any given time)
Implemented in pure C, Di'Mappio accesses the low level audio API(s) for OS. Designed for performance, it does one thing and hopes to do it well: midi mapping and routing.
Di'Mappio runs as a light-weight background process inside of your terminal.
Once you have established your mappings, you can route Di'Mappio's output into your favorite Digital Audio Workstation (eg. Logic, Ableton, etc..)
-
Create flexible virtual midi ports that turns midi input into advance chords and harmonies.
-
Create mapping definitions with support for nesting and many-to-many routes.
- Map arbritrary midi keys to trigger other midi keys
- Supports Single midi key can trigger multiple midi keys
- Supports Multiple Keys Trigger other keys
- Sophisticated rules to allow triggering only when the mapping rule has been fully satisfied
-
Low level integration with raw midi/sequencer API(s) on Linux / OSX
- Runs on Linux via Alsa core lib
- Runs on OSX via CoreAudio
- Todo: WIndows support via WMM
For example, you can remap your drum pads to play in a particular octave - instead of the default C0-octave (which is not easily modifiable, even in a Digital Audio Workstation)
This can allow for a small 25-midi-key device to access it's drum pads to support a wider range of performances.
- Some 25-key midi devices come with up to 16 pressure sensitive drum pads
- Take advantage of those in your performances with advance chord mappings
Usage: dimappio [options] [Mapping]
[Mapping] consists of a comma delimited list of notes.
Within that list, you may nest sub lists to specify
a group of notes to be executed per src trigger
Example:
dimappo -x 32:0 "C3:C3|C4|C5, F#3:F#4"
This will create a virtual interface attached to the device port 32:0.
Then it will map two keys (C3 and F#3) to trigger multiple other keys
Options:
-s, --send=<note> Send midi note to a specifc client
-t, --target=<id:port> Specify a target Midi Client
-x, --source=<id:port> Specify a Midi Client source
-m, --monitor Monitor a MIDI Client
-l, --list List all available midi clients
-z, --debug Turn on debug mode
-h, --help Show application usage
-v, --version Print version
Di' Mappio depends only on audio API(s) provided by your OS. ALSA for Linux, and CoreAudio on OSX.
CMake is used to build the application.
sudo apt-get install cmake libasound-dev
brew install cmake
You will need XCode installed for CoreAudio headers.
$ git clone https://github.com/cosier/dimappo
$ cd dimappo
$ # automated cmake wrappers
$ bin/build
$ bin/install
$ dimappio --help