- Define MVC architecture.
- Explain Spring MVC architecture.
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture can be used to create different kinds of loosely coupled web applications. We will take a look at the components of the MVC architecture and then explore how Spring Web MVC uses this architecture.
The MVC architecture allows us to separate our code into distinct logical units called models, views, and controllers. Here’s what each unit does:
- Model: Defines data representation and relationships.
- View: Presents data to the user and handles user interaction.
- Controller: Controls data flow between models and views.
When a user sends a request to a URL it gets sent to a method in the controller which gets the required data using the model. The controller then passes the data to the view and gets back the data representation for the user. This data is sent back to the user.
The view layer can form a complete webpage and send it back to the client. For example, the view layer can form an HTML file with the required data and send it to the client which can display it without additional data manipulation.
We can also configure the view layer to send back a simple data representation such as JSON instead of a fully formed webpage. The client has to define its own logic to manipulate and display the data.
In order to process user requests in HTTP, we need a servlet container (web server). A servlet container processes HTTP requests and interfaces with a Java application so that the Java application doesn’t have to implement the communication layer.
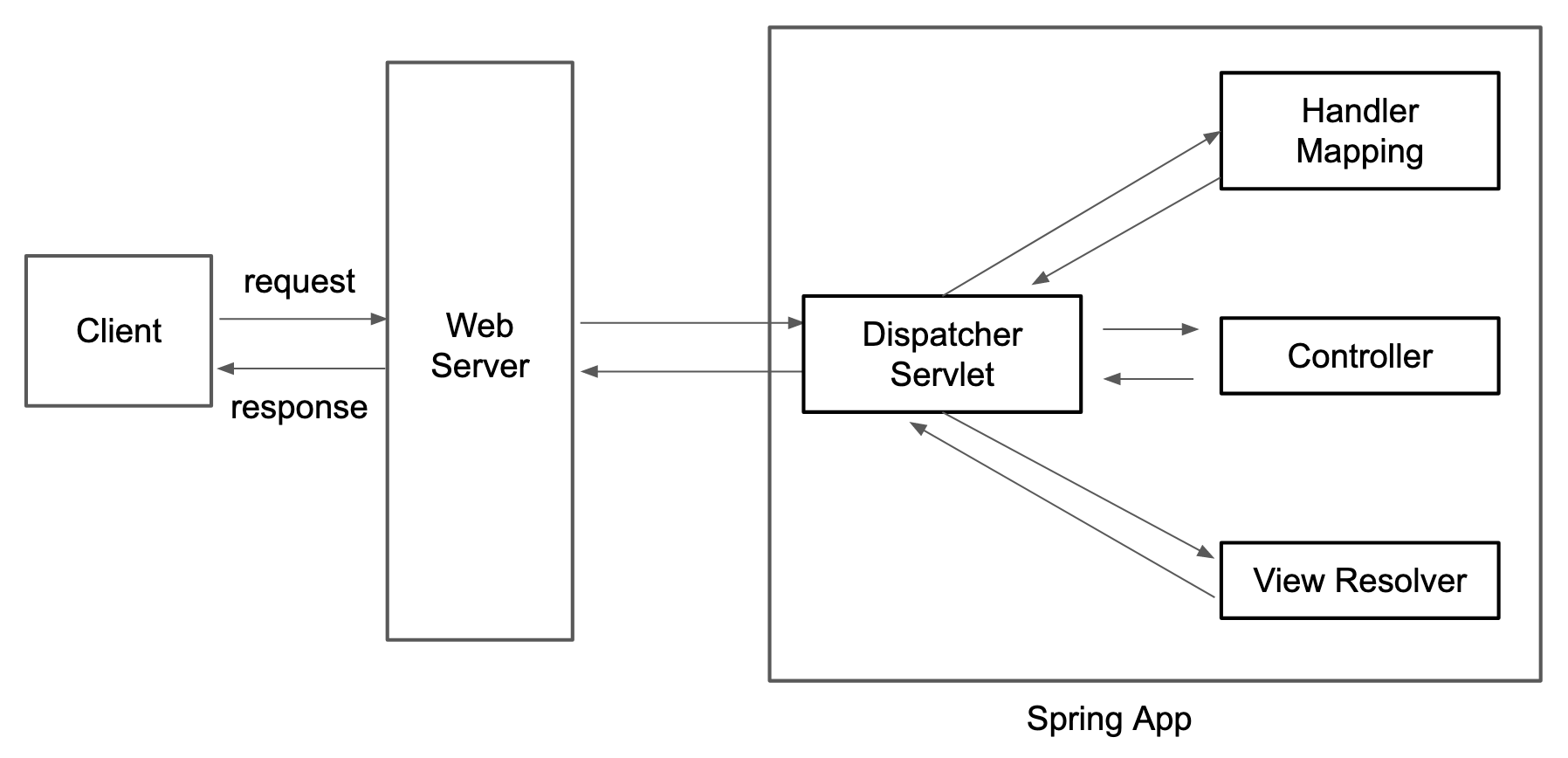
Spring MVC uses a DispatcherServlet that processes HTTP requests. Here are the
steps of a full request-response cycle:
- The client makes an HTTP request.
- The web server accepts the request and delivers it to the dispatcher servlet. This servlet manages the HTTP flow for the rest of the cycle.
- The dispatcher sends the HTTP request to the Handler Mapping component.
- The handler component sends back the HTTP method and path to the dispatcher.
- The dispatcher uses the information to call the corresponding method in the right controller.
- The controller method provides the view name and data needed to render the view.
- The dispatcher uses the View Resolver component to find the view that needs to be rendered.
- An HTTP response is sent back to the client.
- The client side renders the view.
Note that when we are building an API the View Resolver is not required. After step 5, the controller method returns the value that needs to be sent to the client. The response is sent to the client through the web server.
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a common way of client-server interaction. It is a set of rules that define how data should be queried and managed. A service that is written with these rules is called a RESTful service.
The following are the six principle of a RESTful service:
- Client-Server Interaction Model: the application rendering the data and the application processing the data are kept separate.
- Stateless: Every request from a client must contain the necessary information to retrieve or manipulate data on the server. It cannot rely on any stored state on the server.
- Cacheable: A request-response value can be cached on the server so that the server can return repeated requests without having to reprocess data.
- Uniform Interface: All RESTful services follow a consistent naming convention which makes it easy to work across different services.
- Layered System: The client request may be routed through other services before reaching the server. A client doesn’t know if it is directly connected to a server.
- Code on Demand: A client can request executable code from the server in the form of applets or scripts.
Be sure to follow REST resource naming conventions when building a RESTful service.
We have learned about the MVC architecture and how it is implemented in Spring. In the next few lessons, we will building our own API with Spring Web.