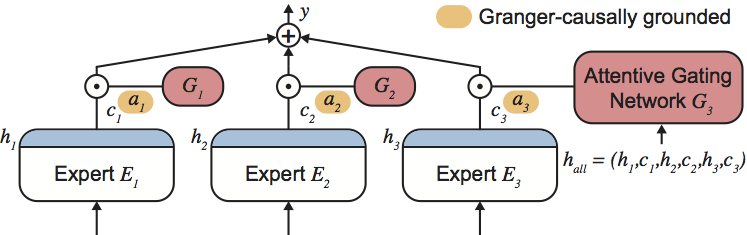
Attentive Mixtures of Experts (AMEs) are a machine-learning method for jointly learning to produce accurate predictions and estimates of feature importance for individual decisions in a single end-to-end trained neural network model. This repository provides a reference implementation of AMEs and the Granger-causal objective using the Keras and TensorFlow frameworks. You can find the manuscript at http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.02195.
Author(s): Patrick Schwab, ETH Zurich patrick.schwab@hest.ethz.ch, Djordje Miladinovic, ETH Zurich djordje.miladinovic@inf.ethz.ch and Walter Karlen, ETH Zurich walter.karlen@hest.ethz.ch
License: MIT, see LICENSE.txt
If you reference or use our methodology, code or results in your work, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{schwab2019ame,
title={{Granger-causal Attentive Mixtures of Experts: Learning Important Features With Neural Networks}},
author={Schwab, Patrick and Djordje Miladinovic and Karlen, Walter},
booktitle={{AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence}},
year={2019}
}
- You can install the package and its dependencies using
pip install .in the project's root directory. - In principle, AMEs can be used with any type of input data (tabular, image, time series, ...). However, the architectures of the experts within the AME have a considerable effect on both predictive and importance estimation accuracy. It is therefore advisable to use optimised expert architectures for different types of input data.
- We provide two optimised implementations for tabular data and image data in this repository (see examples below).
After installing the package's dependencies, you can use the provided example code to train an AME on the boston housing dataset using the following command (see the ame_starter/apps/parameters.py file for descriptions of all the available parameters):
python /path/to/ame/ame_starter/apps/main.py
--dataset="boston_housing"
--batch_size=32
--num_epochs=300
--learning_rate=0.001
--output_directory=/path/to/your/output/directory
--do_train
--do_evaluate
--num_units=16
--num_layers=1
--early_stopping_patience=32
The command will:
- train and save a trained model (
model.npz) to your output directory. The trained model can be reused by the script by setting the--load_existing=/path/to/your/model.npzparameter - report standard performance metrics (loss, Granger-causal error) to stdout
- save tabular CSV files containing the predictions for each sample in the training, validation and test sets (
train_predictions.csv,val_predictions.csv,test_predictions.csv) to your output directory - save tabular CSV files containing the importance scores for each input feature and sample in the training, validation and test sets (
train_attributions.csv,val_attributions.csv,test_attributions.csv) to your output directory
After installing the package's dependencies, you can use the provided example code to train an AME on the MNIST dataset using the following command (see the ame_starter/apps/parameters.py file for descriptions of all the available parameters):
python /path/to/ame/ame_starter/apps/main.py
--dataset="mnist"
--batch_size=100
--num_epochs=300
--learning_rate=0.001
--output_directory=/path/to/your/output/directory
--do_train
--do_evaluate
--num_units=64
--num_layers=1
--early_stopping_patience=32
--l2_weight=0.01
--dropout=0.2
The command will produce the same outputs as the tabular example above, but for the MNIST dataset.
You can extend the ame_starter/apps/main.py script by adding a loading routine for your own dataset in the get_data() function (line 42). See get_data_mnist (line 88) in ame_starter/apps/main.py for an example routine loading the MNIST dataset.
If you dataset is an image dataset, it is important to add your dataset's name to the dataset_is_image function (line 350 ame_starter/apps/main.py) in order to use AMEs optimised for image data.
In addition, it might be necessary to use a higher downsample_factor in ame_starter/models/model_builder.py to reduce the dimensionality of the importance score map if your dataset uses higher resolution images than MNIST in order to keep the number of experts, and therefore the training memory and time requirements, within a reasonable range. We found anything lower than 200 experts to have acceptable performance on standard hardware.
You may also customise the expert architectures and hyperparameters in ame_starter/models/model_builder.py in order to achieve better predictive and importance estimation performances on your dataset.
This work was funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) project No. 167302 within the National Research Program (NRP) 75 "Big Data". We acknowledge the support of the NVIDIA Corporation with the donation of the Titan Xp GPUs used for this research.